Time to check if you ran any of these 33 malicious Chrome extensions
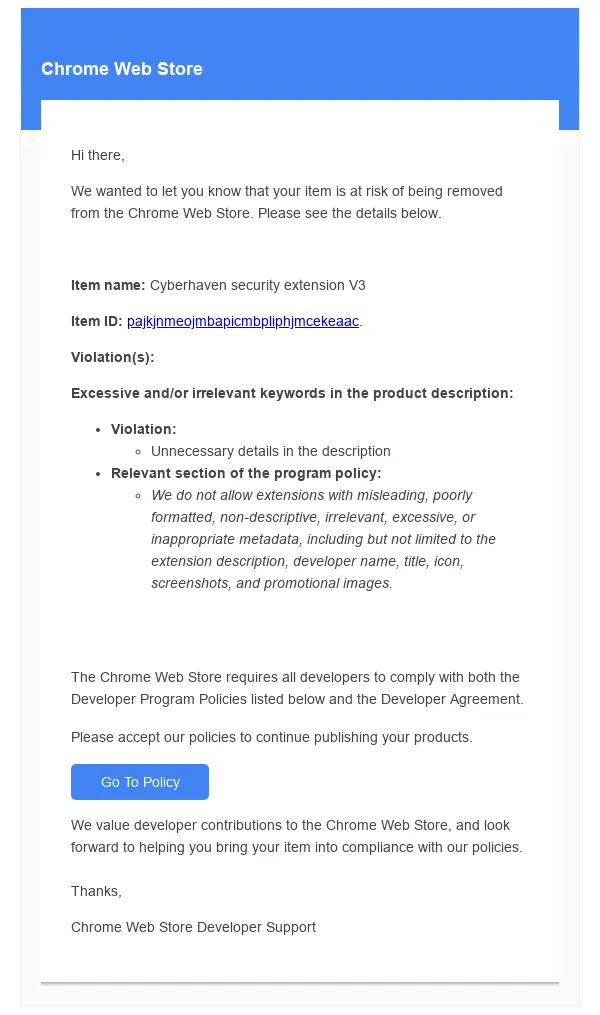
Screenshot showing the phishing email sent to Cyberhaven extension developers. Credit: Amit Assaraf
A link in the email led to a Google consent screen requesting access permission for an OAuth application named Privacy Policy Extension. A Cyberhaven developer granted the permission and, in the process, unknowingly gave the attacker the ability to upload new versions of Cyberhaven’s Chrome extension to the Chrome Web Store. The attacker then used the permission to push out the malicious version 24.10.4.
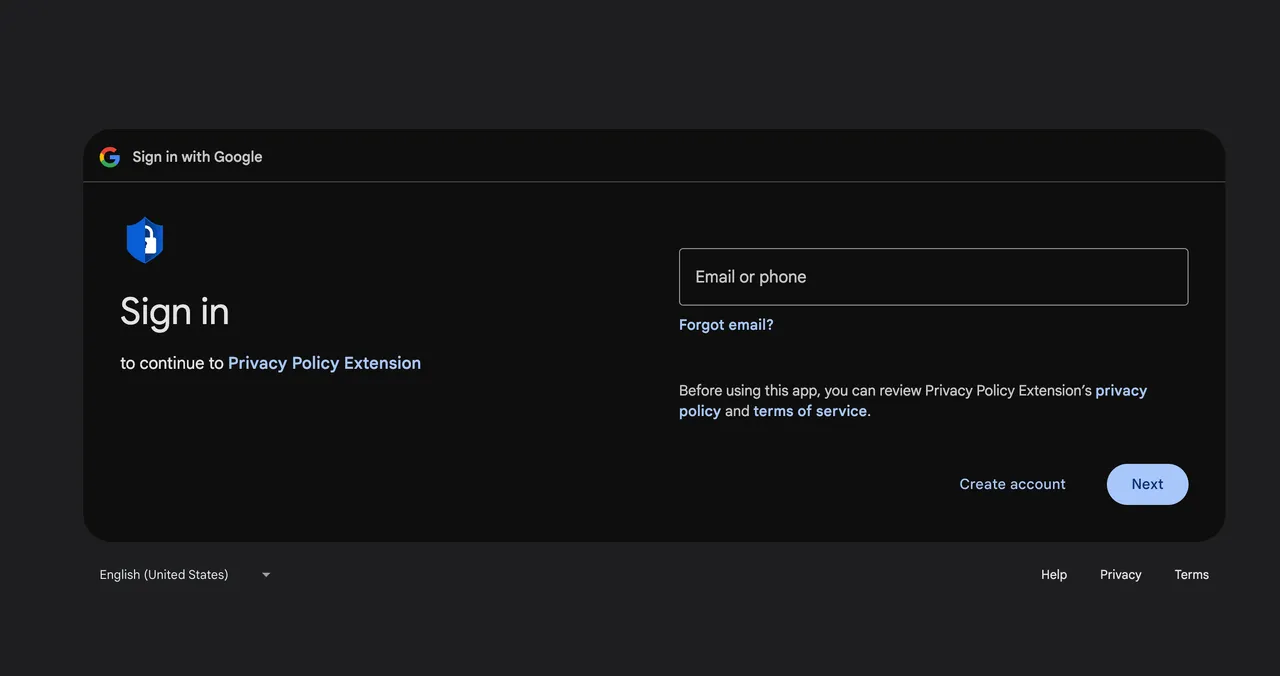
Screenshot showing the Google permission request. Credit: Amit Assaraf
As word of the attack spread in the early hours of December 25, developers and researchers discovered that other extensions were targeted, in many cases successfully, by the same spear phishing campaign. John Tuckner, founder of Secure Annex, a browser extension analysis and management firm, said that as of Thursday afternoon, he knew of 19 other Chrome extensions that were similarly compromised. In every case, the attacker used spear phishing to push a new malicious version and custom, look-alike domains to issue payloads and receive authentication credentials. Collectively, the 20 extensions had 1.46 million downloads.
