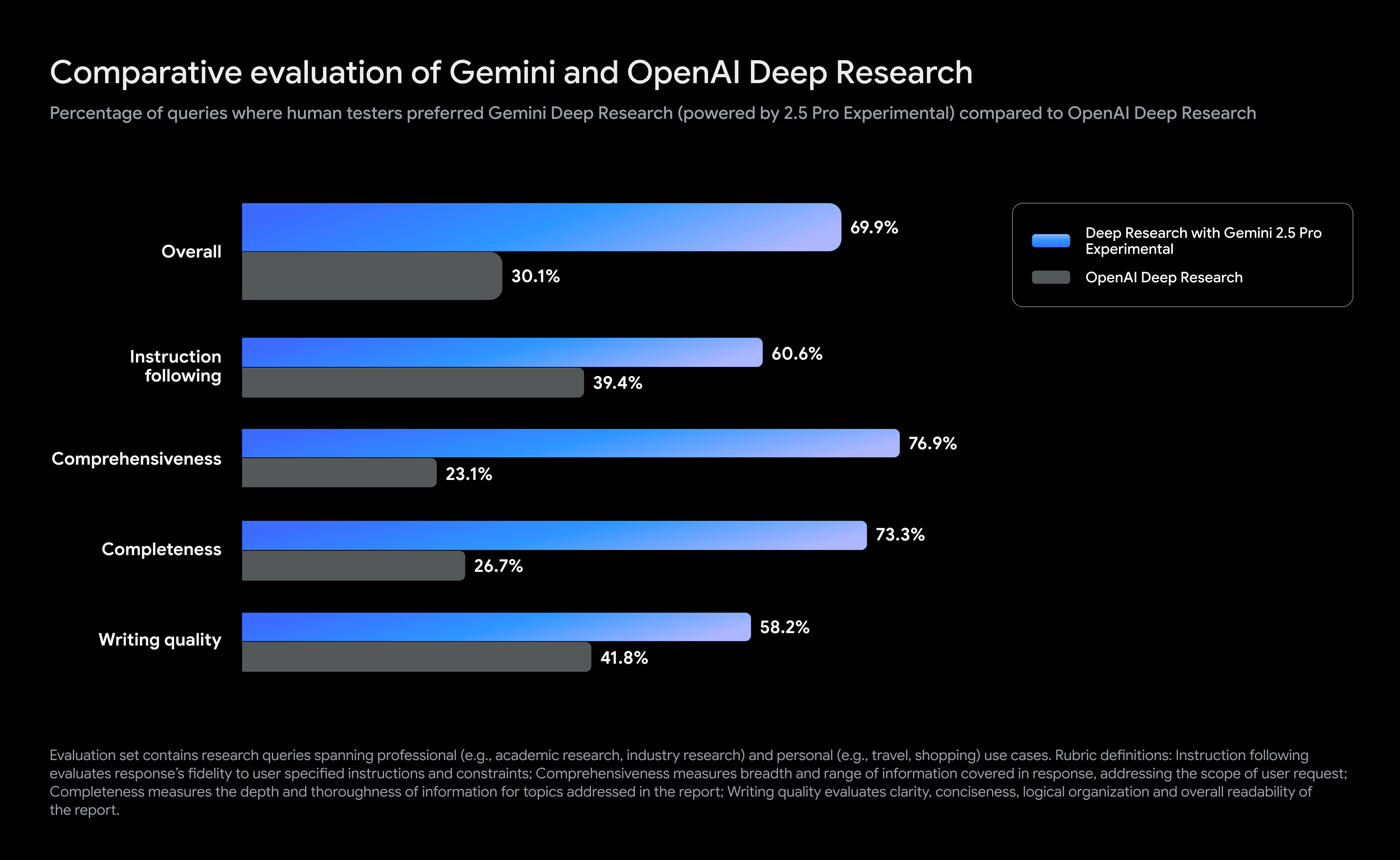
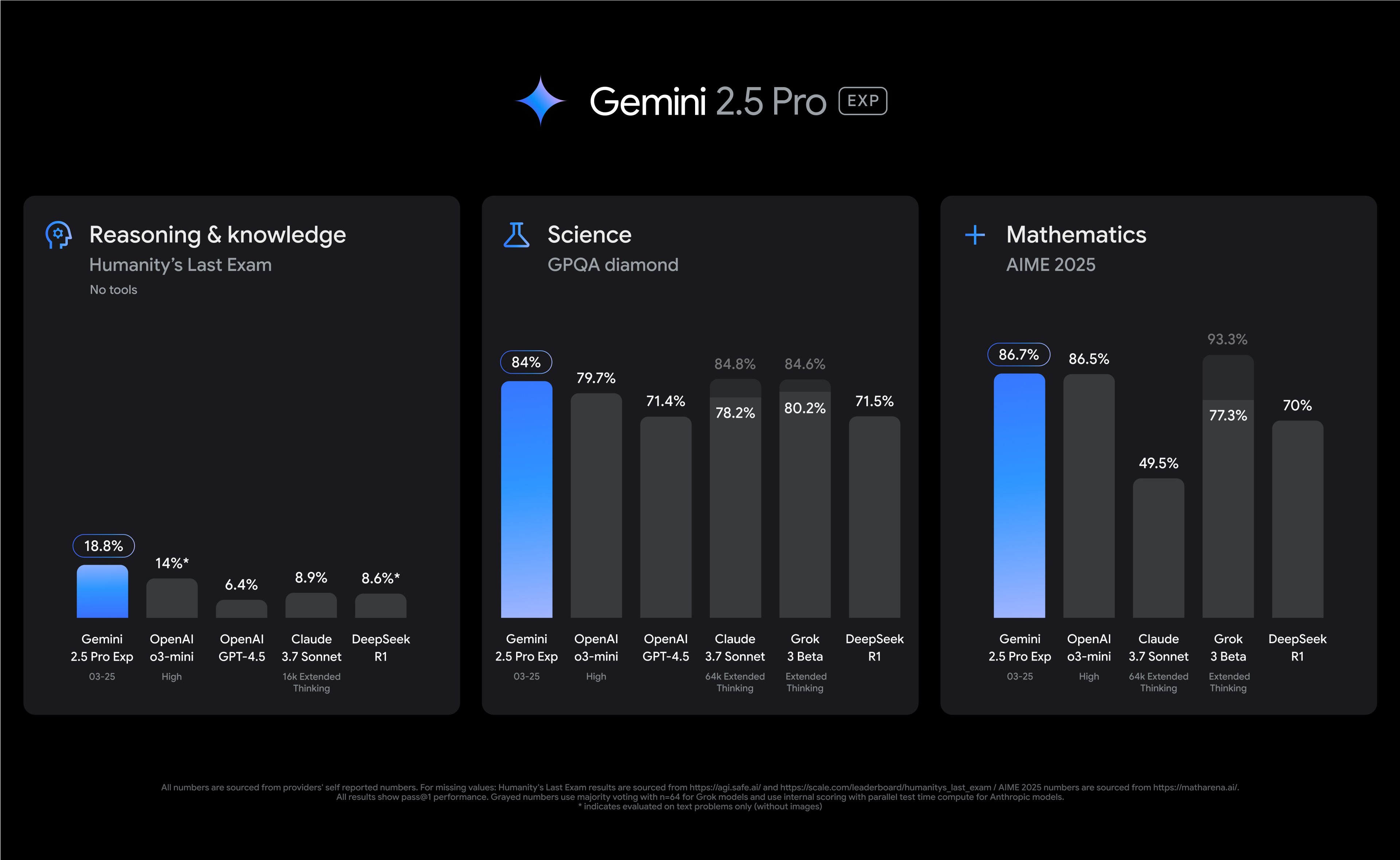
Attackers prompted Gemini over 100,000 times while trying to clone it, Google says
On Thursday, Google announced that “commercially motivated” actors have attempted to clone knowledge from its Gemini AI chatbot by simply prompting it. One adversarial session reportedly prompted the model more than 100,000 times across various non-English languages, collecting responses ostensibly to train a cheaper copycat.
Google published the findings in what amounts to a quarterly self-assessment of threats to its own products that frames the company as the victim and the hero, which is not unusual in these self-authored assessments. Google calls the illicit activity “model extraction” and considers it intellectual property theft, which is a somewhat loaded position, given that Google’s LLM was built from materials scraped from the Internet without permission.
Google is also no stranger to the copycat practice. In 2023, The Information reported that Google’s Bard team had been accused of using ChatGPT outputs from ShareGPT, a public site where users share chatbot conversations, to help train its own chatbot. Senior Google AI researcher Jacob Devlin, who created the influential BERT language model, warned leadership that this violated OpenAI’s terms of service, then resigned and joined OpenAI. Google denied the claim but reportedly stopped using the data.
Even so, Google’s terms of service forbid people from extracting data from its AI models this way, and the report is a window into the world of somewhat shady AI model-cloning tactics. The company believes the culprits are mostly private companies and researchers looking for a competitive edge, and said the attacks have come from around the world. Google declined to name suspects.
The deal with distillation
Typically, the industry calls this practice of training a new model on a previous model’s outputs “distillation,” and it works like this: If you want to build your own large language model (LLM) but lack the billions of dollars and years of work that Google spent training Gemini, you can use a previously trained LLM as a shortcut.
Attackers prompted Gemini over 100,000 times while trying to clone it, Google says Read More »