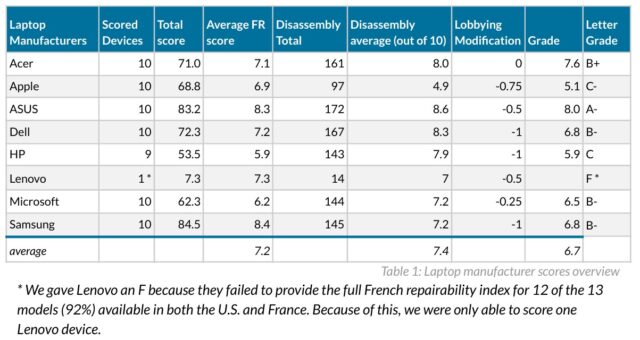
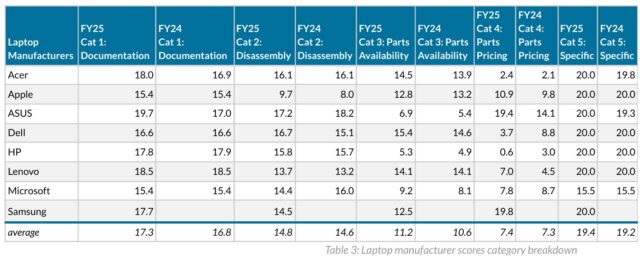
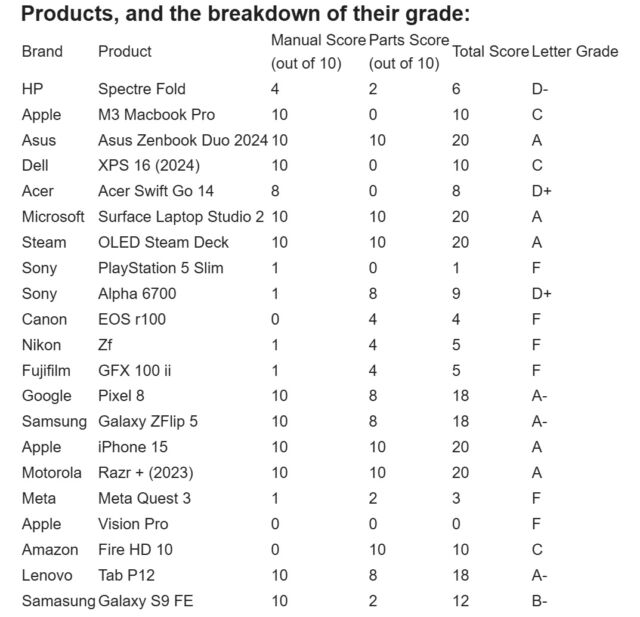
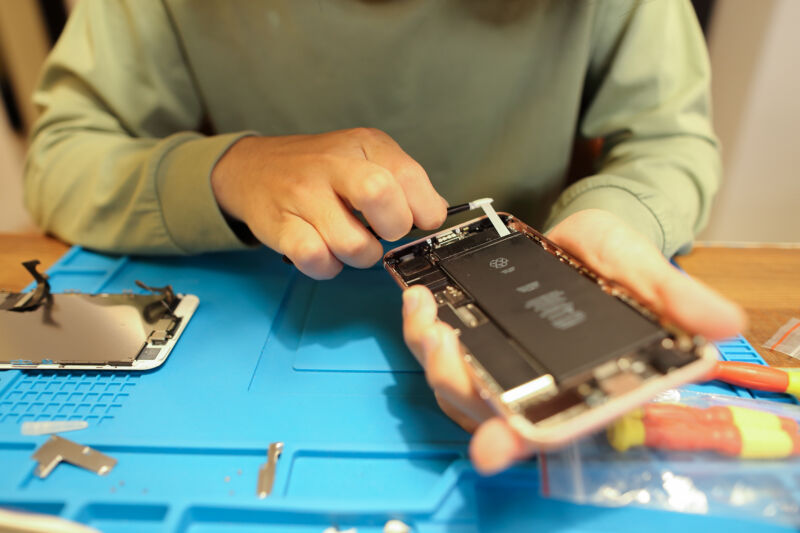
Review: New Framework Laptop 16 takes a fresh stab at the upgradeable laptop GPU
The original Framework Laptop 16 was trying to crack a problem that laptop makers have wrestled with on and off for years: Can you deliver a reasonably powerful, portable workstation and gaming laptop that supports graphics card upgrades just like a desktop PC?
