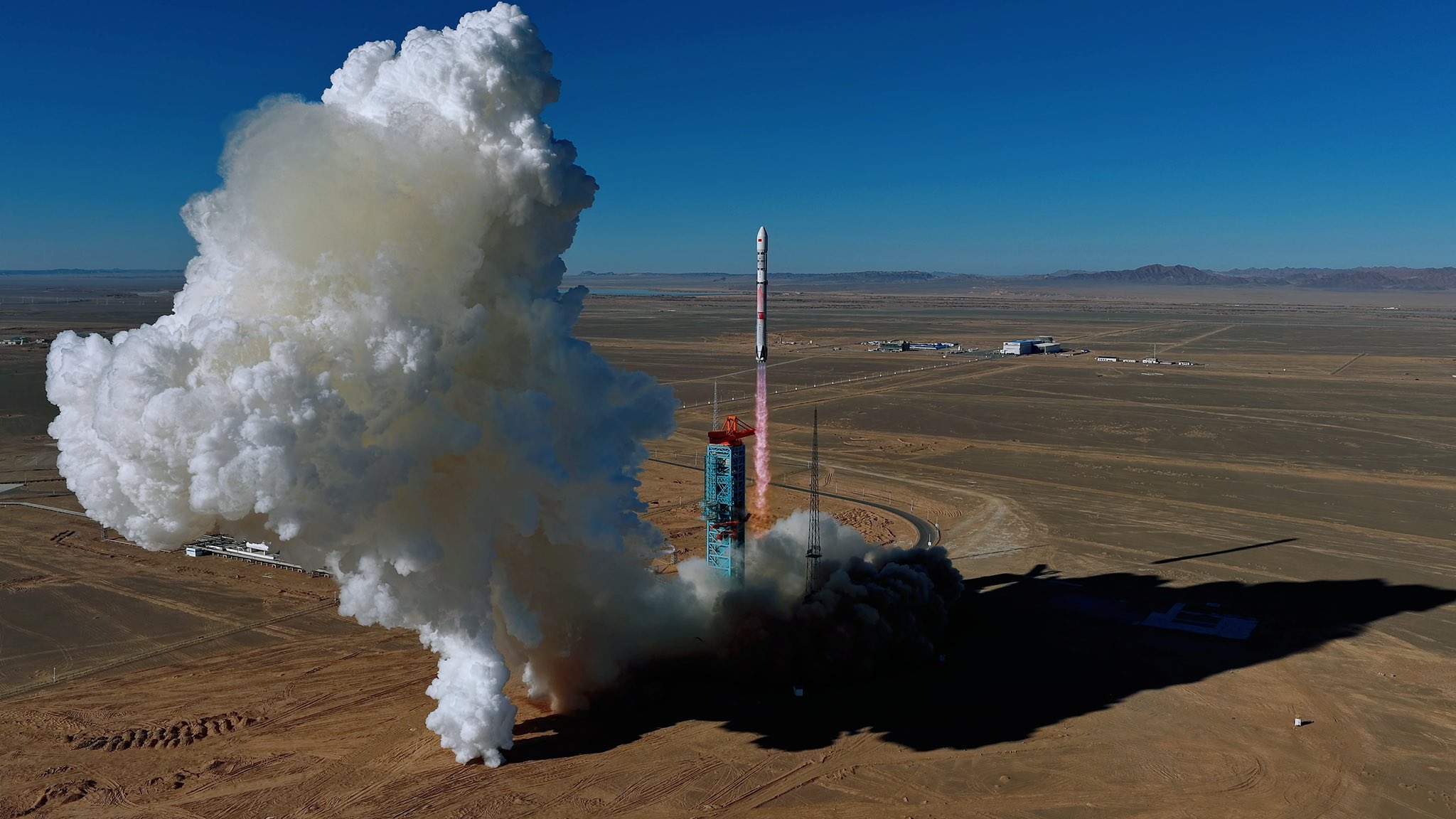
There’s a lot of big talk about sovereign launch—who is doing something about it?
As alliances fray, these are the nations investing in sovereign access to space.
PLD Space shows off a model of its Miura 1 suborbital rocket during a 2021 presentation on the esplanade of the National Museum of Natural Sciences in Madrid. Credit: Oscar Gonzalez/NurPhoto via Getty Images
No one will supplant American and Chinese dominance in the space launch arena anytime soon, but several longtime US allies now see sovereign access to space as a national security imperative.
