RFK Jr. defends $500M cut for mRNA vaccines with pseudoscience gobbledygook
He clearly has no idea what antigenic shift means.
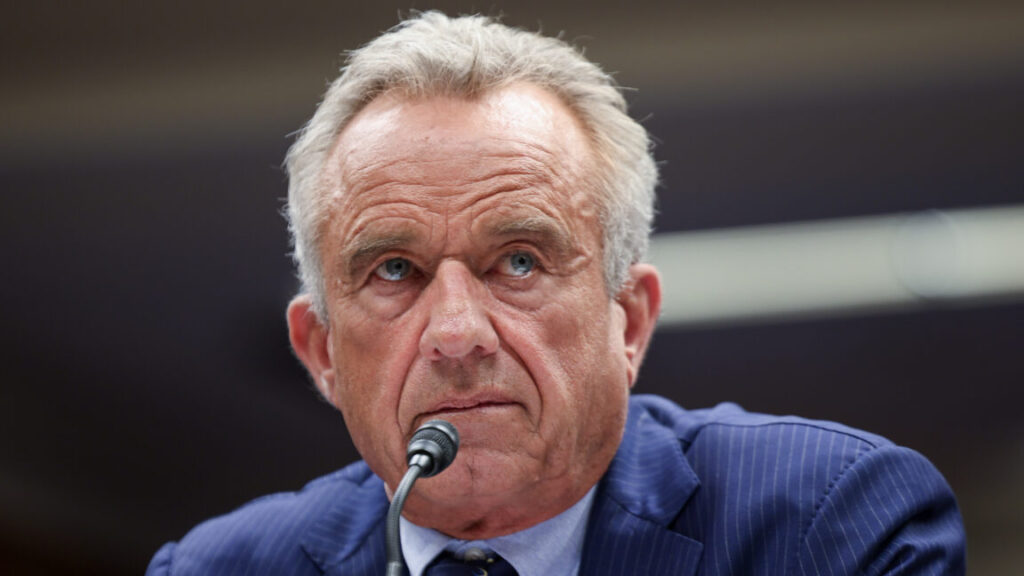
US Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy Jr. testifies before the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions on Capitol Hill on May 20, 2025 in Washington, DC. Credit: Getty | Tasos Katopodis
If anyone needed a reminder that US health secretary and fervent anti-vaccine advocate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has no background in science or medicine, look no further than the video he posted on social media Tuesday evening.
In the two-and-a-half-minute clip, Kennedy announced that he is cancelling nearly $500 million in funding for the development of mRNA-based vaccines against diseases that pose pandemic threats. The funding will be clawed back from 22 now-defunct contracts awarded through the federal agency tasked with developing medical countermeasures to public health threats. The agency is the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA).
Kennedy is generally opposed to vaccines, but he is particularly hostile to mRNA-based vaccines. Since the remarkably successful debut of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic—which were developed and mass-produced with unprecedented speed—Kennedy has continually disparaged and spread misinformation about them.
In the video on Tuesday, Kennedy continued that trend, erroneously saying that, “as the pandemic showed us, mRNA vaccines don’t perform well against viruses that infect the upper respiratory tract.” In reality, COVID-19 vaccines are estimated to have saved more than 3 million lives in the US in just the first two years of the pandemic and additionally prevented more than 18 million hospitalizations in the US in that time. Nearly all COVID-19 vaccines used in the US are mRNA-based.
However, Kennedy’s video only went more off the rails from there. He continued on with this nonsensical explanation:
Here’s the problem: mRNA only codes for a small part of viral proteins usually a single antigen. One mutation, and the vaccine becomes ineffective. This dynamic drives a phenomenon called antigenic shift meaning that the vaccine paradoxically encourages new mutations and can actually prolong pandemics as the virus constantly mutates to escape the protective effects of the vaccine.
Fact-check
To unpack this nonsense, let’s start with how mRNA-based vaccines work. These vaccines deliver a snippet of genetic code—in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA)—to cells. Our cells then translate that mRNA code into a protein that the immune system can, essentially, use for target practice, producing antibodies and cell-based responses against it. After that, if the immune system ever encounters that snippet on an actual invading virus or other germ, it will then recognize it and mount a protective response. Such snippets of germs or other harmful things that can prompt an immune response are generally called antigens.
