Google unveils Gemini 3 AI model and AI-first IDE called Antigravity
Google’s flagship AI model is getting its second major upgrade this year.
Google has kicked its Gemini rollout into high gear over the past year, releasing the much-improved Gemini 2.5 family and cramming various flavors of the model into Search, Gmail, and just about everything else the company makes.
Now, Google’s increasingly unavoidable AI is getting an upgrade. Gemini 3 Pro is available in a limited form today, featuring more immersive, visual outputs and fewer lies, Google says. The company also says Gemini 3 sets a new high-water mark for vibe coding, and Google is announcing a new AI-first integrated development environment (IDE) called Antigravity, which is also available today.
The first member of the Gemini 3 family
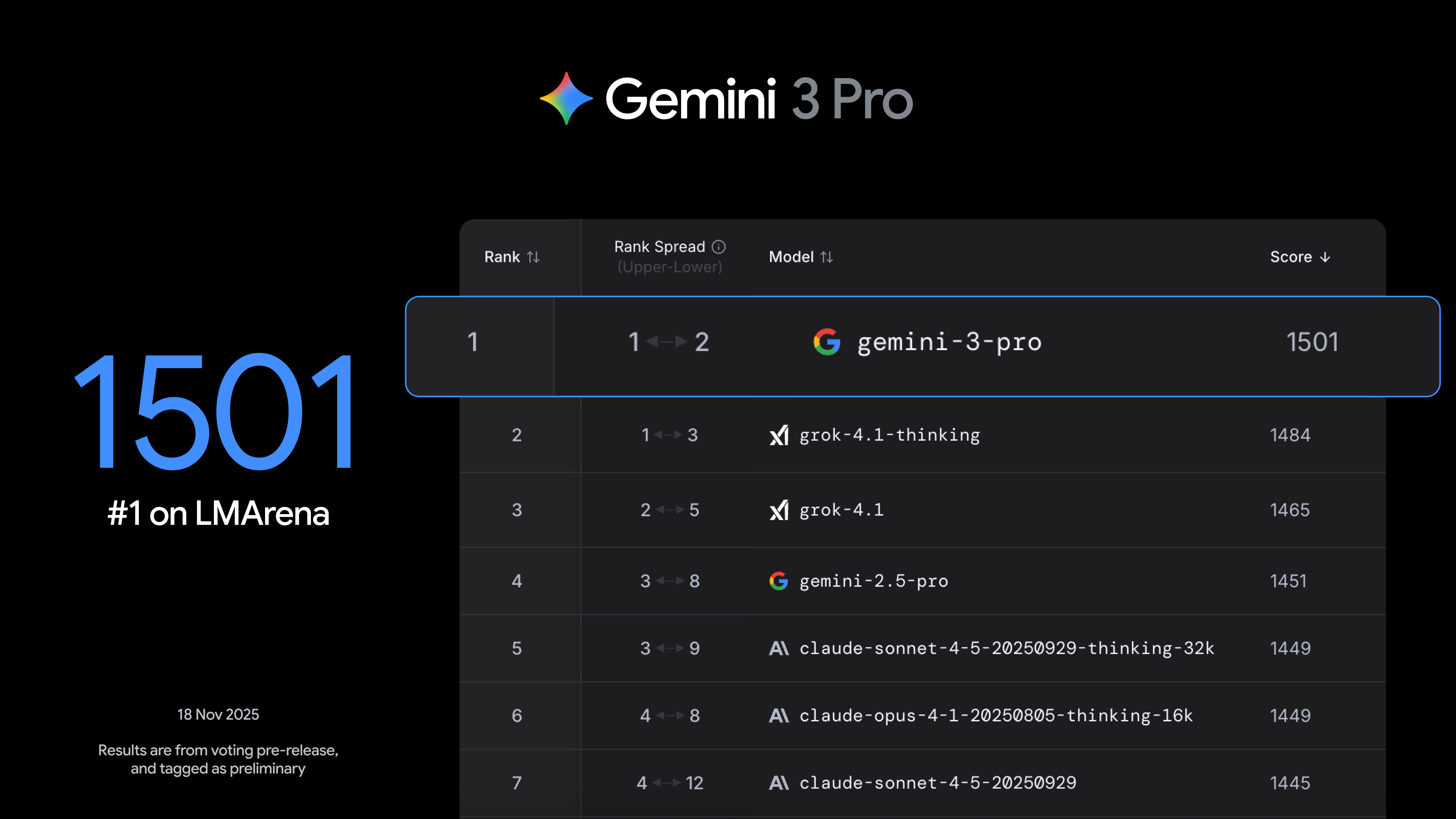
Google says the release of Gemini 3 is yet another step toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). The new version of Google’s flagship AI model has expanded simulated reasoning abilities and shows improved understanding of text, images, and video. So far, testers like it—Google’s latest LLM is once again atop the LMArena leaderboard with an ELO score of 1,501, besting Gemini 2.5 Pro by 50 points.
