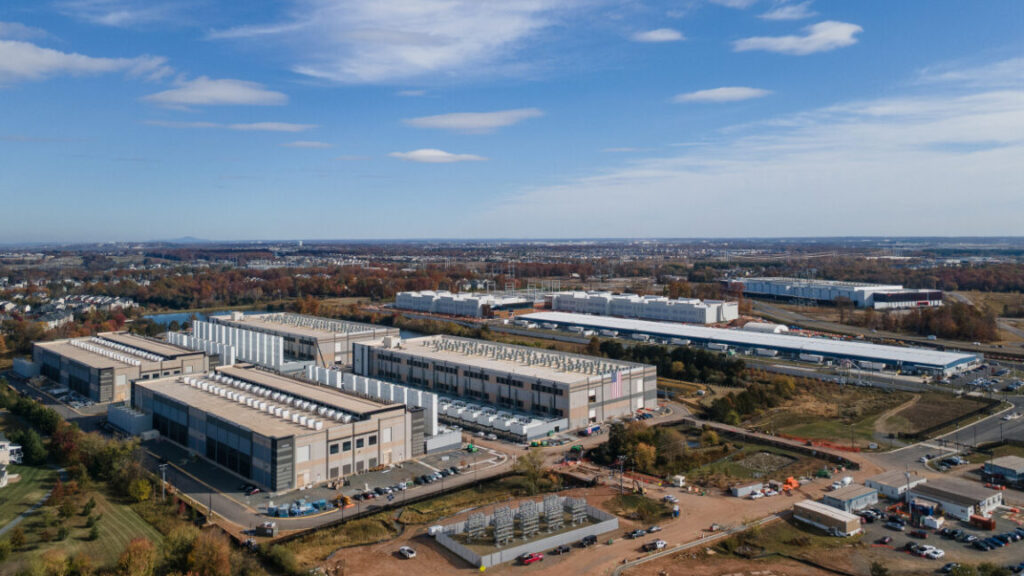
Hegseth wants to integrate Musk’s Grok AI into military networks this month
On Monday, US Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said he plans to integrate Elon Musk’s AI tool, Grok, into Pentagon networks later this month. During remarks at the SpaceX headquarters in Texas reported by The Guardian, Hegseth said the integration would place “the world’s leading AI models on every unclassified and classified network throughout our department.”
The announcement comes weeks after Grok drew international backlash for generating sexualized images of women and children, although the Department of Defense has not released official documentation confirming Hegseth’s announced timeline or implementation details.
During the same appearance, Hegseth rolled out what he called an “AI acceleration strategy” for the Department of Defense. The strategy, he said, will “unleash experimentation, eliminate bureaucratic barriers, focus on investments, and demonstrate the execution approach needed to ensure we lead in military AI and that it grows more dominant into the future.”
As part of the plan, Hegseth directed the DOD’s Chief Digital and Artificial Intelligence Office to use its full authority to enforce department data policies, making information available across all IT systems for AI applications.
“AI is only as good as the data that it receives, and we’re going to make sure that it’s there,” Hegseth said.
If implemented, Grok would join other AI models the Pentagon has adopted in recent months. In July 2025, the defense department issued contracts worth up to $200 million for each of four companies, including Anthropic, Google, OpenAI, and xAI, for developing AI agent systems across different military operations. In December 2025, the Department of Defense selected Google’s Gemini as the foundation for GenAI.mil, an internal AI platform for military use.
Hegseth wants to integrate Musk’s Grok AI into military networks this month Read More »