| Specs at a glance: Framework Laptop 16 (2025) | |
|---|---|
| OS | Windows 11 25H2 |
| CPU | AMD Ryzen AI 7 350 (4 Zen 5 cores, 4 Zen 5c cores) |
| RAM | 32GB DDR5-5600 (upgradeable) |
| GPU | AMD Radeon 860M (integrated)/Nvidia GeForce RTX 5070 Mobile (dedicated) |
| SSD | 1TB Western Digital Black SN770 |
| Battery | 85 WHr |
| Display | 16-inch 2560×1600 165 Hz matte non-touchscreen |
| Connectivity | 6x recessed USB-C ports (2x USB 4, 4x USB 3.2) with customizable “Expansion Card” dongles |
| Weight | 4.63 pounds (2.1 kg) without GPU, 5.29 pounds (2.4 kg) with GPU |
| Price as tested | Roughly $2,649 for pre-built edition; $2,517 for DIY edition with no OS |
Even in these days of mostly incremental, not-too-exciting GPU upgrades, the graphics card in a gaming PC or graphics-centric workstation will still feel its age faster than your CPU will. And the chance to upgrade that one component for hundreds of dollars instead of spending thousands replacing the entire machine is an appealing proposition.
Upgradeable, swappable GPUs would also make your laptop more flexible—you can pick and choose from various GPUs from multiple vendors based on what you want and need, whether that’s raw performance, power efficiency, Linux support, or CUDA capabilities.
Framework’s first upgrade to the Laptop 16—the company’s first upgrade to any of its products aside from the original Laptop 13—gets us pretty close to that reality. The laptop can now support two interchangeable motherboards: one with an older AMD Ryzen 7040-series CPU and one with a new Ryzen AI 300-series CPU. And both motherboards can be used either with just an integrated GPU or with dedicated GPUs from both AMD and Nvidia.
The Nvidia GeForce 5070 graphics module is the most exciting and significant part of this batch of updates, but there are plenty of other updates and revisions to the laptop’s external and internal components, too. These upgrades don’t address all of our problems with the initial version of the laptop, but they do help quite a bit. And a steady flow of updates like these would definitely make the Laptop 16 a platform worth investing in.
Re-meet the Framework Laptop 16

Framework’s Laptop 13 stacked on top of the 16. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Framework treats each of its laptops as a platform to be modified and built upon rather than something to be wholly redesigned and replaced every time it’s updated. So these reviews necessarily re-cover ground we have already covered—I’ve also reused some of the photos from last time, since this is quite literally the same laptop in most respects. I’ll point you to the earlier review for detailed notes on the build process and how the laptop is put together.
To summarize our high-level notes about the look, feel, and design of the Framework Laptop 16: While the Framework Laptop 13 can plausibly claim to be in the same size and weight class as portables like the 13-inch MacBook Air, the Framework Laptop 16 is generally larger and heavier than the likes of the 16-inch MacBook Pro or portable PC workstations like the Lenovo ThinkPad P1 or Dell 16 Premium. That’s doubly true once you actually add a dedicated graphics module to the Laptop 16—these protrude a couple of inches from the back of the laptop and add around two-thirds of a pound to its weight.
| Frame-work 16 (no GPU) | Frame-work 16 (GPU) | Apple 16-inch MBP | Dell 16 Premium | Lenovo ThinkPad P1 Gen 8 | HP ZBook X G1i | Lenovo Legion Pro 5i Gen 10 | Razer Blade 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (H x W x D inches) | 0.71 x 14.04 x 10.63 | 0.82 x 14.04 x 11.43 | 0.66 x 14.01 x 9.77 | 0.75 x 14.1 x 9.4 | 0.39-0.62 x 13.95 x 9.49 | 0.9 x 14.02 x 9.88 | 0.85-1.01 x 14.34 x 10.55 | 0.59-0.69 x 13.98 x 9.86 |
| Weight | 4.63 lbs | 5.29 lbs | 4.7-4.8 lbs | 4.65 pounds | 4.06 lbs | 4.5 lbs | 5.56 lbs | 4.71 lbs |
You certainly can find laptops from the major PC OEMs that come close to or even exceed the size and weight of the Laptop 16. But in most cases, you’ll find that comparably specced and priced laptops are an inch or two less deep and at least half a pound lighter than the Laptop 16 with a dedicated GPU installed.
But if you’re buying from Framework, you’re probably at least notionally interested in customizing, upgrading, and repairing your laptop over time, all things that Framework continues to do better than any other company.
The Laptop 16’s customizable keyboard deck is still probably its coolest feature—it’s a magnetically attached series of panels that allows you to remove and replace components without worrying about the delicate and finicky ribbon cables the Laptop 13 uses. Practically, the most important aspect of this customizable keyboard area is that it lets you decide whether you want to install a dedicated number pad or not; this also allows you to choose whether you want the trackpad to be aligned with the center of the laptop or with wherever the middle of the keyboard is.