Taking advantage of private launch initiatives already underway within their own borders, several middle and regional powers have approved substantial government funding for commercial startups to help them reach the launch pad. Australia, Canada, Germany, and Spain are among the nations that currently lack the ability to independently put their own satellites into orbit but which are now spending money to establish a domestic launch industry. Others talk a big game but haven’t committed the cash to back up their ambitions.
The moves are part of a wider trend among US allies to increase defense spending amid strained relations with the Trump administration. Tariffs, trade wars, and threats to invade the territory of a NATO ally have changed the tune of many foreign leaders. In Europe, there’s even talk of fielding a nuclear deterrent independent of the nuclear umbrella provided by the US military.
Trump’s relationship with Elon Musk, the head of the world’s leading space launch company, has further soured foreign appetite for using the United States for launch services. Today, that usually means choosing to pay Musk’s SpaceX.
Commercial satellite companies will still choose the cheapest, most reliable path to space, of course. This means SpaceX will win the overwhelming majority of commercial launch contracts put up for global competition. But there’s a captive market for many satellite projects, especially those with government backing. US government satellites typically launch on US rockets, just as Chinese satellites fly on Chinese rockets.
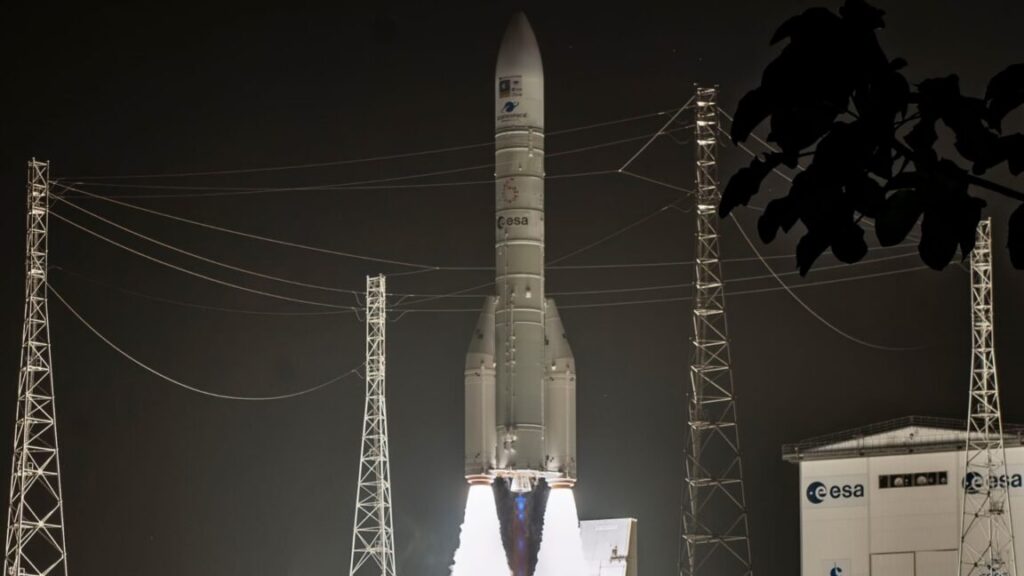
The picture is more opaque in Europe. The European Space Agency and the European Union prefer to launch their satellites on European rockets, but that’s not always possible. ESA and the EU launched several key satellite missions on SpaceX rockets while waiting on the debut of Europe’s long-delayed Ariane 6 rocket. The Ariane 6 is now launching reliably, ending Europe’s reliance on SpaceX.
Many European nations have their own satellite projects. Historically, their preference for launching on European rockets has not been as strong as it is for pan-European programs managed by ESA and the EU. So it has never been unusual to see a British, German, Spanish, or Italian satellite launching on a foreign rocket.
This posture is starting to change. All four of these nations have invested in homegrown rockets in recent years. Germany made the biggest splash last year when the government announced $41 billion (35 billion euros) in space spending over the next five years. “Satellite networks today are an Achilles’ heel of modern societies. Whoever attacks them paralyzes entire nations,” said Boris Pistorius, Germany’s defense minister, during the announcement.
