Never-before-seen Linux malware is “far more advanced than typical”
Researchers have discovered a never-before-seen framework that infects Linux machines with a wide assortment of modules that are notable for the range of advanced capabilities they provide to attackers.
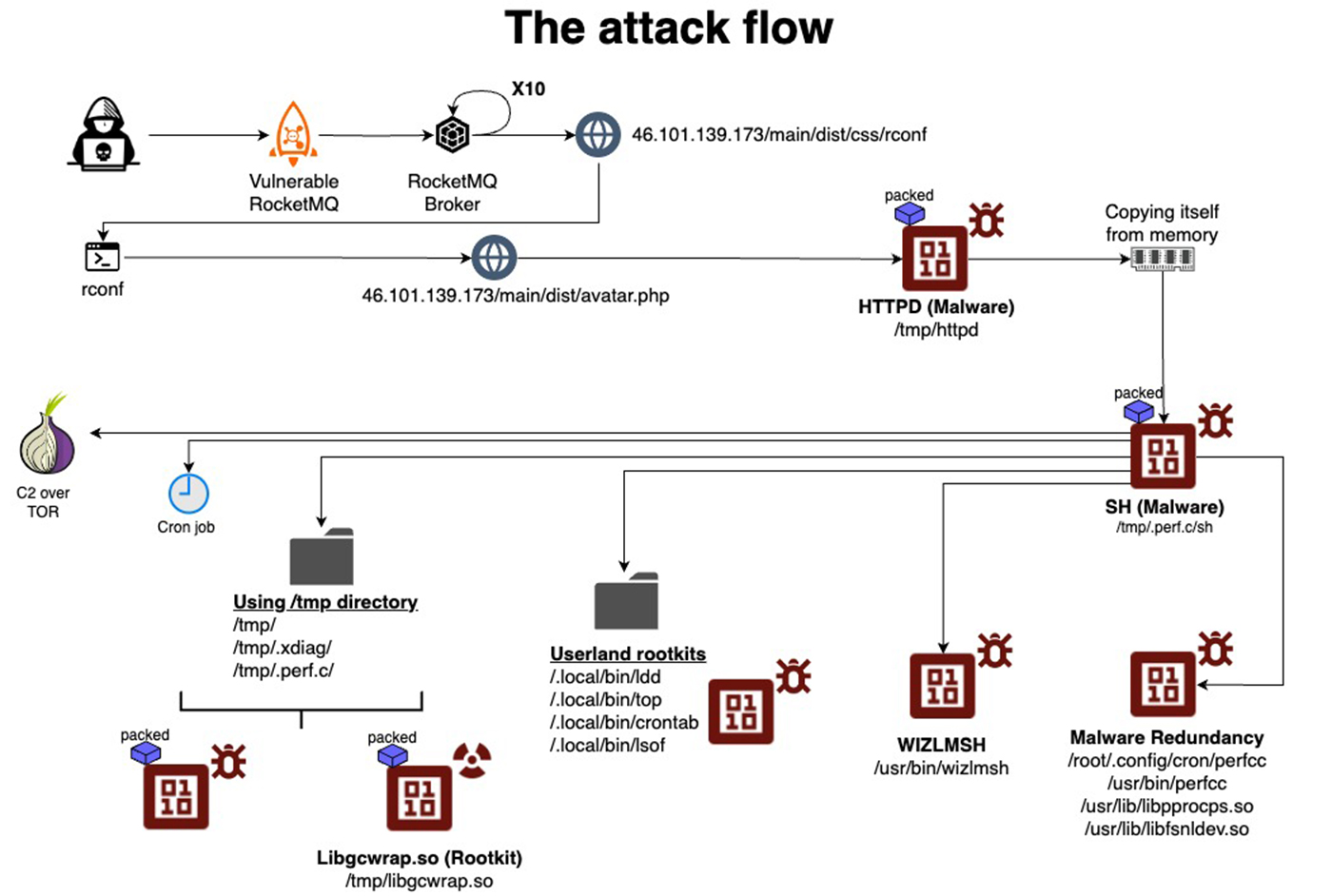
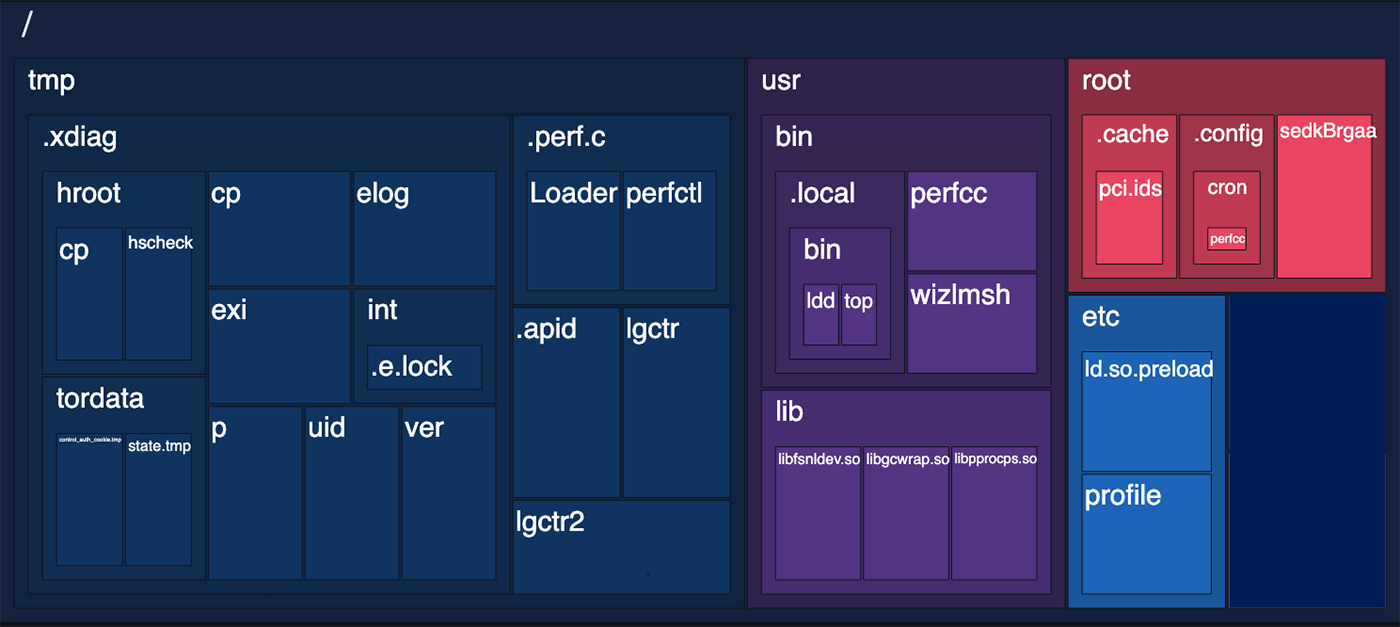
The framework, referred to as VoidLink by its source code, features more than 30 modules that can be used to customize capabilities to meet attackers’ needs for each infected machine. These modules can provide additional stealth and specific tools for reconnaissance, privilege escalation, and lateral movement inside a compromised network. The components can be easily added or removed as objectives change over the course of a campaign.
A focus on Linux inside the cloud
VoidLink can target machines within popular cloud services by detecting if an infected machine is hosted inside AWS, GCP, Azure, Alibaba, and Tencent, and there are indications that developers plan to add detections for Huawei, DigitalOcean, and Vultr in future releases. To detect which cloud service hosts the machine, VoidLink examines metadata using the respective vendor’s API.
Similar frameworks targeting Windows servers have flourished for years. They are less common on Linux machines. The feature set is unusually broad and is “far more advanced than typical Linux malware,” said researchers from Checkpoint, the security firm that discovered VoidLink. Its creation may indicate that the attacker’s focus is increasingly expanding to include Linux systems, cloud infrastructure, and application deployment environments, as organizations increasingly move workloads to these environments.
“VoidLink is a comprehensive ecosystem designed to maintain long-term, stealthy access to compromised Linux systems, particularly those running on public cloud platforms and in containerized environments,” the researchers said in a separate post. “Its design reflects a level of planning and investment typically associated with professional threat actors rather than opportunistic attackers, raising the stakes for defenders who may never realize their infrastructure has been quietly taken over.”
Never-before-seen Linux malware is “far more advanced than typical” Read More »