Google says it dropped the energy cost of AI queries by 33x in one year
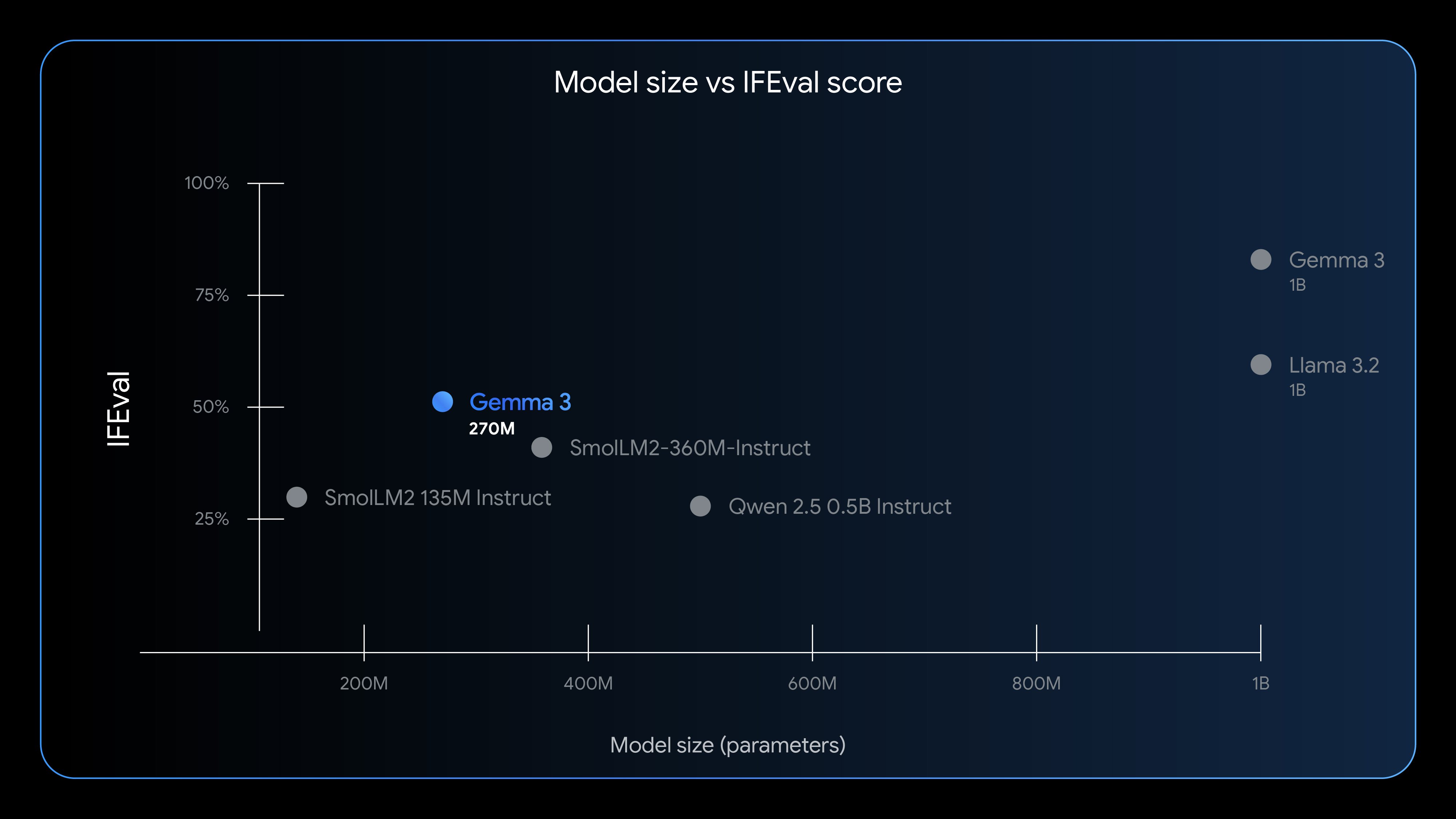
To come up with typical numbers, the team that did the analysis tracked requests and the hardware that served them for a 24 hour period, as well as the idle time for that hardware. This gives them an energy per request estimate, which differs based on the model being used. For each day, they identify the median prompt and use that to calculate the environmental impact.