It might look a little rough, but the customizable keyboard deck is still probably the coolest thing about the Laptop 16 in day-to-day use. Andrew Cunningham
But Framework also sells an assortment of other functional and cosmetic panels and spacers to let users customize the laptop to their liking. The coolest, oddest accessories are still probably the LED matrix spacers and the clear, legend-less keyboard and number pad modules. We still think this assortment of panels gives the system a vaguely unfinished look, but Framework is clearly going for function over form here.
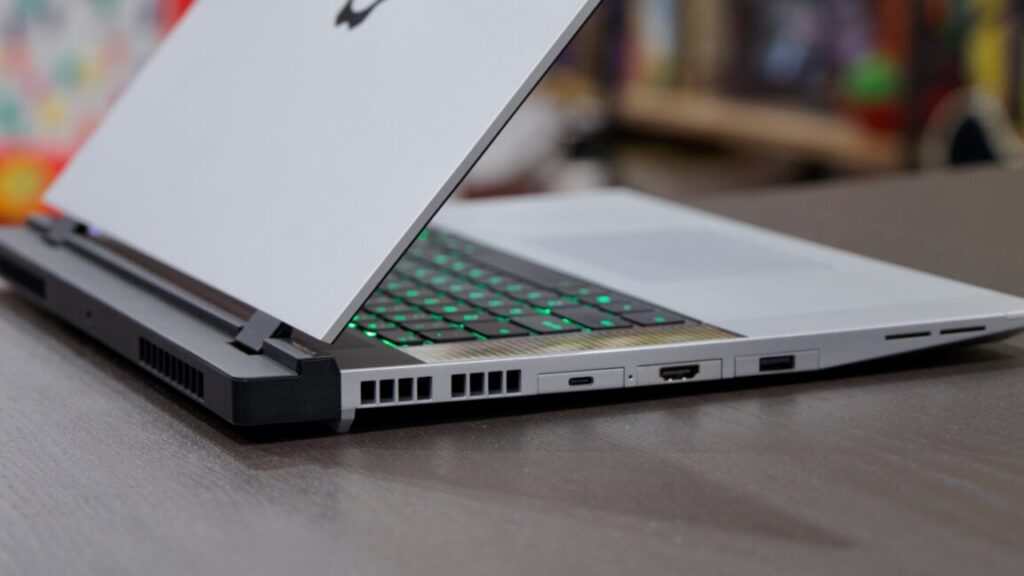
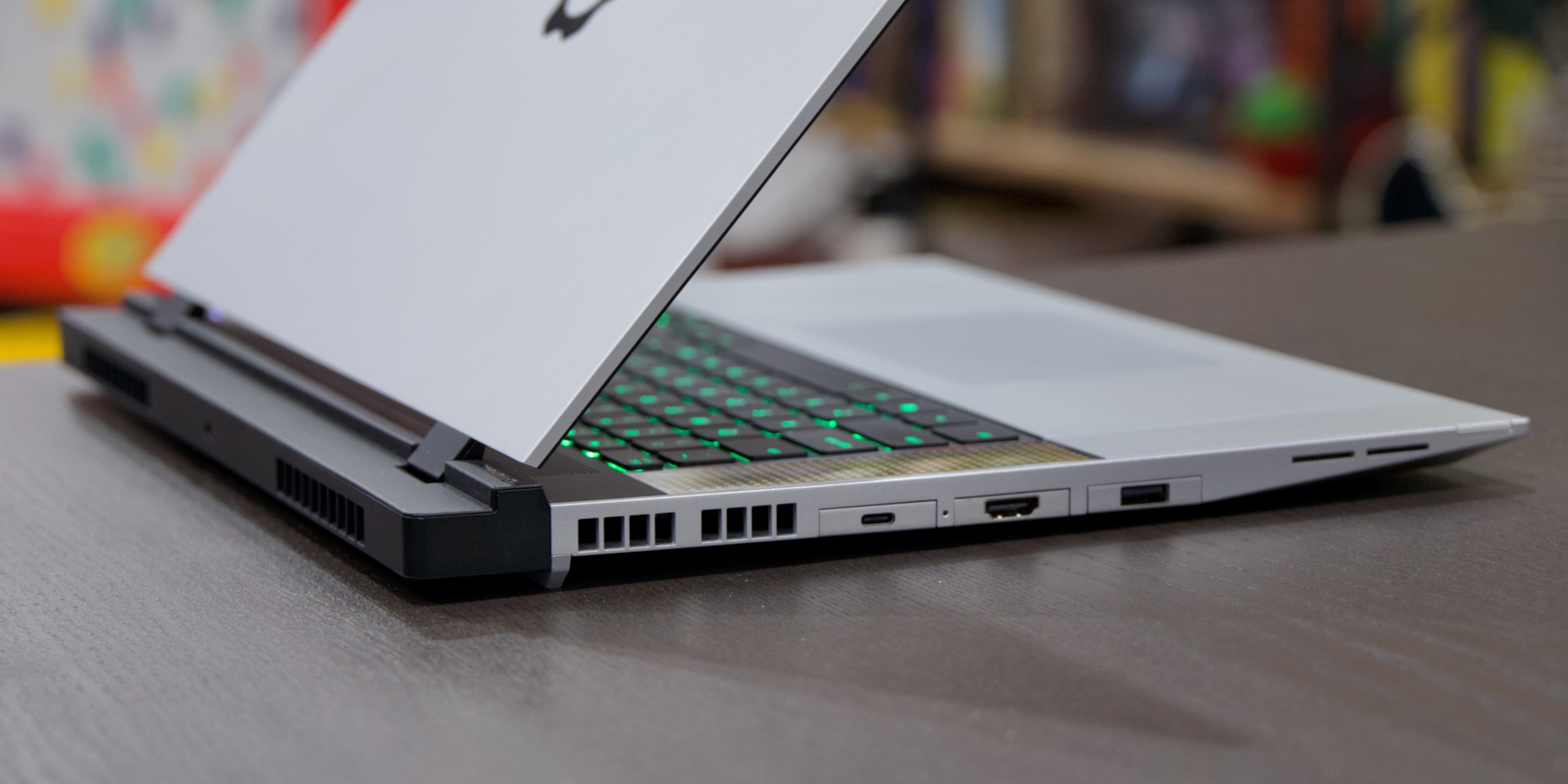
The Laptop 16 also continues to use Framework’s customizable, swappable Expansion Card modules. In theory, these let you pick the number and type of ports your laptop has, as well as customize your port setup on the fly based on what you need. But as with all AMD Ryzen-based Framework Laptops, there are some limits to what each port can do.
According to Framework’s support page, there’s no single Expansion Card slot that is truly universal:
- Ports 1 and 4 support full 40Gbps USB 4 transfer speeds, display outputs, and up to 240 W charging, but if you use a USB-A Expansion Card in those slots, you’ll increase power use and reduce battery life.
