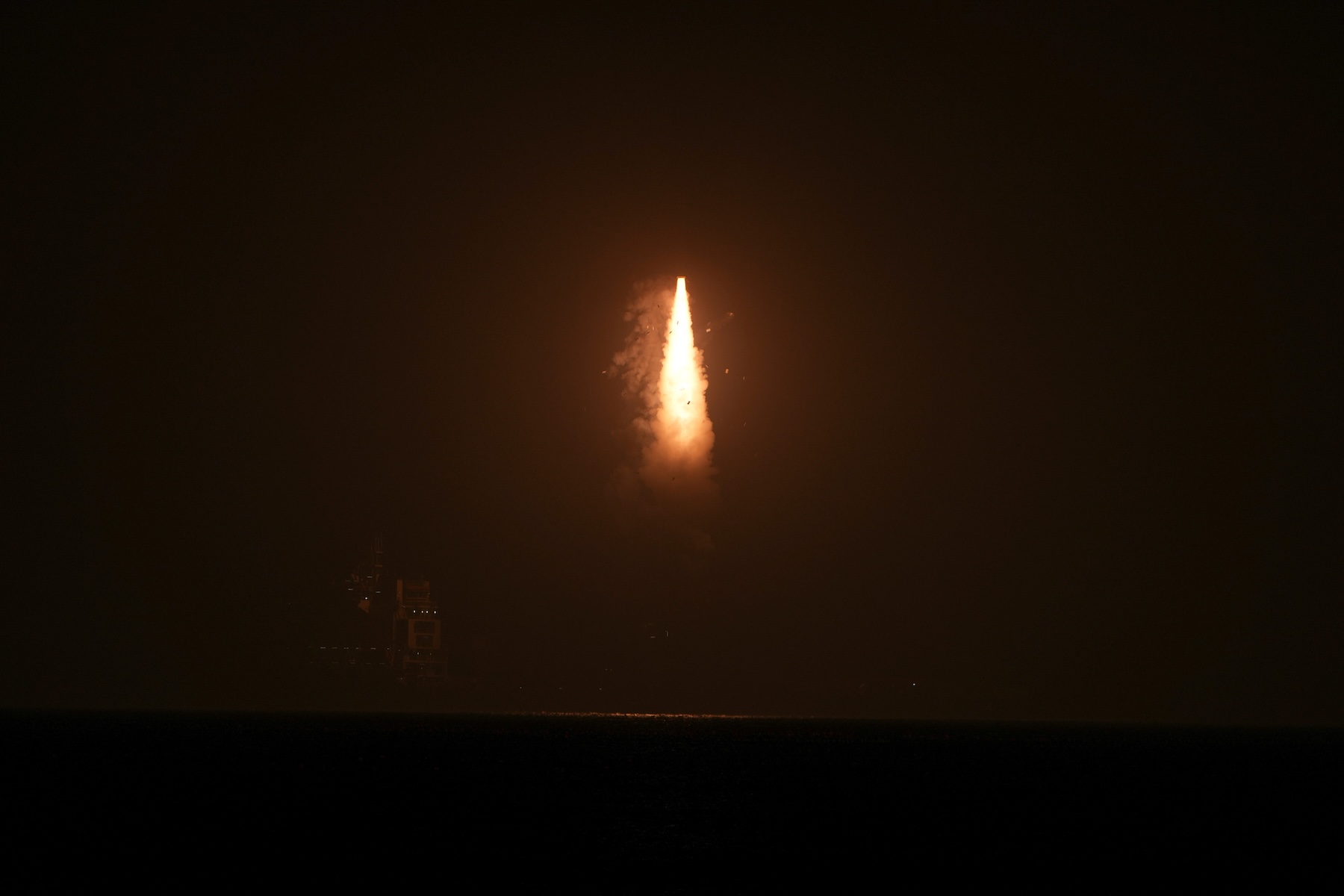
World’s oldest RNA extracted from ice age woolly mammoth
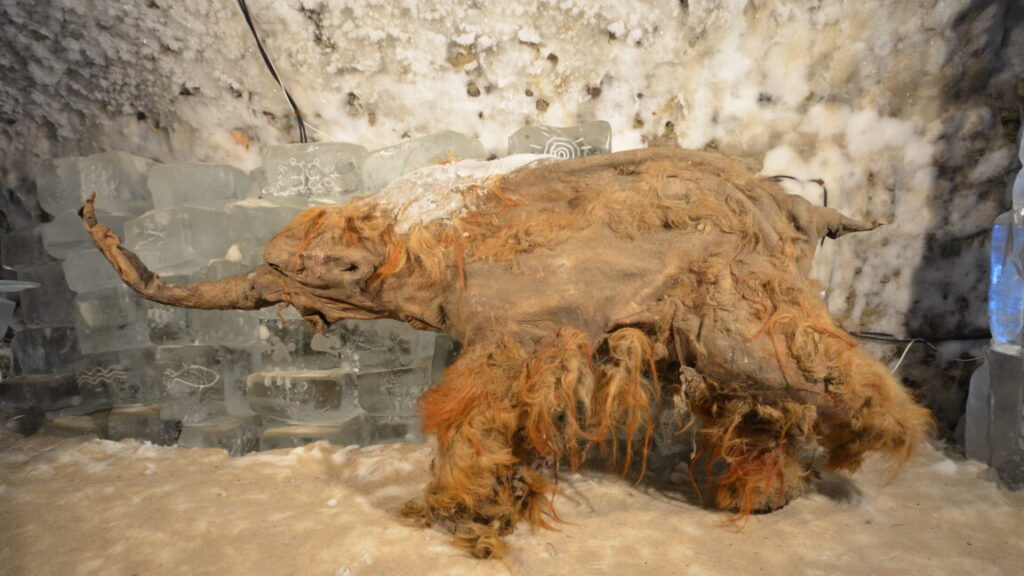
A young woolly mammoth now known as Yuka was frozen in the Siberian permafrost for about 40,000 years before it was discovered by local tusk hunters in 2010. The hunters soon handed it over to scientists, who were excited to see its exquisite level of preservation, with skin, muscle tissue, and even reddish hair intact. Later research showed that, while full cloning was impossible, Yuka’s DNA was in such good condition that some cell nuclei could even begin limited activity when placed inside mouse eggs.
Now, a team has successfully sequenced Yuka’s RNA—a feat many researchers once thought impossible. Researchers at Stockholm University carefully ground up bits of muscle and other tissue from Yuka and nine other woolly mammoths, then used special chemical treatments to pull out any remaining RNA fragments, which are normally thought to be much too fragile to survive even a few hours after an organism has died. Scientists go to great lengths to extract RNA even from fresh samples, and most previous attempts with very old specimens have either failed or been contaminated.
A different view
The team used RNA-handling methods adapted for ancient, fragmented molecules. Their scientific séance allowed them to explore information that had never been accessible before, including which genes were active when Yuka died. In the creature’s final panicked moments, its muscles were tensing and its cells were signaling distress—perhaps unsurprising since Yuka is thought to have died as a result of a cave lion attack.
It’s an exquisite level of detail, and one that scientists can’t get from just analyzing DNA. “With RNA, you can access the actual biology of the cell or tissue happening in real time within the last moments of life of the organism,” said Emilio Mármol, a researcher who led the study. “In simple terms, studying DNA alone can give you lots of information about the whole evolutionary history and ancestry of the organism under study. “Obtaining this fragile and mostly forgotten layer of the cell biology in old tissues/specimens, you can get for the first time a full picture of the whole pipeline of life (from DNA to proteins, with RNA as an intermediate messenger).”
World’s oldest RNA extracted from ice age woolly mammoth Read More »