5 changes to know about in Apple’s latest iOS, macOS, and iPadOS betas
This week, Apple released the first developer betas for iOS 26.4, iPadOS 26.4, macOS 26.4, and its other operating systems. On Tuesday, it followed those up with public beta versions of the same updates.
Usually released around the midpoint between one major iOS release and the next, the *.4 updates to its operating system usually include a significant batch of new features and other refinements, and if the first beta is any indication, this year’s releases uphold that tradition.
A new “Playlist Playground” feature will let Apple Music subscribers generate playlists with text prompts, and native support for video podcasts is coming to the Podcasts app. The Creator Studio version of the Freeform drawing and collaboration app is also available in the 26.4 updates, allowing subscribers to access stock images from Apple’s Content Hub and to insert AI-generated images.
But we’ve spent time digging through the betas to identify some of the more below-the-surface improvements and changes that Apple is testing. Some of these changes won’t come to the public versions of the software until a later release; others may be removed or changed between now and when the 26.4 update is made available to the general public. But generally, Apple’s betas give us a good idea of what the final release will look like.
One feature that hasn’t appeared in these betas? The new “more intelligent Siri” that Apple has been promising since the iOS 18 launch in 2024. Apple delayed the feature until sometime in 2026, citing that it wasn’t meeting the company’s standards for quality and reliability.
Reports indicated that the company had been planning to make the new Siri part of the 26.4 update, but as of earlier this month, Apple has reportedly decided to push it to the 26.5 release or later; even releasing it as part of iOS 27 in the fall would technically not run afoul of the “2026” promise.
Before we begin, the standard warning about installing beta software on hardware you rely on day to day. Although these point updates are generally more stable than the major releases Apple tests in the summer and fall, they can still contain major bugs and may cause your device to behave strangely. The first beta, in particular, tends to be the roughest—more stable versions will be released in the coming weeks, and we should see the final version of the update within the next couple months.
Charging limits for MacBooks
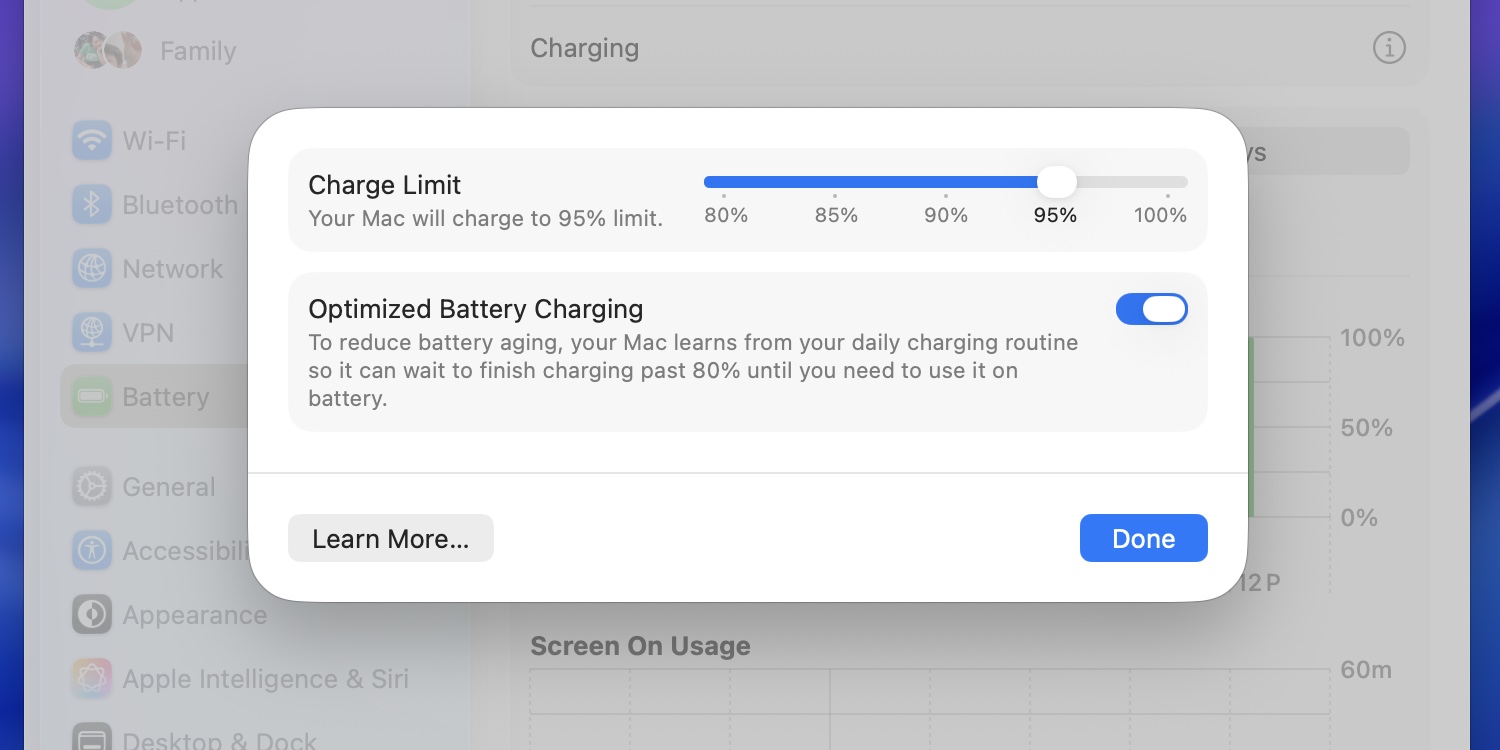
The macOS 26.4 update includes a slider for manually limiting your Mac’s battery charge percentage. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
In macOS 11 Big Sur, Apple added an on-by-default “Optimized Battery Charging” toggle to the operating system that would allow macOS to limit your battery’s charge percentage to 80 percent based on your usage and charging behavior. The idea is to limit the time your battery spends charging while full, something that can gradually reduce its capacity.