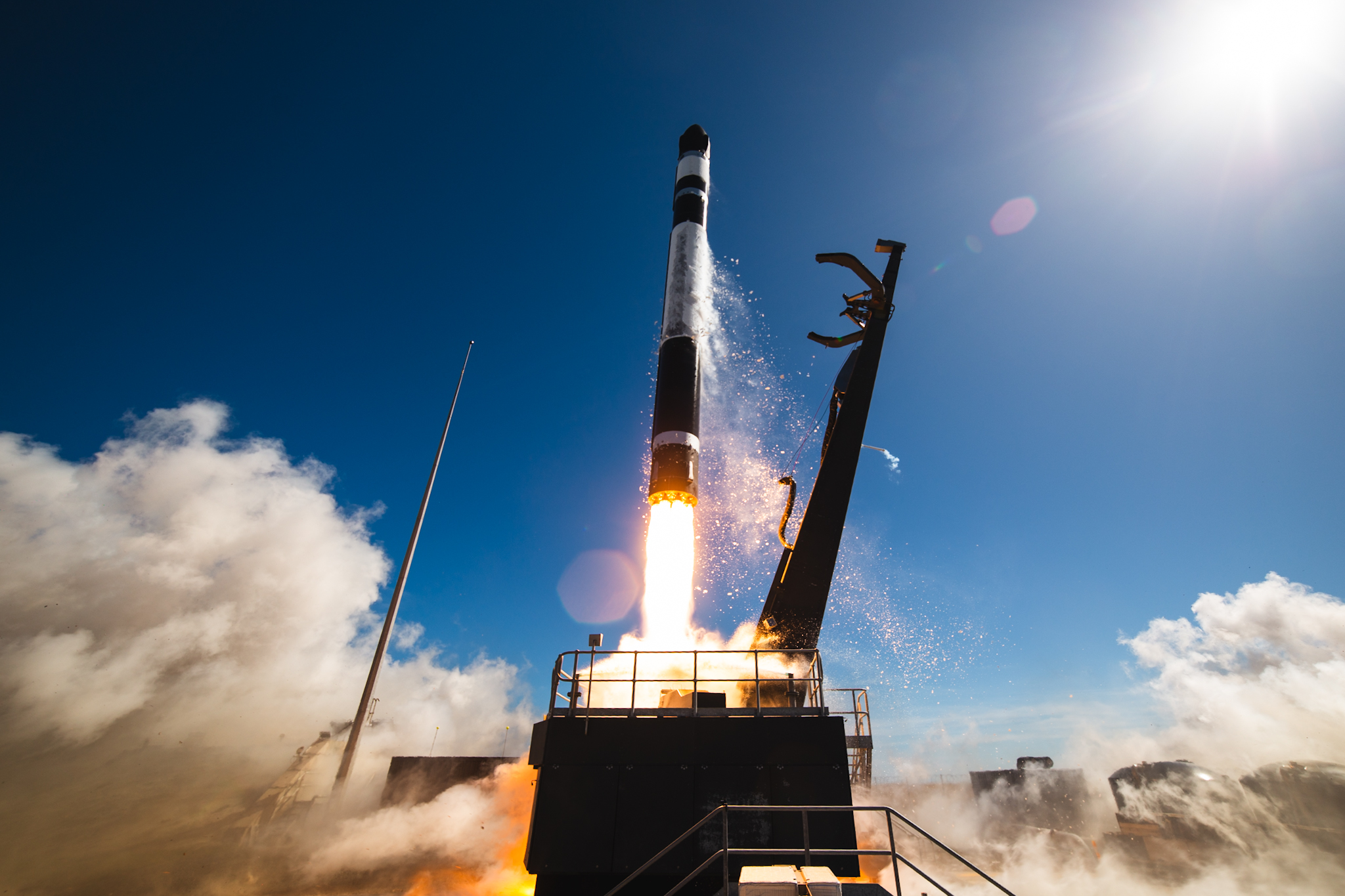
Every satellite network needs a launch pad and a rocket. In late 2024, the German federal government made more than $110 million (95 million euros) available to three German launch startups: Isar Aerospace, Rocket Factory Augsburg, and HyImpulse. All three are also backed by private funding, with Isar leading the pack with approximately $650 million (550 million euros) from investors. None have reached orbit yet. For comparison, Rocket Lab, the world’s most successful launch startup not founded by a billionaire, raised $148 million (approximately $200 million adjusted for inflation) before reaching orbit in 2018. Nearly all of it came from private sources.