- Ports 2 and 4 support display outputs, up to 240 W charging, and lower power usage for USB-A ports, but they top out at 10Gbps USB 3.2 transfer speeds. Additionally, port 5 (the middle port on the right side of the laptop, if you’re looking at it head-on) supports the DisplayPort 1.4 standard where the others support DisplayPort 2.1.
- Ports 3 and 4 are limited to 10Gbps USB 3.2 transfer speeds and don’t support display outputs or charging.
The Laptop 16 also doesn’t include a dedicated headphone jack, so users will need to burn one of their Expansion Card slots to get one.
Practically speaking, most users will be able to come up with a port arrangement that fits their needs, and it’s still handy to be able to add and remove things like Ethernet ports, HDMI ports, or SD card readers on an as-needed basis. But choosing the right Expansion Card slot for the job will still require some forethought, and customizable ports aren’t as much of a selling point for a 16-inch laptop as they are for a 13-inch laptop (the Framework Laptop 13 was partly a response to laptops like the MacBook Air and Dell XPS 13 that only came with a small number of USB-C ports; larger laptops have mostly kept their larger number and variety of ports).
What’s new in 2025’s Framework Laptop 16?
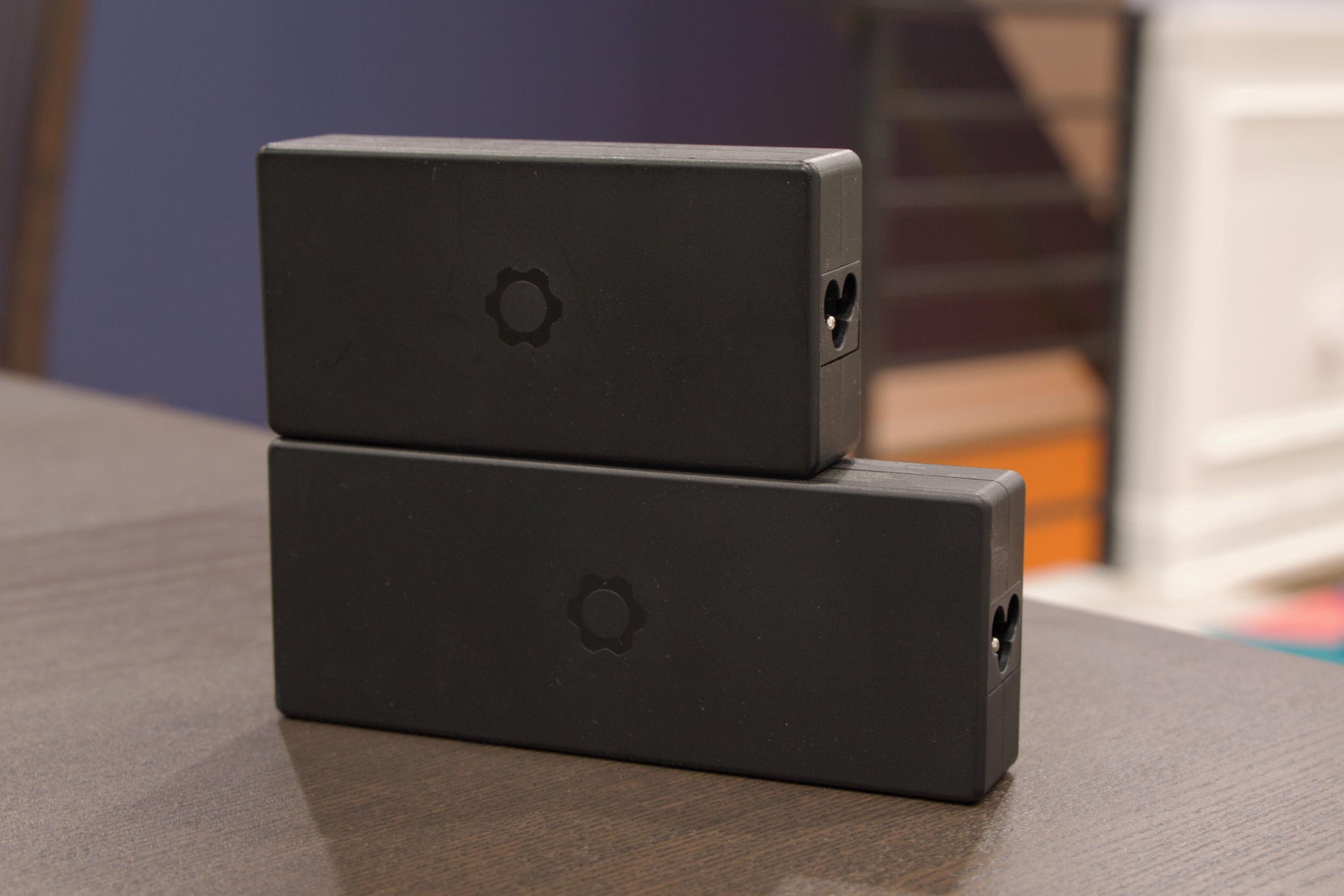