The macOS 26.4 update adds a new slider similar to the one in iOS, further allowing users to manually specify a maximum charge limit that is always observed, no matter what. It’s adjustable in 5 percent increments from 80 to 100 percent.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that limiting your charge percentage can lengthen the useful life of your battery and reduce wear, but there’s nothing that will fully prevent a battery from wearing out and losing capacity over time. It’s up to users to decide whether an immediately noticeable everyday hit to battery life is worth a slightly longer service life.
In the current macOS betas, enabling a charge limit manually doesn’t disable the Optimized Battery Charging feature the way it does in iOS. It’s unclear if this is an early bug or an intentional difference in how the feature is implemented in macOS.
End-to-end encryption (and other improvements) for non-Apple texting
Apple has been infamously slow to adopt support for the Rich Communication Services (RCS) messaging protocol used by most modern Android phones. Apple-to-Apple messaging was handled using iMessage, which supports end-to-end encryption among many other features. But for many years, it stuck by the aging SMS standard for “green bubble” texting between Apple’s platforms and others, to the enduring frustration of anyone with a single Android-using friend in a group chat.
Apple finally began supporting RCS messaging for major cellular carriers in iOS 18, and has slowly expanded support to other networks in subsequent releases. But Apple’s implementation still doesn’t support end-to-end encryption, which was added to the RCS standard about a year ago.
The 26.4 update is the first to begin testing encryption for RCS messages. But as with the initial RCS rollout, Apple is moving slowly and deliberately: for now, encrypted RCS messaging only works when texting between Apple devices, and not between Apple devices and Android phones. The feature also won’t be included in the final 26.4 release—it’s only included in the betas for testing purposes, and it “will be available to customers in a future software update for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, and watchOS.”
Encrypted iMessage and RCS chats will be labeled with a lock icon, much like how most web browsers label HTTPS sites.
To support encrypted messaging, Apple will jump from version 2.4 of the RCS Universal Profile to version 3.0. This should also enable support for several improvements in versions 2.5, 2.6, and 2.7 of the RCS standard, including previously iMessage-exclusive things like editing and recalling messages and replying to specific messages inline.