Rocket Lab, which operates the Electron small satellite launcher seen in this image, is the most successful modern commercial launch startup not founded by a billionaire. Rocket Lab went public in 2021, three years after its first successful orbital launch. Credit: Rocket Lab
In 2023, the Italian government committed more than $300 million in support of Avio, the company that already builds and operates the Vega satellite launcher. Avio is based in Italy and is using the funds to develop methane propulsion, among other things.
With help from other ESA member states, Italy is one of the countries that already has a rocket made largely of domestic or European components. The United States, Russia, China, France, Japan, the United Kingdom, India, Israel, Iran, North Korea, South Korea, and New Zealand have also successfully launched satellites using their own rockets.
The UK no longer possesses such a capability, and France’s access to space is currently tied to the Ariane rocket, a pan-European program. France, like Italy, is pouring money into domestic launch startups to buttress the Ariane program.
Let’s look at the countries not among the list of active launching states that have committed substantial public funds to join (or rejoin) the club. To the best of our ability, we list these nations in the order of how much they are currently investing in sovereign launch programs.
Germany
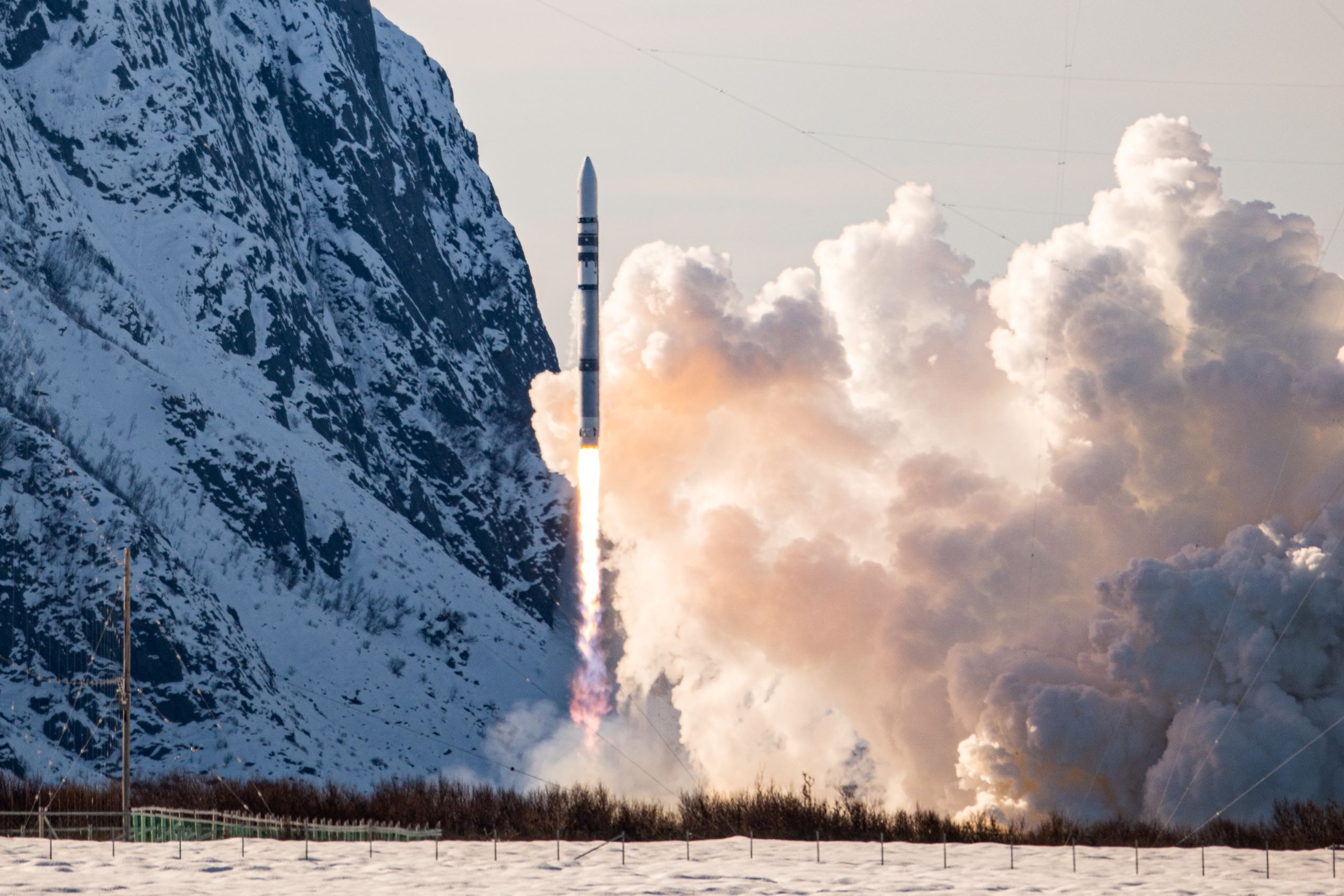
Germany is probably closest to bringing a new commercial rocket into service. Isar Aerospace, Europe’s most well-funded launch startup, made its first orbital launch attempt last year from a spaceport in Norway. The company’s Spectrum rocket failed moments after liftoff, but Isar is readying a second rocket for another test flight as soon as next month. Rocket Factory Augsburg and HyImpulse, Germany’s other two launch startups with significant funding, currently trail Isar in the race to orbit.
