Google claims win for everyone as text scammers lost their cloud server
The day after Google filed a lawsuit to end text scams primarily targeting Americans, the criminal network behind the phishing scams was “disrupted,” a Google spokesperson told Ars.
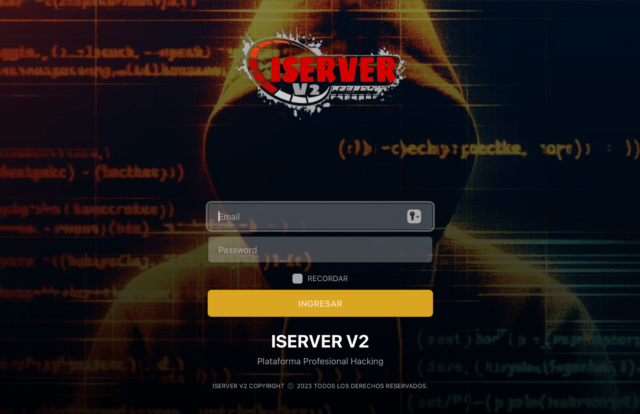
According to messages that the “ringleader” of the so-called “Lighthouse enterprise” posted on his Telegram channel, the phishing gang’s cloud server was “blocked due to malicious complaints.”
“We will restore it as soon as possible!” the leader posted on the channel—which Google’s lawsuit noted helps over 2,500 members coordinate phishing attacks that have resulted in losses of “over a billion dollars.”
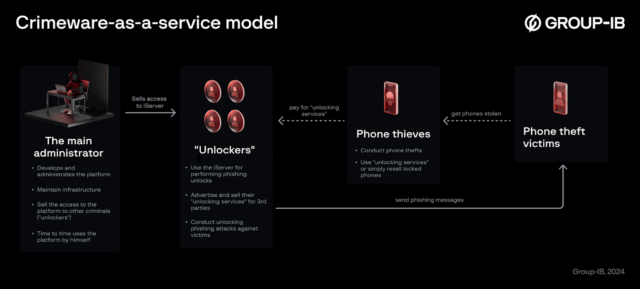
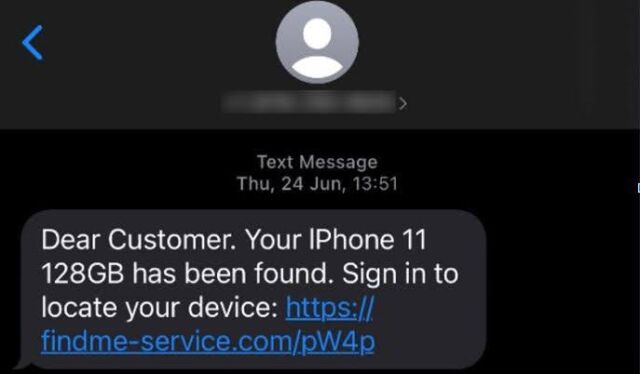
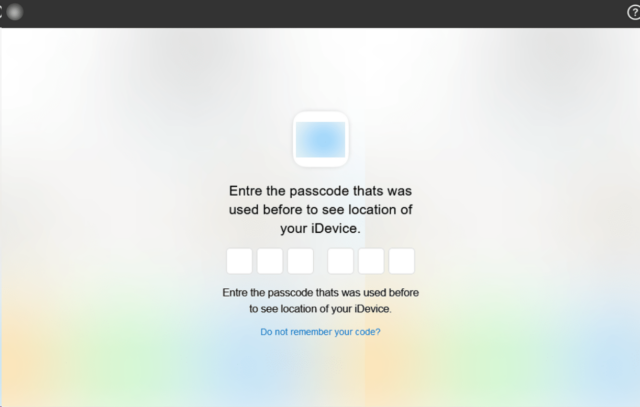
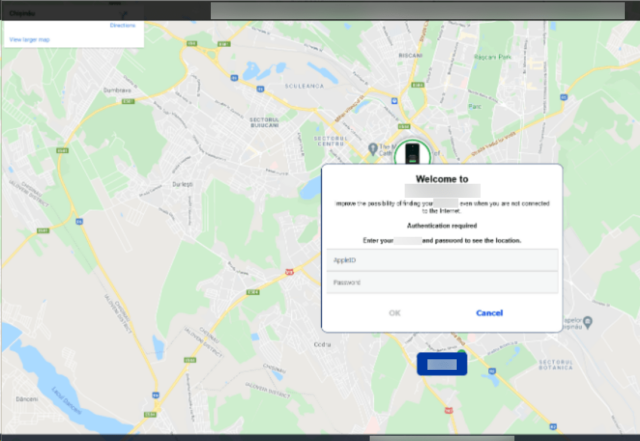
Google has alleged that the Lighthouse enterprise is a “criminal group in China” that sells “phishing for dummies” kits that make it easier for scammers with little tech savvy to launch massive phishing campaigns. So far, “millions” of Americans have been harmed, Google alleged, as scammers disproportionately impersonate US institutions, like the Postal Service, as well as well-known brands like E-ZPass.
The company’s lawsuit seeks to dismantle the entire Lighthouse criminal enterprise, so the company was pleased to see Lighthouse communities go dark. In a statement, Halimah DeLaine Prado, Google’s general counsel, told Ars that “this shutdown of Lighthouse’s operations is a win for everyone.
Google claims win for everyone as text scammers lost their cloud server Read More »