An upgraded motherboard and a new graphics module form the heart of this year’s Laptop 16 upgrade. The motherboard steps up from AMD Ryzen 7040-series processors to AMD Ryzen AI 7 350 and Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 chips. These are the same processors Framework put into the Laptop 13 earlier this year, though they ought to be able to run a bit faster in the Laptop 16 due to its larger heatsink and dual-fan cooling system.
Along with an upgrade from Zen 4-based CPU cores to Zen 5 cores, the Ryzen AI series includes an upgraded neural processing unit (NPU) that is fast enough to earn Microsoft’s Copilot+ PC label. These PCs have access to a handful of unique Windows 11 AI and machine-learning features (yes, Recall, but not just Recall) that are processed locally rather than in the cloud. If you don’t care about these features, you can mostly just ignore them, but if you do care, this is the first version of the Laptop 16 to support them.
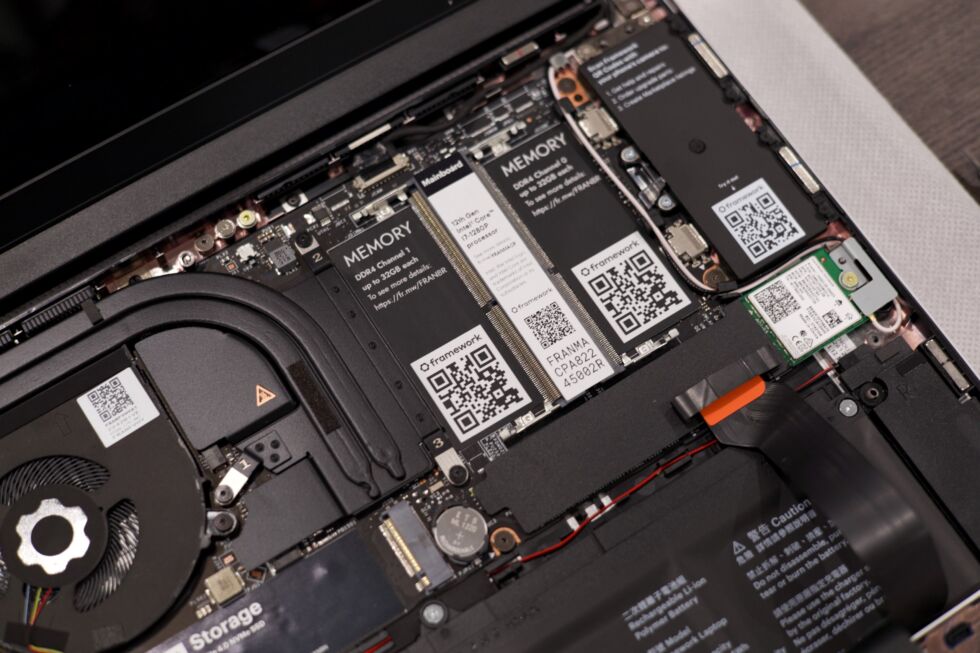
Most of the new motherboard’s other specs and features are pretty similar to the first-generation version; there are two SO-DIMM slots for up to 96GB of DDR5-5600, one M.2 2280 slot for the system’s main SSD, and one M.2 2230 slot for a secondary SSD. Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth connectivity are provided by an AMD RZ717 Wi-Fi card that can at least theoretically also be replaced with something faster down the line if you want.
