Blood Typers is a terrifically tense, terror-filled typing tutor
When you think about it, the keyboard is the most complex video game controller in common use today, with over 100 distinct inputs arranged in a vast grid. Yet even the most complex keyboard-controlled games today tend to only use a relative handful of all those available keys for actual gameplay purposes.
The biggest exception to this rule is a typing game, which by definition asks players to send their fingers flying across every single letter on the keyboard (and then some) in quick succession. By default, though, typing games tend to take the form of extremely basic typing tutorials, where the gameplay amounts to little more than typing out words and sentences by rote as they appear on screen, maybe with a few cute accompanying animations.
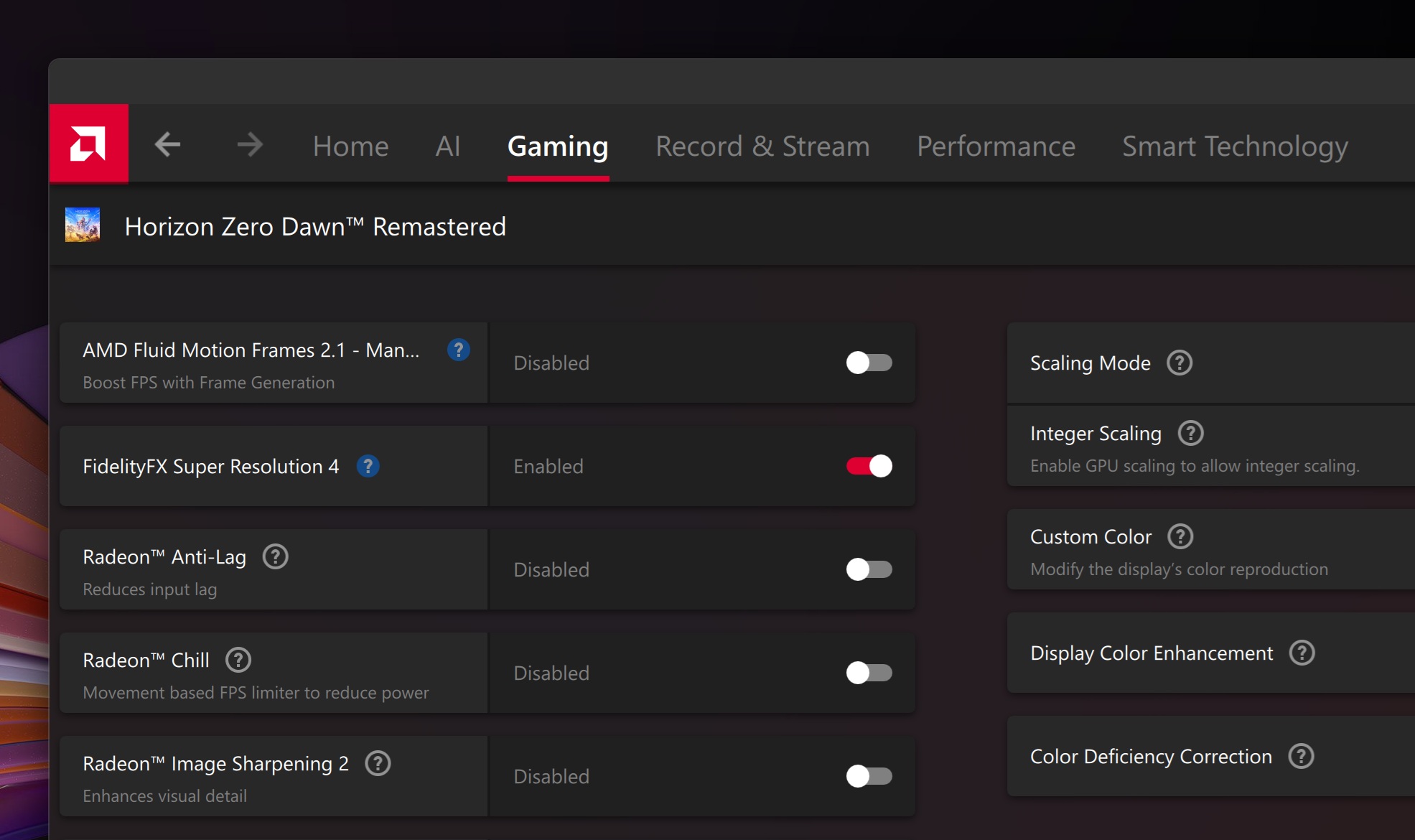
Typing “gibbon” quickly has rarely felt this tense or important. Credit: Outer Brain Studios
Blood Typers adds some much-needed complexity to that basic type-the-word-you-see concept, layering its typing tests on top of a full-fledged survival horror game reminiscent of the original PlayStation era. The result is an amazingly tense and compelling action adventure that also serves as a great way to hone your touch-typing skills.
