In 1982, a physics joke gone wrong sparked the invention of the emoticon
A simple proposal on a 1982 electronic bulletin board helped sarcasm flourish online.
Credit: Benj Edwards / DEC
On September 19, 1982, Carnegie Mellon University computer science research assistant professor Scott Fahlman posted a message to the university’s bulletin board software that would later come to shape how people communicate online. His proposal: use 🙂 and 🙁 as markers to distinguish jokes from serious comments. While Fahlman describes himself as “the inventor… or at least one of the inventors” of what would later be called the smiley face emoticon, the full story reveals something more interesting than a lone genius moment.
The whole episode started three days earlier when computer scientist Neil Swartz posed a physics problem to colleagues on Carnegie Mellon’s “bboard,” which was an early online message board. The discussion thread had been exploring what happens to objects in a free-falling elevator, and Swartz presented a specific scenario involving a lit candle and a drop of mercury.
That evening, computer scientist Howard Gayle responded with a facetious message titled “WARNING!” He claimed that an elevator had been “contaminated with mercury” and suffered “some slight fire damage” due to a physics experiment. Despite clarifying posts noting the warning was a joke, some people took it seriously.

A DECSYSTEM-20 KL-10 (1974) seen at the Living Computer Museum in Seattle. Scott Fahlman used a similar system with a terminal to propose his smiley concept. Credit: Jason Scott
The incident sparked immediate discussion about how to prevent such misunderstandings and the “flame wars” (heated arguments) that could result from misread intent.
“This problem caused some of us to suggest (only half seriously) that maybe it would be a good idea to explicitly mark posts that were not to be taken seriously,” Fahlman later wrote in a retrospective post published on his CMU website. “After all, when using text-based online communication, we lack the body language or tone-of-voice cues that convey this information when we talk in person or on the phone.”
On September 17, 1982, the next day after the misunderstanding on the CMU bboard, Swartz made the first concrete proposal: “Maybe we should adopt a convention of putting a star
Within hours, multiple Carnegie Mellon computer scientists weighed in with alternative proposals. Joseph Ginder suggested using % instead of *. Anthony Stentz proposed a nuanced system: “How about using for good jokes and % for bad jokes?” Keith Wright championed the ampersand (&), arguing it “looks funny” and “sounds funny.” Leonard Hamey suggested # because “it looks like two lips with teeth showing between them.”
Meanwhile, some Carnegie Mellon users were already using their own solution. A group on the Gandalf VAX system later revealed they had been using __/ as “universally known as a smile” to mark jokes. But it apparently didn’t catch on beyond that local system.
The winning formula
Two days after Swartz’s initial proposal, Fahlman entered the discussion with his now-famous post: “I propose that the following character sequence for joke markers: 🙂 Read it sideways.” He added that serious messages could use :-(, noting, “Maybe we should mark things that are NOT jokes, given current trends.”
What made Fahlman’s proposal work wasn’t that he invented the concept of joke markers—Swartz had done that. It wasn’t that he invented smile symbols at Carnegie Mellon, since the __/ already existed. Rather, Fahlman synthesized the best elements from the ongoing discussion: the simplicity of single-character proposals, the visual clarity of face-like symbols, the sideways-reading principle hinted at by Hamey’s #, and a complete binary system that covered both humor 🙂 and seriousness :-(.