The more exciting upgrade, however, may be the GeForce RTX 5070 GPU. This is the first time Framework has offered an Nvidia product—its other GPUs have all come from either Intel or AMD—and it gives the new Laptop 16 access to Nvidia technologies like DLSS and CUDA, as well as much-improved performance for games with ray-traced lighting effects.
Those hoping for truly high-end graphics options for the Laptop 16 will need to keep waiting, though. The laptop version of the RTX 5070 is actually the same chip as the desktop version of the RTX 5060, a $300 graphics card with 8GB of RAM. As much as it adds to the Laptop 16, it still won’t let you come anywhere near 4K in most modern games, and for some, it may even struggle to take full advantage of the internal 165 Hz 1600p screen. Professional workloads (including AI workloads) that require more graphics RAM will also find the mobile 5070 lacking.

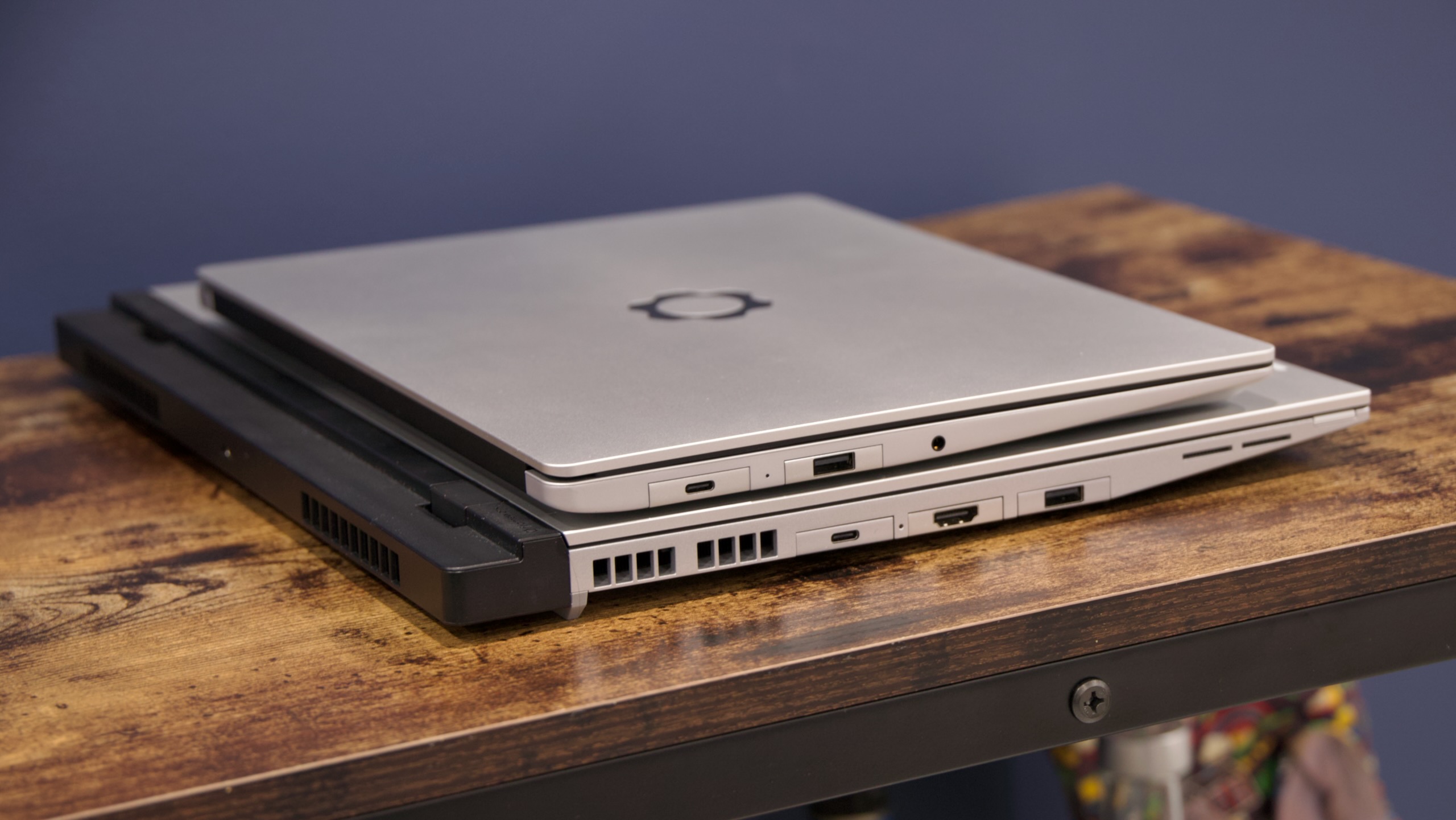
Old 180 W charger on top, new 240 W charger on bottom. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Other components have gotten small updates as well. For those who upgrade an existing Laptop 16 with the new motherboard, Framework is selling 2nd-generation keyboard and number pad components. But their main update over the originals is new firmware that “includes a fix to prevent the system from waking while carried in a bag.” Owners of the original keyboard can install a firmware update to get the same functionality (and make their input modules compatible with the new board).
Upgraders should also note that the original system’s 180 W power adapter has been replaced with a 240 W model, the maximum amount of power that current USB-C and USB-PD standards are capable of delivering. You can charge the laptop with just about any USB-C power brick, but anything lower than 240 W risks reducing performance (or having the battery drain faster than it can charge).
Finally, the laptop uses a second-generation 16-inch, 2560×1600, 165 Hz LCD screen. It’s essentially identical in every way to the first-generation screen, but it formally supports G-Sync, Nvidia’s adaptive sync implementation. The original screen can still be used with the new motherboard, but it only supports AMD’s FreeSync, and Framework told us a few months ago that the panel supplier had no experience providing consumer-facing firmware updates that might add G-Sync to the old display. It’s probably not worth replacing the entire screen for, but it’s worth noting whether you’re upgrading the laptop or buying a new one.
Performance
