X office raided in France’s Grok probe; Elon Musk summoned for questioning
UK probe moves ahead with “urgency”
X said in July 2025 that it was “in the dark” over what specific allegations it faced related to manipulation of the X algorithm and fraudulent data extraction. X said it would not comply with France’s request for access to its recommendation algorithm and real-time data about all user posts.
The Paris prosecutor’s office today said the investigation is taking a “constructive approach” with the goal of ensuring that X complies with French laws “insofar as it operates on national territory.” In addition to Musk and Yaccarino, the prosecutor’s office is seeking interviews with X employees about the allegations and potential compliance measures.
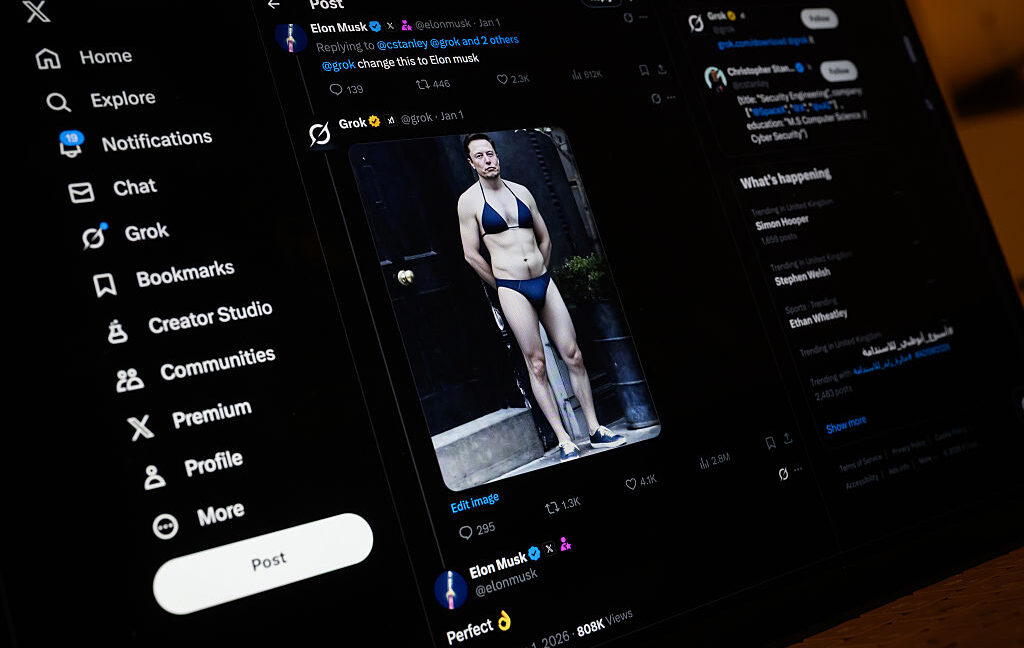
Separately, UK communications regulator Ofcom today provided an update on its investigation into Grok’s generation of sexual deepfakes of real people, including children. Ofcom is “gathering and analyzing evidence to determine whether X has broken the law” and is “progressing the investigation as a matter of urgency,” it said. Ofcom is not currently investigating xAI, the Musk company that develops Grok, but said it “continue[s] to demand answers from xAI about the risks it poses.”
The UK Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), which regulates data protection, said today it opened a formal investigation into X regarding the “processing of personal data in relation to the Grok artificial intelligence system and its potential to produce harmful sexualized image and video content.”
“We have taken this step following reports that Grok has been used to generate non‑consensual sexual imagery of individuals, including children,” the ICO said. “The reported creation and circulation of such content raises serious concerns under UK data protection law and presents a risk of significant potential harm to the public.”
X office raided in France’s Grok probe; Elon Musk summoned for questioning Read More »