In a space safety and security strategy released last year, Germany’s defense ministry included access to space among its lines of effort. The ministry said it aims to develop “sufficient responsive launch transport capacity to ensure national and European strategic independence in all payload classes and transport scenarios.”
In addition to the German government’s $110 million commitment to Isar, RFA, and HyImpulse, Germany is the leading contributor to ESA’s European Launcher Challenge program, which is designed to funnel money into multiple European rocket startups. Germany is the only European country with two companies—Isar and RFA—participating in the challenge. ESA member states approved nearly $1.1 billion (902 million euros) for the challenge last year. Germany is providing about 40 percent of the money and directing most of it to Isar and RFA.
Isar Aerospace’s Spectrum rocket lifts off from Andøya Spaceport, Norway, on March 30, 2025. Credit: Isar Aerospace/Brady Kenniston/NASASpaceflight.com
Spain
The government of Spain is the second-largest contributor to ESA’s European Launcher Challenge, with $200 million (169 million euros) unlocked to support PLD Space, the country’s leading launch startup. PLD Space is developing a small satellite launcher named Miura 5, which the company says will begin demonstration flights later this year. PLD Space’s most recent private fundraising round was in 2024, when the company reported raising more than $140 million (120 million euros) in total investment. ESA’s European Launcher Challenge will more than double this figure. Apart from the ESA challenge, Spain’s government provided more than $47 million (40.5 million euros) to PLD Space in 2024 through the PERTE Aerospace initiative, established to support independent Spanish access to space.
The Spanish government called access to space “one of Spain’s key areas of focus.” In a statement from November, Spain’s science ministry wrote, “PLD Space has been supported by the Spanish government from the beginning with Miura 1, the first suborbital rocket.”
“We have supported PLD Space at the national level until now,” said Diana Morant, Spain’s science minister. “We will now also do so through ESA so that our launcher, a European and Spanish brand, is part of that family of launchers planned for the future.”