The return of the “Compact” Safari tab bar
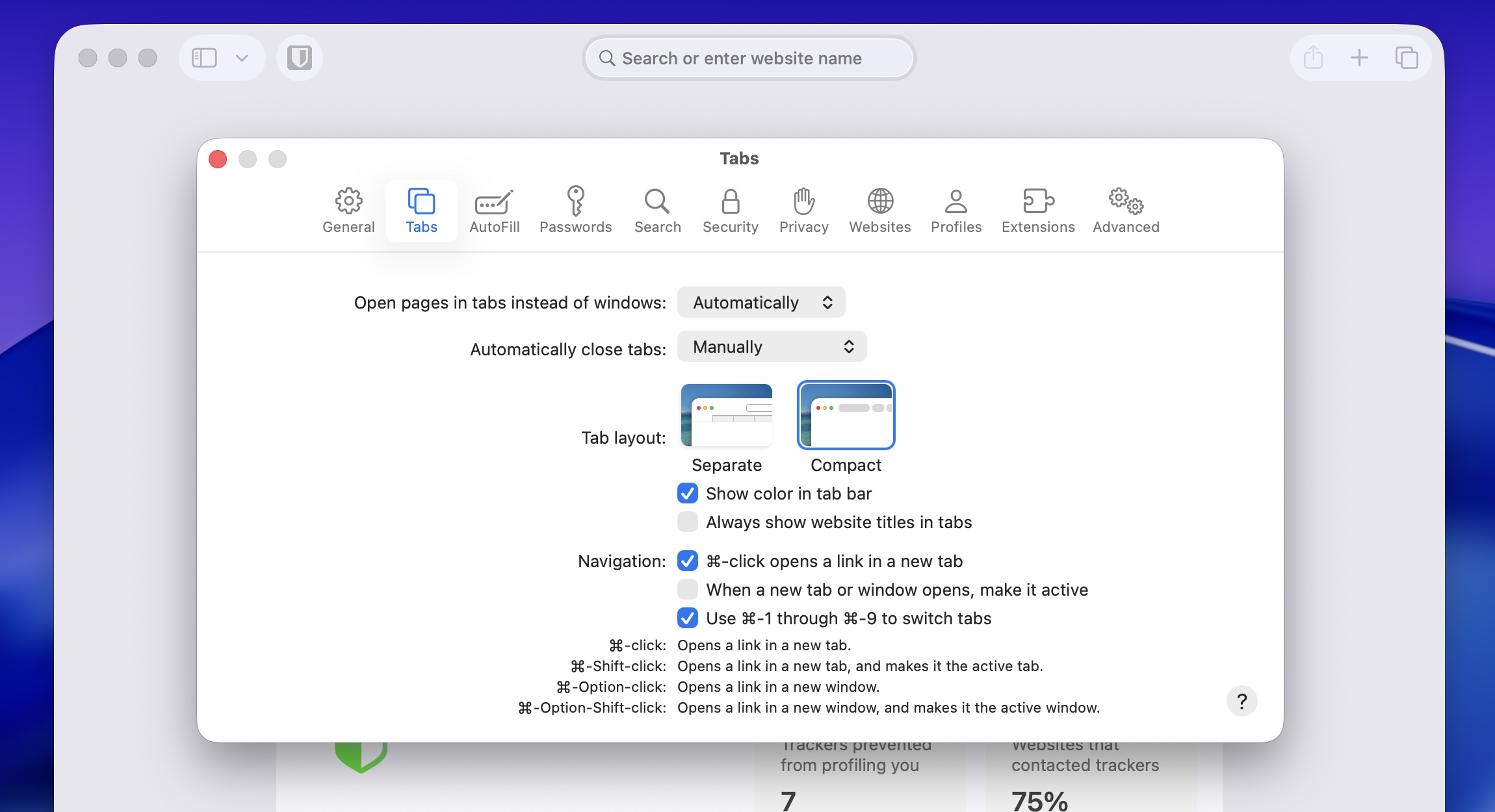
The Compact tab view returns to Safari 26.4 and iPadOS 26.4. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
As part of the macOS 12 Monterey/iPadOS 15 beta cycle in 2021, Apple attempted a pretty radical redesign of the Safari browser that combined your tabs and the address bar into one, with the goal of increasing the amount of viewable space on the pages you were viewing. By the time both operating systems were released to the public, Safari’s default design had more or less reverted to its previous state, but the “compact” tab view lived on as an optional view in the settings for those who liked it.