Framework sent us the lower-end Ryzen AI 7 350 processor configuration for our new board, making it difficult to do straightforward apples-to-apples comparisons to the high-end Ryzen 9 7940HS in our first-generation Framework board. We did test the new chip, and you’ll see its results in our charts.
We’ve also provided numbers from the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 in the Asus Zenbook S16 UM5606W to show approximately where you can expect the high-end Framework Laptop 16 configuration to land (Framework’s integrated graphics performance will be marginally worse since it’s using slower socketed RAM rather than LPDDR5X; other numbers may differ based on how each manufacturer has configured the chip’s power usage and thermal behavior). We’ve also included numbers from the same chip in the Framework Laptop 13, though Framework’s spec sheets indicate that the chips have different power limits and thus will perform differently.
We were able to test the new GeForce GPU in multiple configurations—both paired with the new Ryzen AI 7 350 processor and with the old Ryzen 9 7940HS chip. This should give anyone who bought the original Laptop 16 an idea of what kind of performance increase they can expect from the new GPU alone. In all, we’ve tested or re-tested:
- The Ryzen 7 7940HS CPU from the first-generation Laptop 16 and its integrated Radeon 780M GPU
- The Ryzen 7 7940HS and the original Radeon RX 7700S GPU module
- The Ryzen 7 7940HS and the new GeForce RTX 5070 GPU module, for upgraders who only want to grab the new GPU
- The Ryzen AI 7 350 CPU and the GeForce RTX 5070 GPU
We also did some light testing on the Radeon 860M integrated GPU included with the Ryzen AI 7 350.
All the Laptop 16 performance tests were run with Windows’ Best Performance power preset enabled, which will slightly boost performance at the expense of power efficiency.
Given all of those hardware combinations, we simply ran out of time to test the new motherboard with the old Radeon RX 7700S GPU—Framework is continuing to sell it, so it is a realistic combination of components. But our RTX 5070 testing suggests that these GPUs will perform pretty much the same regardless of which CPU you pair them with.
If you’re buying the cheaper Laptop 16 with the Ryzen AI 7 350, the good news is that it generally performs at least as well as—and usually a bit better than—the high-end Ryzen 9 7940HS from the last-generation model. Performance is also pretty similar to the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 in smaller, thinner laptops—the extra power and cooling capacity in the Laptop 16 is paying off here. People choosing between a PC and a Mac should note that none of these Ryzen chips come anywhere near the M4 Pro used in comparably priced 16-inch MacBook Pros, but that’s just where the PC ecosystem is these days.