United Kingdom
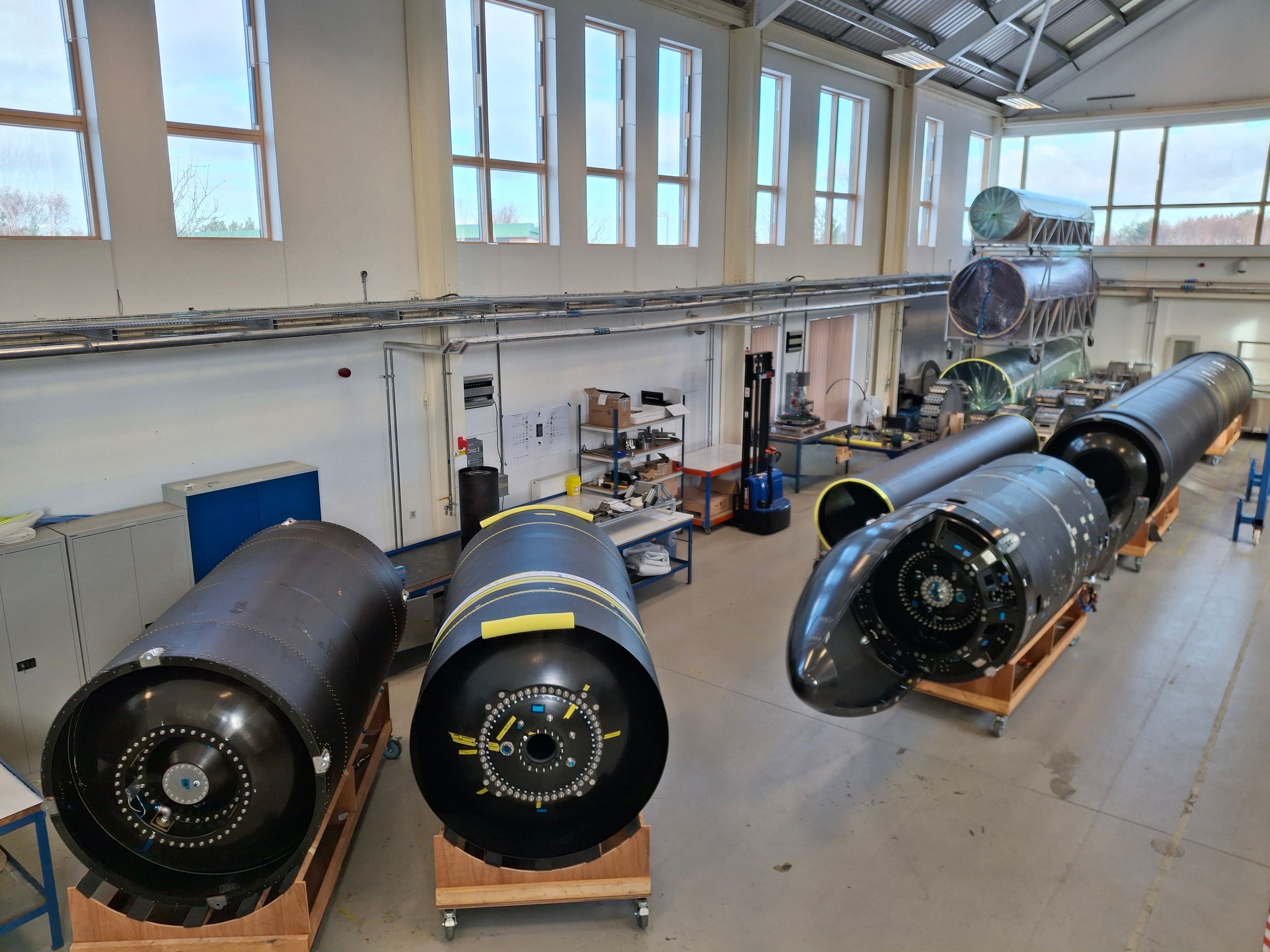
The UK’s position on this list should carry an asterisk following the collapse of the Scottish launch company Orbex. More than a decade into its run, Orbex entered insolvency proceedings last week after “fundraising, merger and acquisition opportunities had all concluded unsuccessfully.” Orbex never made it far on the road to space, despite raising $175 million (£129 million) from private and public investors. Despite its failure, Orbex was by far the most well-capitalized UK launch company. Skyrora, another Scottish launch startup, has expressed interest in buying Orbex’s assets, including land for a privately developed spaceport.
Early last year, the UK government announced a direct investment of more than $27 million (£20 million) to support the development of Orbex’s small satellite launcher. That was followed in November with the UK government’s $170 million (144 million euro) contribution to ESA’s European Launcher Challenge program. UK officials likely saw Orbex’s pending collapse and left nearly 80 percent of the challenge funding unallocated. It remains to be seen how the UK will divide its remaining budget for the launcher challenge.
Orbex released images showing structural elements of its Prime small satellite launcher in “near-flight configuration” after entering insolvency proceedings earlier this month. Credit: Orbex
Canada
In November, Canada’s government announced an investment of approximately $130 million (182.6 million Canadian dollars) for sovereign launch capability. The initiative “seeks to accelerate the advancement of Canadian-designed space launch vehicles and supporting technologies,” the government said in the announcement. The goal is to develop the capability to launch Canadian payloads from Canadian soil with “light lift” rockets by 2028. More than half the funding will support a launch challenge in which the government will offer grants over three years to selected participants who must meet predetermined milestones to win prizes.