Tahoe, the Safari 26 update, and iPadOS 26 all removed that Compact view entirely, though a version of the Compact view became the default for the iPhone version of Safari. The macOS 26.4, Safari 26.4, and iPadOS 26.4 updates restore the Compact tab option to the other versions of Safari.
On-by-default Stolen Device Protection
Originally introduced in the iOS 17.3 update, Apple’s “Stolen Device Protection” toggle for iPhones added an extra layer of security for users whose phones were stolen by people who had learned their passcodes. With Stolen Device Protection enabled, an iPhone that had been removed from “familiar locations, such as home or work” would require biometric Face ID or Touch ID authentication before accessing stored passwords and credit cards, erasing your phone, or changing Apple Account passwords. Normally, users can enter their passcodes as a fallback; Stolen Device Protection removes that fallback.
The iOS 26.4 update will make Stolen Device Protection on by default. Generally, you won’t notice a difference in how your phone behaves, but if you’re traveling or away from places where you regularly use your phone and you can’t use your passcode to access certain information, this is why.
It’s possible to switch off Stolen Device protection, but doing so requires biometric authentication, an hour-long wait, and then a second biometric authentication. (This extended wait is also required for disabling Find My, changing your phone’s passcode, or changing Touch ID and Face ID settings.)
Rosetta’s end approaches
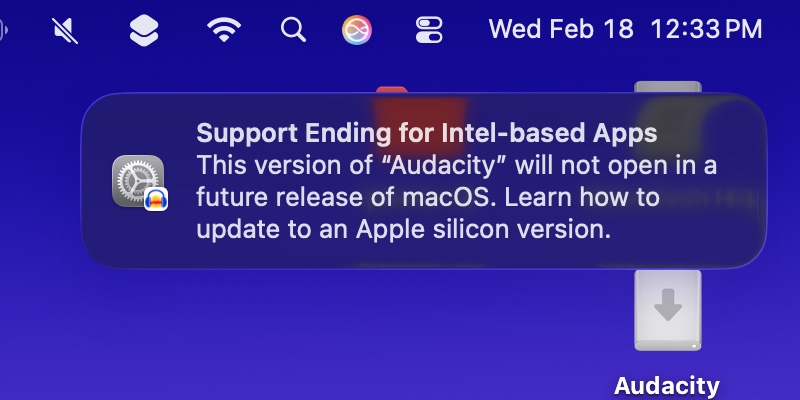
The macOS 26.4 update will add the first user-facing notifications about the end of Rosetta support, currently slated for macOS 28 in 2027. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Apple’s Rosetta 2 was a crucial support beam in the bridge from the Intel Mac era to the Apple Silicon era, enabling unmodified Intel-native apps to run on the M1 and later processors, with noticeable but manageable performance and responsiveness hits. As with the original Rosetta, it allowed Apple to execute a major CPU architecture switch while keeping it mostly invisible to Mac users, and it bought developers time to release Arm-native versions of their apps so they could take full advantage of the new chips.
But now that the transition is complete and the last Intel Macs are fading into the rearview, Apple plans to remove the translation layer from future versions of macOS, with some exceptions for games that rely on the technology.
Rosetta 2 won’t be completely removed until macOS 28, but macOS 26.4 will be the first to begin warning users about the end of Rosetta when they launch Intel-native apps. Those notifications link to an Apple support page about identifying and updating Intel-only apps to Apple Silicon-native versions (or universal binaries that support both architectures).
Apple has deployed this “adding notifications without removing functionality” approach to deprecating older apps before. Versions 10.13 and 10.14 of macOS would show users pop-ups about the end of support for 32-bit apps for a couple of years before that support was removed in macOS 10.15, for example.
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
5 changes to know about in Apple’s latest iOS, macOS, and iPadOS betas Read More »