How big an upgrade the GeForce 5070 will be depends on the game you’re playing. In titles like Borderlands 3 that naturally run a bit better on AMD’s GPUs, there’s not much of a difference at all. In games like Cyberpunk 2077 with heavy ray-tracing effects enabled, the mobile RTX 5070 can be nearly twice as fast as the RX 7700S.
Most games will fall somewhere in between those two extremes; our tests show that the improvements hover between 20 and 30 percent most of the time, just a shade less than the 30 to 40 percent improvement that Framework claimed in its original announcement.
Beyond raw performance, the other thing you get with an Nvidia GPU is access to a bunch of important proprietary technologies like DLSS upscaling and CUDA—these technologies are often better and more widely supported than the equivalent technologies that AMD’s or Intel’s GPUs use, thanks in part to Nvidia’s overall dominance of the dedicated GPU market.
In the tests we’ve run on them, the Radeon 860M and 890M are both respectable integrated GPUs (the lower-end 860M typically falls just short of last generation’s top-end 780M, but it’s very close). They’re never able to provide more than a fraction of the Radeon RX 7700S’s performance, let alone the RTX 5070, but they’ll handle a lot of lighter games at 1080p. I would not buy a system this large or heavy just to use it with an integrated GPU.
Better to be unique than perfect

It’s expensive and quirky, but the Framework Laptop 16 is worth considering because it’s so different from what most other laptop makers are doing. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Our original Framework Laptop 16 review called it “fascinating but flawed,” and the parts that made it flawed haven’t really changed much over the last two years. It’s still relatively large and heavy; the Expansion Card system still makes less sense in a larger laptop than it does in a thin-and-light; the puzzle-like grid of input modules and spacers looks kind of rough and unfinished.
But the upgrades do help to shift things in the Laptop 16’s favor. Its modular and upgradeable design was always a theoretical selling point, but the laptop now actually offers options that other laptops don’t.
The presence of both AMD and Nvidia GPUs is a big step up in flexibility for both gaming and professional applications. The GeForce module is a better all-around choice, with slightly to significantly faster game performance and proprietary technologies like DLSS and CUDA, while the Radeon GPU is a cheaper option with better support for Linux.
Given their cost, I still wish that these GPUs were more powerful—they’re between $350 or $449 for the Radeon RX 7700S and between $650 and $699 for the RTX 5070 (prices vary a bit and are cheaper when you’re buying them together with a new laptop rather than buying them separately). You’ll basically always spend more for a gaming laptop than you will for a gaming desktop with similar or better performance, but that does feel like an awful lot to spend for GPUs that are still limited to 8GB of RAM.
Cost is a major issue for the Laptop 16 in general. You may save money in the long run by buying a laptop that you can replace piece-by-piece as you need to rather than all at once. But it’s not even remotely difficult to find similar specs from the major PC makers for hundreds of dollars less. We can’t vouch for the build quality or longevity of any of those PCs, but it does mean that you have to be willing to pay an awful lot just for Framework’s modularity and upgradeability. That’s true to some degree of the Laptop 13 as well, but the price gap between the 13 and competing systems isn’t as large as it is for the 16.
Whatever its lingering issues, the Framework Laptop 16 is still worth considering because there’s nothing else quite like it, at least if you’re in the market for something semi-portable and semi-powerful. The MacBook Pro exists if you want something more appliance-like, and there’s a whole spectrum of gaming and workstation PCs in between with all kinds of specs, sizes, and prices. To stand out from those devices, it’s probably better to be unique than to be perfect, and the reformulated Laptop 16 certainly clears that bar.
The good
- Modular, repairable, upgradeable design that’s made to last
- Cool, customizable keyboard deck
- Nvidia GeForce GPU option gives the Laptop 16 access to some gaming and GPU computing features that weren’t usable with AMD GPUs
- GPU upgrade can be added to first-generation Framework Laptop 16
- New processors are a decent performance improvement and are worth considering for new buyers
- Old Ryzen 7040-series motherboard is sticking around as an entry-level option, knocking $100 off the former base price ($1,299 and up for a barebones DIY edition, $1,599 and up for the cheapest pre-built)
- Framework’s software support has gotten better in the last year
The bad
- Big and bulky for the specs you get
- Mix-and-match input modules and spacers give it a rough, unfinished sort of look
- Ryzen AI motherboards are more expensive than the originals were when they launched
The ugly
- It’ll cost you—the absolute bare minimum price for Ryzen AI 7 350 and RTX 5070 combo is $2,149, and that’s without RAM, an SSD, or an operating system
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
Review: New Framework Laptop 16 takes a fresh stab at the upgradeable laptop GPU Read More »