See it, type it, do it
For some, Blood Typers may bring up first-glance memories of Typing of the Dead, Sega’s campy, typing-controlled take on the House of the Dead light gun game series. But Blood Typers goes well beyond Typing of the Dead‘s on-rails shooting, offering an experience that’s more like a typing-controlled version of Resident Evil.
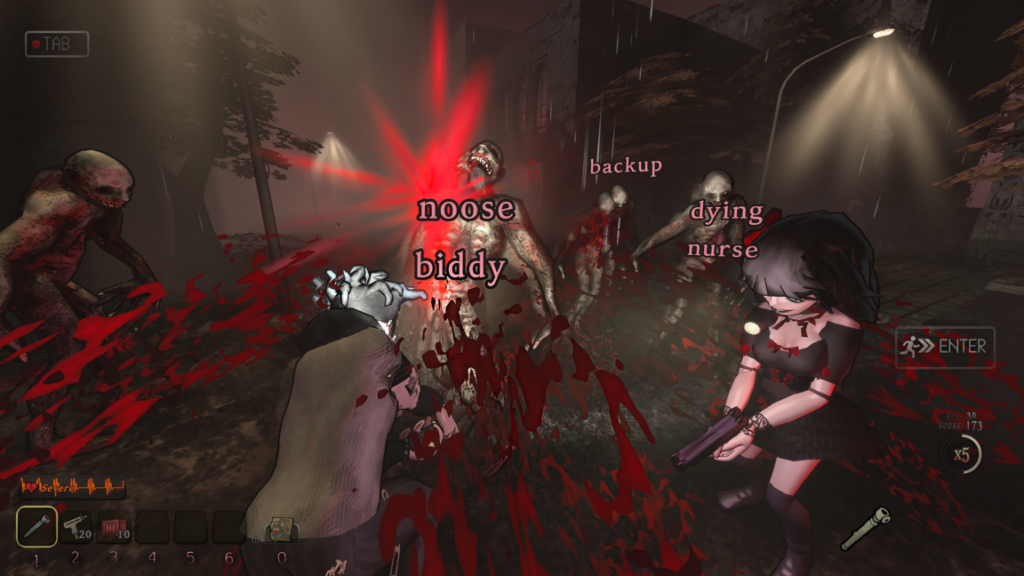
Practically every action in Blood Typers requires typing a word that you see on-screen. That includes basic locomotion, which is accomplished by typing any of a number of short words scattered at key points in your surroundings in order to automatically walk to that point. It’s a bit awkward at first, but quickly becomes second nature as you memorize the names of various checkpoints and adjust to using the shift keys to turn that camera as you move.
Each of those words on the ground is a waypoint that you can type to move toward. Credit: Outer Brain Studios
When any number of undead enemies appear, a quick tap of the tab key switches you to combat mode, which asks you to type longer words that appear above those enemies to use your weapons. More difficult enemies require multiple words to take down, including some with armor that means typing a single word repeatedly before you can move on.
While you start each scenario in Blood Typers with a handy melee weapon, you’ll end up juggling a wide variety of projectile firearms that feel uniquely tuned to the typing gameplay. The powerful shotgun, for instance, can take out larger enemies with just a single word, while the rapid-fire SMG lets you type only the first few letters of each word, allowing for a sort of rapid fire feel. The flamethrower, on the other hand, can set whole groups of nearby enemies aflame, which makes each subsequent attack word that much shorter and faster.
Blood Typers is a terrifically tense, terror-filled typing tutor Read More »