Credit: Google
Factuality has been a problem for all gen AI models, but Google says Gemini 3 is a big step in the right direction, and there are myriad benchmarks to tell the story. In the 1,000-question SimpleQA Verified test, Gemini 3 scored a record 72.1 percent. Yes, that means the state-of-the-art LLM still screws up almost 30 percent of general knowledge questions, but Google says this still shows substantial progress. On the much more difficult Humanity’s Last Exam, which tests PhD-level knowledge and reasoning, Gemini set another record, scoring 37.5 percent without tool use.
Math and coding are also a focus of Gemini 3. The model set new records in MathArena Apex (23.4 percent) and WebDev Arena (1487 ELO). In the SWE-bench Verified, which tests a model’s ability to generate code, Gemini 3 hit an impressive 76.2 percent.
So there are plenty of respectable but modest benchmark improvements, but Gemini 3 also won’t make you cringe as much. Google says it has tamped down on sycophancy, a common problem in all these overly polite LLMs. Outputs from Gemini 3 Pro are reportedly more concise, with less of what you want to hear and more of what you need to hear.
You can also expect Gemini 3 Pro to produce noticeably richer outputs. Google claims Gemini’s expanded reasoning capabilities keep it on task more effectively, allowing it to take action on your behalf. For example, Gemini 3 can triage and take action on your emails, creating to-do lists, summaries, recommended replies, and handy buttons to trigger suggested actions. This differs from the current Gemini models, which would only create a text-based to-do list with similar prompts.
The model also has what Google calls a “generative interface,” which comes in the form of two experimental output modes called visual layout and dynamic view. The former is a magazine-style interface that includes lots of images in a scrollable UI. Dynamic view leverages Gemini’s coding abilities to create custom interfaces—for example, a web app that explores the life and work of Vincent Van Gogh.
There will also be a Deep Think mode for Gemini 3, but that’s not ready for prime time yet. Google says it’s being tested by a small group for later release, but you should expect big things. Deep Think mode manages 41 percent in Humanity’s Last Exam without tools. Believe it or not, that’s an impressive score.
Coding with vibes
Google has offered several ways of generating and modifying code with Gemini models, but the launch of Gemini 3 adds a new one: Google Antigravity. This is Google’s new agentic development platform—it’s essentially an IDE designed around agentic AI, and it’s available in preview today.
With Antigravity, Google promises that you (the human) can get more work done by letting intelligent agents do the legwork. Google says you should think of Antigravity as a “mission control” for creating and monitoring multiple development agents. The AI in Antigravity can operate autonomously across the editor, terminal, and browser to create and modify projects, but everything they do is relayed to the user in the form of “Artifacts.” These sub-tasks are designed to be easily verifiable so you can keep on top of what the agent is doing. Gemini will be at the core of the Antigravity experience, but it’s not just Google’s bot. Antigravity also supports Claude Sonnet 4.5 and GPT-OSS agents.
Of course, developers can still plug into the Gemini API for coding tasks. With Gemini 3, Google is adding a client-side bash tool, which lets the AI generate shell commands in its workflow. The model can access file systems and automate operations, and a server-side bash tool will help generate code in multiple languages. This feature is starting in early access, though.
AI Studio is designed to be a faster way to build something with Gemini 3. Google says Gemini 3 Pro’s strong instruction following makes it the best vibe coding model yet, allowing non-programmers to create more complex projects.
A big experiment
Google will eventually have a whole family of Gemini 3 models, but there’s just the one for now. Gemini 3 Pro is rolling out in the Gemini app, AI Studio, Vertex AI, and the API starting today as an experiment. If you want to tinker with the new model in Google’s Antigravity IDE, that’s also available for testing today on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Gemini 3 will also launch in the Google search experience on day one. You’ll have the option to enable Gemini 3 Pro in AI Mode, where Google says it will provide more useful information about a query. The generative interface capabilities from the Gemini app will be available here as well, allowing Gemini to create tools and simulations when appropriate to answer the user’s question. Google says these generative interfaces are strongly preferred in its user testing. This feature is available today, but only for AI Pro and Ultra subscribers.
Because the Pro model is the only Gemini 3 variant available in the preview, AI Overviews isn’t getting an immediate upgrade. That will come, but for now, Overviews will only reach out to Gemini 3 Pro for especially difficult search queries—basically the kind of thing Google thinks you should have used AI Mode to do in the first place.
There’s no official timeline for releasing more Gemini 3 models or graduating the Pro variant to general availability. However, given the wide rollout of the experimental release, it probably won’t be long.
Ryan Whitwam is a senior technology reporter at Ars Technica, covering the ways Google, AI, and mobile technology continue to change the world. Over his 20-year career, he’s written for Android Police, ExtremeTech, Wirecutter, NY Times, and more. He has reviewed more phones than most people will ever own. You can follow him on Bluesky, where you will see photos of his dozens of mechanical keyboards.
Google unveils Gemini 3 AI model and AI-first IDE called Antigravity Read More »