Several Canadian startups, such as Maritime Launch Services, Reaction Dynamics, and NordSpace, are working on commercial satellite launchers, but none appear close to making an orbital launch attempt. The Canadian government’s announcement last year came days after MDA Space, the largest established space company in Canada, announced its own multimillion-dollar investment in Maritime Launch Services. Eventually, Canada plans to launch a second challenge to foster the development of a larger medium-lift rocket.
Australia
There’s just one launch startup in Australia with any chance of putting a satellite into orbit anytime soon. This company, named Gilmour Space, launched its first test flight last July, but the rocket stalled moments after clearing the launch pad. Gilmour raised approximately $90 million, primarily from venture capital firms, before the first flight of its Eris rocket. The firm more than tripled this figure with a bountiful fundraising round amounting to more than $300 million last month, led by the National Reconstruction Fund Corporation, a public financing firm established by the Australian government.
The NRFC said it is investing more than $50 million (75 million Australian dollars) into Gilmour to further develop the company’s Eris rocket, scale its satellite and rocket manufacturing, and expand its spaceport in Queensland. “By building sovereign space capability that underpins our everyday life—from Earth observation and communications to national security—Gilmour’s efforts will secure Australia’s access to essential space services, strengthen the country’s advanced manufacturing base, and create highly-skilled jobs and opportunities in the region,” said David Gall, NRFC’s CEO.
Brazil
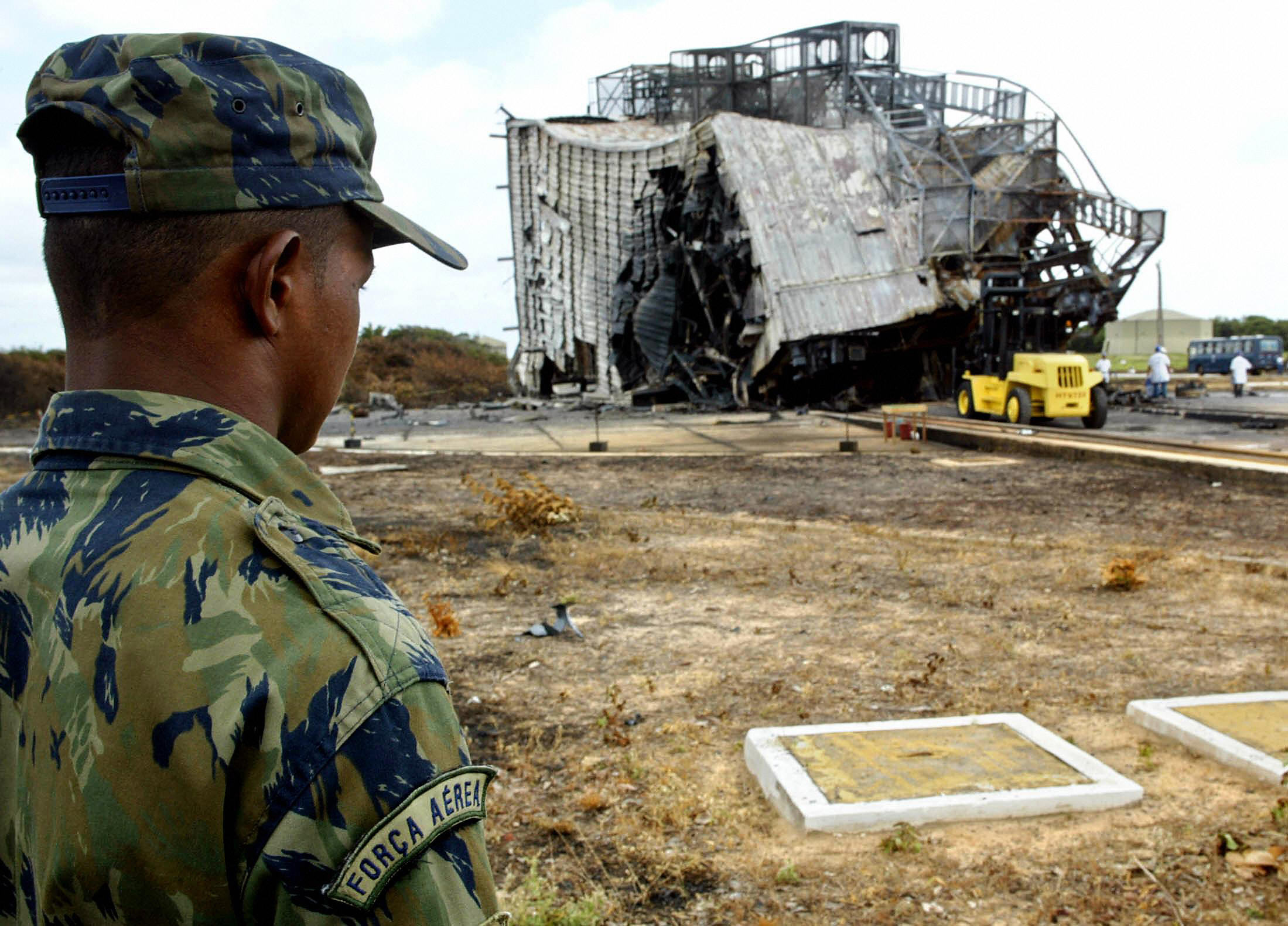
The most populous nation in Latin America has tried longer than any other to cultivate an independent space launch capability. The efforts date back to the 1980s, but they have repeatedly misfired, and in one case, the results were fatal. The country’s VLS-1 rocket exploded on the ground in 2003, killing 21 Brazilian technicians working at a launch pad on the country’s northern Atlantic coast. The tragedy led the Brazilian government to eventually cancel the VLS satellite launcher and set a new course with a less powerful rocket sized for launching microsatellites.
The new rocket, named VLM, is under development by the Brazilian Space Agency and the Brazilian Air Force in partnership with Germany, but there have been few signs of tangible progress since a test-firing of a solid-fueled rocket motor in 2021. The Brazilian aerospace company working with the government on the VLM rocket filed for bankruptcy in 2022, and its future remains uncertain amid court-ordered restructuring. At that time, Brazil’s government had reportedly committed between $30 million and $40 million to the VLM rocket project.