In the case of COVID-19 vaccines, the mRNA snippet codes for a portion of the SARS-CoV-2 virus’s spike protein, which is a critical external protein that the virus uses to attach to and infect cells. That portion of the spike protein is considered an antigen.
SARS-CoV-2, including its spike protein, is continually evolving, regardless of whether people are vaccinated or not, let alone what type of vaccine they’ve received. The virus racks up mutations as it continuously replicates. Some of these mutations help a virus evade immune responses, whether they’re from vaccination or previous infection. These immune-evading mutations can accumulate and give rise to new variants or strains, making it part of a process called antigenic drift (not shift). Antigenic drift does reduce the efficacy of vaccines over time. It’s why, for example, people can get influenza repeatedly in their lifetimes, and why flu shots are updated annually. However, it does not mean that vaccines are immediately rendered ineffective upon single mutations, as Kennedy says.
For example, the current leading SARS-CoV-2 variant in the US is NB.1.8.1, which has six notable mutations in its spike protein compared to the previous leading variant, LP.8.1. Further, NB.1.8.1 has seven notable spike mutations compared to the JN.1 variant, an ancestor for this line of variants. Yet, studies suggest that current mRNA COVID-19 vaccines targeting JN.1 are still effective against NB.1.8.1. In fact, the Food and Drug Administration, in line with its expert advisors, left open the possibility that vaccine makers could carry over the same JN.1-targeting seasonal COVID-19 vaccine formula from last season for use in this season.
Drift vs. shift
While antigenic drift is an accumulation of small, immune-evading mutations over time, Kennedy mentioned antigenic shift, which is something different. Antigenic shift is much more dramatic, infrequent, and is typically discussed in the context of influenza viruses, which have segmented genomes. Antigenic shift is often defined as “the reassortment of viral gene segments between various influenza viruses of human or zoological origin, which leads to the emergence of new strains.” The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention gives an example of such a shift in 2009. That’s when a new influenza virus with a collection of genome segments from influenza viruses found in North American swine, Eurasian swine, humans, and birds emerged to cause the H1N1 pandemic.
In the video, Kennedy went on to muddle these concepts of drifts and shifts, saying:
Millions of people maybe even you or someone you know caught the omicron variant despite being vaccinated, that’s because a single mutation can make mRNA vaccines ineffective.
Among the COVID-19 variants that have risen to dominance only to be quickly usurped, there’s usually a small handful of mutations—like the examples above with six or seven mutations in the spike protein. But omicron was a different story. Omicron emerged carrying an extremely large suite of mutations—there were 37 mutations in its spike protein compared to its predecessors. Kennedy’s suggestion that it rose to prominence because of a single mutation is egregiously false.
However, due to the extreme number of mutations, some researchers have suggested that omicron does represent an antigenic shift for SARS-CoV-2. Although the pandemic virus—which is a coronavirus—does not have a segmented genome, the “magnitude of Omicron-mediated immune evasion” fits with an antigenic shift, the researchers said.
“Highly vulnerable”
While long-term drifts and rare shifts can reduce the effectiveness of vaccines, creating the need for updated shots, the point only bolsters the case for using mRNA vaccines in the event of another health emergency. Currently, no other vaccine platform beats the development and production speeds of mRNA vaccines. Kennedy said that instead of mRNA vaccines, he’ll shift to developing vaccines using strategies like whole-virus vaccines. But this decades-old strategy requires growing up large supplies of virus in eggs or cell culture, which takes months longer than mRNA vaccines. Further, using whole, inactivated viruses can often produce more side effects than other types of vaccines because they include more antigens.
Overall, experts were aghast that Kennedy has abandoned mRNA vaccines for pandemic preparedness programs. One expert, who asked not to be named for fear of reprisal, told Stat News: “It’s self-evident that this is the single best technology we have now to rapidly produce a vaccine for the largest number of people,” the expert said. “And you are throwing away a technology which was exceedingly valuable in saving lives during the most recent pandemic.”
Michael Osterholm, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy, told the outlet that the move “leaves us highly vulnerable. Highly vulnerable.”
Beth is Ars Technica’s Senior Health Reporter. Beth has a Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and attended the Science Communication program at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She specializes in covering infectious diseases, public health, and microbes.
RFK Jr. defends $500M cut for mRNA vaccines with pseudoscience gobbledygook Read More »