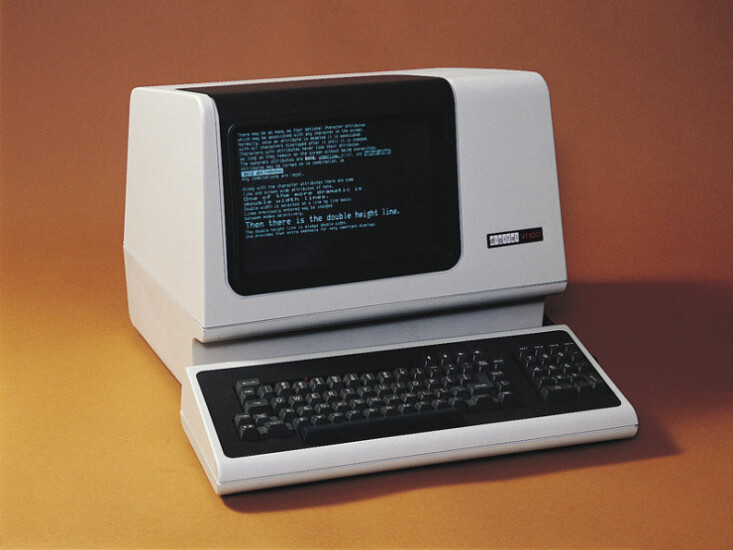

Early computer terminals like the DEC VT-100 did not support graphics, requiring typographic solutions for displaying “images.” Credit: Digital Equipment Corporation
The simplicity of Fahlman’s emoticons was key to their adoption. The university’s network ran on large DEC mainframes accessed via video terminals (Fahlman himself made his posts from a terminal attached to a DECSYSTEM-20) that were strictly limited to the 95 printable characters of the US-ASCII set. With no ability to display graphics or draw pixels, Fahlman’s solution used the only tools available: standard punctuation marks rearranging the strict grid of the terminal screen into a “picture.”
The emoticons spread quickly across ARPAnet, the precursor to the modern Internet, reaching other universities and research labs. By November 10, 1982—less than two months later—Carnegie Mellon researcher James Morris began introducing the smiley emoticon concept to colleagues at Xerox PARC, complete with a growing list of variations. What started as an internal Carnegie Mellon convention over time became a standard feature of online communication, often simplified without the hyphen nose to 🙂 or :(, among many other variations.
Lost backup tapes
There’s an interesting coda to this story: For years, the original bboard thread existed only in fading memory. The bulletin board posts had been deleted, and Carnegie Mellon’s computer science department had moved to new systems. The old messages seemed lost forever.
Between 2001 and 2002, Mike Jones, a former Carnegie Mellon researcher then working at Microsoft, sponsored what Fahlman calls a “digital archaeology” project. Jeff Baird and the Carnegie Mellon facilities staff undertook a painstaking effort: locating backup tapes from 1982, finding working tape drives that could read the obsolete media, decoding old file formats, and searching for the actual posts. The team recovered the thread, revealing not just Fahlman’s famous post but the entire three-day community discussion that led to it.
The recovered messages, which you can read here, show how collaboratively the emoticon was developed—not a lone genius moment but an ongoing conversation proposing, refining, and building on the group’s ideas. Fahlman had no idea his synthesis would become a fundamental part of how humans express themselves in digital text, but neither did Swartz, who first suggested marking jokes, or the Gandalf VAX users who were already using their own smile symbols.
From emoticon to emoji
While Fahlman’s text-based emoticons spread across Western online culture and remained text-character-based for a long time, Japanese mobile phone users in the late 1990s developed a parallel system: emoji. For years, Shigetaka Kurita’s 1999 set for NTT DoCoMo was widely cited as the original. However, recent discoveries have revealed earlier origins. SoftBank released a picture-based character set on mobile phones in 1997, and the Sharp PA-8500 personal organizer featured selectable icon characters as early as 1988.
Unlike emoticons that required reading sideways, emoji were small pictographic images that could convey emotion, objects, and ideas with more detail. When Unicode standardized emoji in 2010 and Apple added an emoji keyboard to iOS in 2011, the format exploded globally. Today, emoji have largely replaced emoticons in casual communication, though Fahlman’s sideways faces still appear regularly in text messages and social media posts.
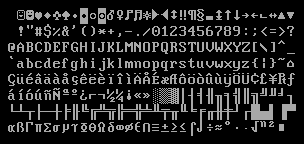
IBM’s Code Page 437 character set included a smiley face as early as 1981. Credit: Matt Giuca
As Fahlman himself notes on his website, he may not have been “the first person ever to type these three letters in sequence.” Others, including teletype operators and private correspondents, may have used similar symbols before 1982, perhaps even as far back as 1648. Author Vladimir Nabokov suggested before 1982 that “there should exist a special typographical sign for a smile.” And the original IBM PC included a dedicated smiley character as early as 1981 (perhaps that should be considered the first emoji).
What made Fahlman’s contribution significant wasn’t absolute originality but rather proposing the right solution at the right time in the right context. From there, the smiley could spread across the emerging global computer network, and no one would ever misunderstand a joke online again. 🙂
In 1982, a physics joke gone wrong sparked the invention of the emoticon Read More »