Given that situation, Brazil’s best bet to field a new orbital-class rocket appears to be through a public-private partnership. Through a public financing agency, the Brazilian government also agreed to provide $30 million to $40 million to a domestic industrial consortium for an indigenous microlauncher known as MLBR, according to the Brazilian financial newspaper Valor Econômico. The team leading the MLBR project has released regular updates on LinkedIn, unlike the VLM project, but progress on early-stage ground tests remains slow.
Brazil’s long-running effort to develop a domestic launch capability has been colored by tragedy. Here, a member of the Brazilian Air Force overlooks the rubble from the deadly explosion of the VLS-1 rocket on its launch pad in August 2003. Credit: Evaristo Sa/AFP via Getty Images
Taiwan
Taiwan’s government is increasing funding for the country’s space program, but the Taiwan Space Agency’s annual budget remains modest at approximately $200 million per year. The nation’s efforts in the space sector have primarily focused on building satellites and instruments for Earth observation, weather monitoring, and scientific research. Last year, the Taiwan Space Agency announced a goal of launching a homegrown rocket into orbit by 2034, with more than $25 million in the agency’s 2026 budget to kick-start the program. The space agency says flight testing of the new rocket, designed to haul up to 440 pounds (200 kilograms) to low-Earth orbit, could begin by 2029.
Argentina
Argentina also has a long-running project aiming to onshore access to space. The centerpiece of this project is the Tronador II rocket, a two-stage, liquid-fueled vehicle designed to deliver small payloads to low-Earth orbit. Argentina’s economic woes have blocked any serious progress on the Tronador II. In a pair of announcements in late 2021 and late 2022, the government of Argentina pledged more than 14 billion pesos to develop a new orbital-class launch vehicle. At the time, this was equivalent to more than $100 million, but the subsequent devaluation of Argentine currency means the investment would be worth just $10 million today. The government of Argentine President Javier Milei has cut spending on research and technology programs, so Tronador is going nowhere fast.
Others
The United Arab Emirates is another up-and-coming space power with the resources to support the development of a commercial launch provider, though the government hasn’t yet revealed a budget to support such an effort. Several other countries, such as Indonesia, South Africa, and Turkey, have said they aspire to develop an indigenous orbital launch capability, but with little in the way of firm, significant financial commitments or substantive progress.
There’s a lot of big talk about sovereign launch—who is doing something about it? Read More »