Going down
Using those estimates, they find that the impact of an individual text request is pretty small. “We estimate the median Gemini Apps text prompt uses 0.24 watt-hours of energy, emits 0.03 grams of carbon dioxide equivalent (gCO2e), and consumes 0.26 milliliters (or about five drops) of water,” they conclude. To put that in context, they estimate that the energy use is similar to about nine seconds of TV viewing.
The bad news is that the volume of requests is undoubtedly very high. The company has chosen to execute an AI operation with every single search request, a compute demand that simply didn’t exist a couple of years ago. So, while the individual impact is small, the cumulative cost is likely to be considerable.
The good news? Just a year ago, it would have been far, far worse.
Some of this is just down to circumstances. With the boom in solar power in the US and elsewhere, it has gotten easier for Google to arrange for renewable power. As a result, the carbon emissions per unit of energy consumed saw a 1.4x reduction over the past year. But the biggest wins have been on the software side, where different approaches have led to a 33x reduction in energy consumed per prompt.
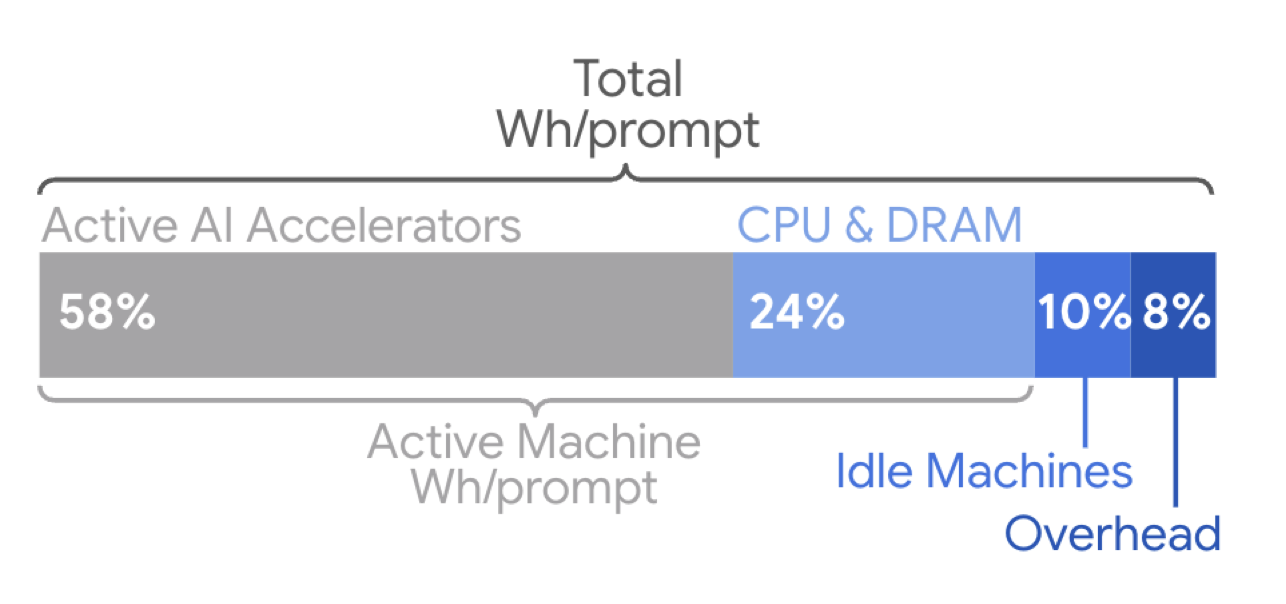
Most of the energy use in serving AI requests comes from time spent in the custom accelerator chips. Credit: Elsworth, et. al.
The Google team describes a number of optimizations the company has made that contribute to this. One is an approach termed Mixture-of-Experts, which involves figuring out how to only activate the portion of an AI model needed to handle specific requests, which can drop computational needs by a factor of 10 to 100. They’ve developed a number of compact versions of their main model, which also reduce the computational load. Data center management also plays a role, as the company can make sure that any active hardware is fully utilized, while allowing the rest to stay in a low-power state.
Google says it dropped the energy cost of AI queries by 33x in one year Read More »