Nobel laureate David Baltimore dead at 87
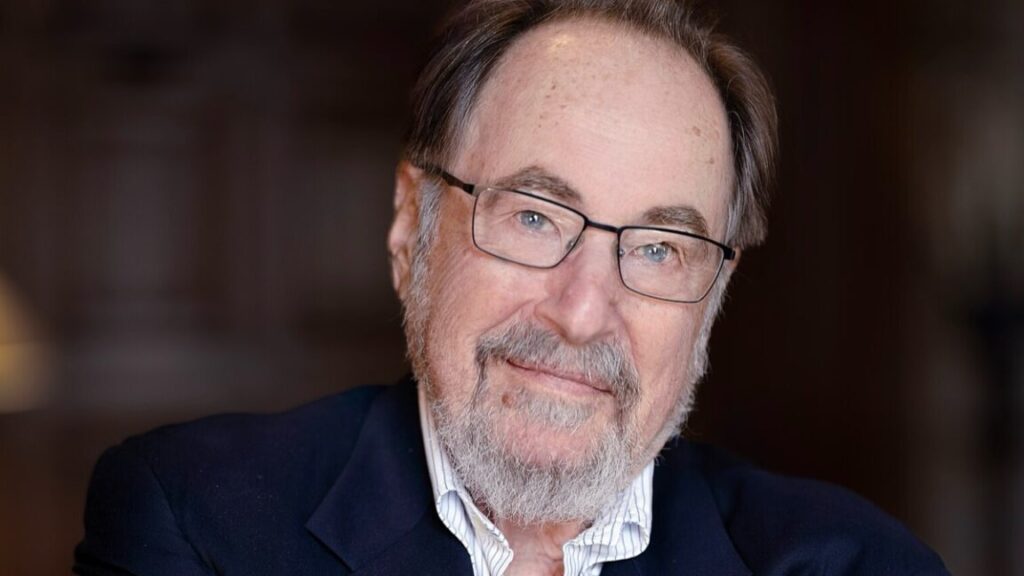
Nobel Prize-winning molecular biologist and former Caltech president David Baltimore—who found himself at the center of controversial allegations of fraud against a co-author—has died at 87 from cancer complications. He shared the 1975 Nobel Prize in Physiology for his work upending the then-consensus that cellular information flowed only in one direction. Baltimore is survived by his wife of 57 years, biologist Alice Huang, as well as a daughter and granddaughter.
“David Baltimore’s contributions as a virologist, discerning fundamental mechanisms and applying those insights to immunology, to cancer, to AIDS, have transformed biology and medicine,” current Caltech President Thomas F. Rosenbaum said in a statement. “David’s profound influence as a mentor to generations of students and postdocs, his generosity as a colleague, his leadership of great scientific institutions, and his deep involvement in international efforts to define ethical boundaries for biological advances fill out an extraordinary intellectual life.”
Baltimore was born in New York City in 1938. His father worked in the garment industry, and his mother later became a psychologist at the New School and Sarah Lawrence. Young David was academically precocious and decided he wanted to be a scientist after spending a high school summer learning about mouse genetics at the Jackson Laboratory in Maine. He graduated from Swarthmore College and earned his PhD in biology from Rockefeller University in 1964 with a thesis on the study of viruses in animal cells. He joined the Salk Institute in San Diego, married Huang, and moved to MIT in 1982, founding the Whitehead Institute.
Baltimore initially studied viruses like polio and mengovirus that make RNA copies of the RNA genomes to replicate, but later turned his attention to retroviruses, which have enzymes that make DNA copies of viral RNA. He made a major breakthrough when he proved the existence of that viral enzyme, now known as reverse transcriptase. Previously scientists had thought that the flow of information went from DNA to RNA to protein synthesis. Baltimore showed that process could be reversed, ultimately enabling researchers to use disabled retroviruses to insert genes into human DNA to correct genetic diseases.
Nobel laureate David Baltimore dead at 87 Read More »