“For many I talk to, managing browser extensions can be a lower priority item in their security program,” Tuckner wrote in an email. “Folks know they can present a threat, but rarely are teams taking action on them. We’ve often seen in security [that] one or two incidents can cause a reevaluation of an organization’s security posture. Incidents like this often result in teams scrambling to find a way to gain visibility and understanding of impact to their organizations.”
The earliest compromise occurred in May 2024. Tuckner provided the following spreadsheet:
| Name | ID | Version | Patch | Available | Users | Start | End |
| VPNCity | nnpnnpemnckcfdebeekibpiijlicmpom | 2.0.1 | FALSE | 10,000 | 12/12/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Parrot Talks | kkodiihpgodmdankclfibbiphjkfdenh | 1.16.2 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/25/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Uvoice | oaikpkmjciadfpddlpjjdapglcihgdle | 1.0.12 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/26/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Internxt VPN | dpggmcodlahmljkhlmpgpdcffdaoccni | 1.1.1 | 1.2.0 | TRUE | 10,000 | 12/25/24 | 12/29/24 |
| Bookmark Favicon Changer | acmfnomgphggonodopogfbmkneepfgnh | 4.00 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/25/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Castorus | mnhffkhmpnefgklngfmlndmkimimbphc | 4.40 | 4.41 | TRUE | 50,000 | 12/26/24 | 12/27/24 |
| Wayin AI | cedgndijpacnfbdggppddacngjfdkaca | 0.0.11 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/19/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Search Copilot AI Assistant for Chrome | bbdnohkpnbkdkmnkddobeafboooinpla | 1.0.1 | TRUE | 20,000 | 7/17/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| VidHelper – Video Downloader | egmennebgadmncfjafcemlecimkepcle | 2.2.7 | TRUE | 20,000 | 12/26/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| AI Assistant – ChatGPT and Gemini for Chrome | bibjgkidgpfbblifamdlkdlhgihmfohh | 0.1.3 | FALSE | 4,000 | 5/31/24 | 10/25/24 | |
| TinaMind – The GPT-4o-powered AI Assistant! | befflofjcniongenjmbkgkoljhgliihe | 2.13.0 | 2.14.0 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/15/24 | 12/20/24 |
| Bard AI chat | pkgciiiancapdlpcbppfkmeaieppikkk | 1.3.7 | FALSE | 100,000 | 9/5/24 | 10/22/24 | |
| Reader Mode | llimhhconnjiflfimocjggfjdlmlhblm | 1.5.7 | FALSE | 300,000 | 12/18/24 | 12/19/24 | |
| Primus (prev. PADO) | oeiomhmbaapihbilkfkhmlajkeegnjhe | 3.18.0 | 3.20.0 | TRUE | 40,000 | 12/18/24 | 12/25/24 |
| Cyberhaven security extension V3 | pajkjnmeojmbapicmbpliphjmcekeaac | 24.10.4 | 24.10.5 | TRUE | 400,000 | 12/24/24 | 12/26/24 |
| GraphQL Network Inspector | ndlbedplllcgconngcnfmkadhokfaaln | 2.22.6 | 2.22.7 | TRUE | 80,000 | 12/29/24 | 12/30/24 |
| GPT 4 Summary with OpenAI | epdjhgbipjpbbhoccdeipghoihibnfja | 1.4 | FALSE | 10,000 | 5/31/24 | 9/29/24 | |
| Vidnoz Flex – Video recorder & Video share | cplhlgabfijoiabgkigdafklbhhdkahj | 1.0.161 | FALSE | 6,000 | 12/25/24 | 12/29/24 | |
| YesCaptcha assistant | jiofmdifioeejeilfkpegipdjiopiekl | 1.1.61 | TRUE | 200,000 | 12/29/24 | 12/31/24 | |
| Proxy SwitchyOmega (V3) | hihblcmlaaademjlakdpicchbjnnnkbo | 3.0.2 | TRUE | 10,000 | 12/30/24 | 12/31/24 |
But wait, there’s more
One of the compromised extensions is called Reader Mode. Further analysis showed it had been compromised not just in the campaign targeting the other 19 extensions but in a separate campaign that started no later than April 2023. Tuckner said the source of the compromise appears to be a code library developers can use to monetize their extensions. The code library collects details about each web visit a browser makes. In exchange for incorporating the library into the extensions, developers receive a commission from the library creator.
Time to check if you ran any of these 33 malicious Chrome extensions Read More »