Lawmakers writing NASA’s budget want a cheaper upper stage for the SLS rocket
Eliminating the Block 1B upgrade now would save NASA at least $500 million per year.
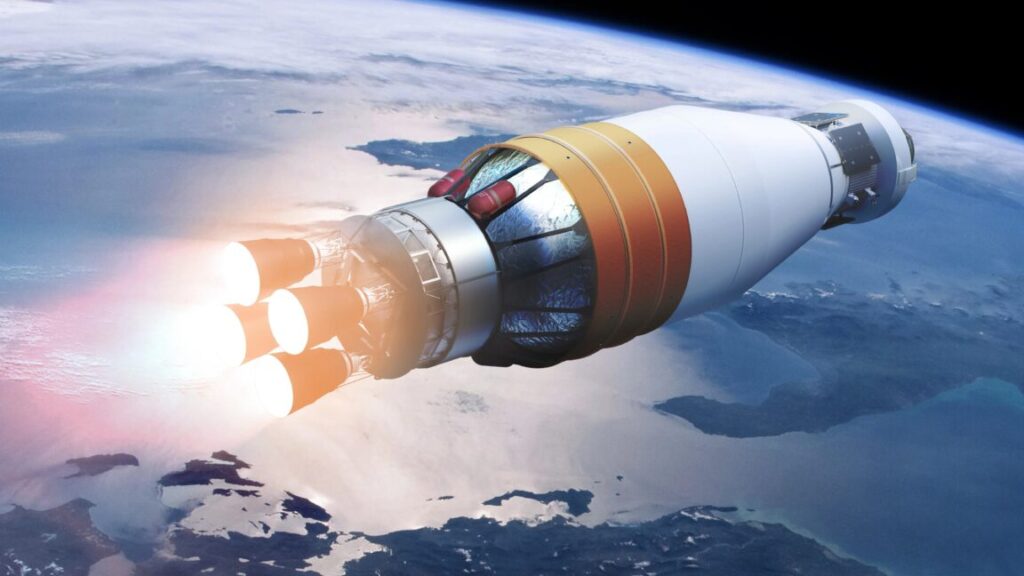
Artist’s illustration of the Boeing-developed Exploration Upper Stage, with four hydrogen-fueled RL10 engines. Credit: NASA
Not surprisingly, Congress is pushing back against the Trump administration’s proposal to cancel the Space Launch System, the behemoth rocket NASA has developed to propel astronauts back to the Moon.
Spending bills making their way through both houses of Congress reject the White House’s plan to wind down the SLS rocket after two more launches, but the text of a draft budget recently released by the House Appropriations Committee suggests an openness to making some major changes to the program.
The next SLS flight, called Artemis II, is scheduled to lift off early next year to send a crew of four astronauts around the far side of the Moon. Artemis III will follow a few years later on a mission to attempt a crew lunar landing at the Moon’s south pole. These missions follow Artemis I, a successful unpiloted test flight in 2022.
After Artemis III, the official policy of the Trump administration is to terminate the SLS program, along with the Orion crew capsule designed to launch on top of the rocket. The White House also proposed canceling NASA’s Gateway, a mini-space station to be placed in orbit around the Moon. NASA would instead procure commercial launches and commercial spacecraft to ferry astronauts between the Earth and the Moon, while focusing the agency’s long-term gaze toward Mars.
CYA EUS?
House and Senate appropriations bills would preserve SLS, Orion, and the Gateway. However, the House version of NASA’s budget has an interesting paragraph directing NASA to explore cheaper, faster options for a new SLS upper stage.
NASA has tasked Boeing, which also builds SLS core stages, to develop an Exploration Upper Stage for debut on the Artemis IV mission, the fourth flight of the Space Launch System. This new upper stage would have large propellant tanks and carry four engines instead of the single engine used on the rocket’s interim upper stage, which NASA is using for the first three SLS flights.
The House version of NASA’s fiscal year 2026 budget raises questions about the long-term future of the Exploration Upper Stage. In one section of the bill, House lawmakers would direct NASA to “evaluate alternatives to the current Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) design for SLS.” The committee members wrote the evaluation should focus on reducing development and production costs, shortening the schedule, and maintaining the SLS rocket’s lift capability.
“NASA should also evaluate how alternative designs could support the long-term evolution of SLS and broader exploration goals beyond low-Earth orbit,” the lawmakers wrote. “NASA is directed to assess various propulsion systems, stage configurations, infrastructure compatibility, commercial and international collaboration opportunities, and the cost and schedule impacts of each alternative.”
The SLS rocket is expensive, projected to cost at least $2.5 billion per launch, not counting development costs or expenses related to the Orion spacecraft and the ground systems required to launch it at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Those figures bring the total cost of an Artemis mission using SLS and Orion to more than $4 billion, according to NASA’s inspector general.
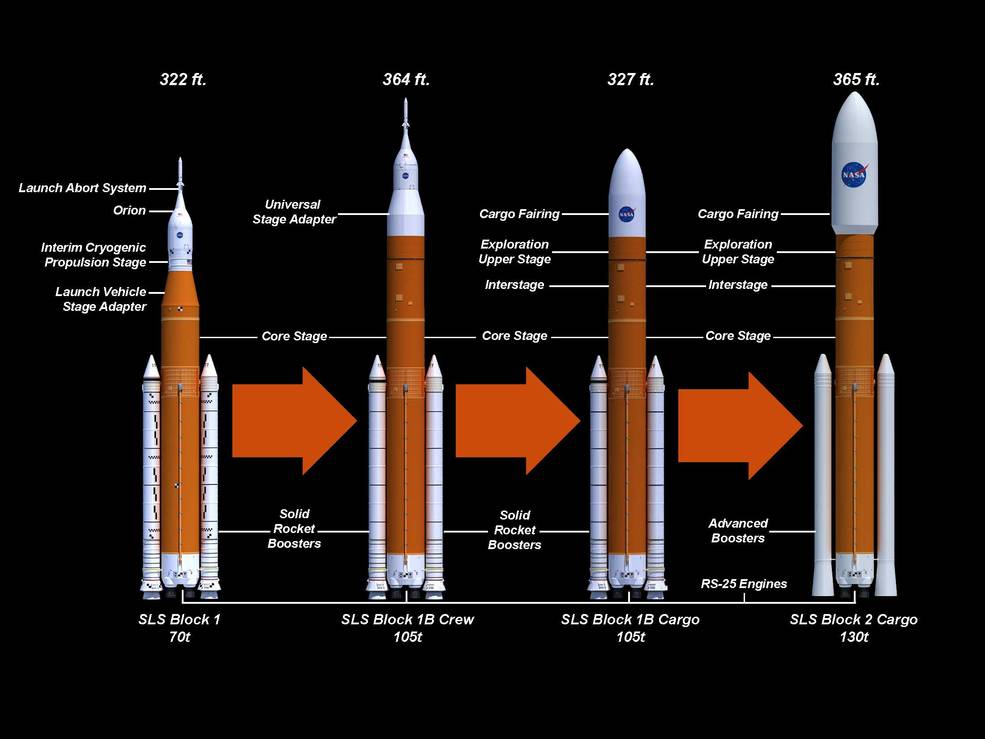
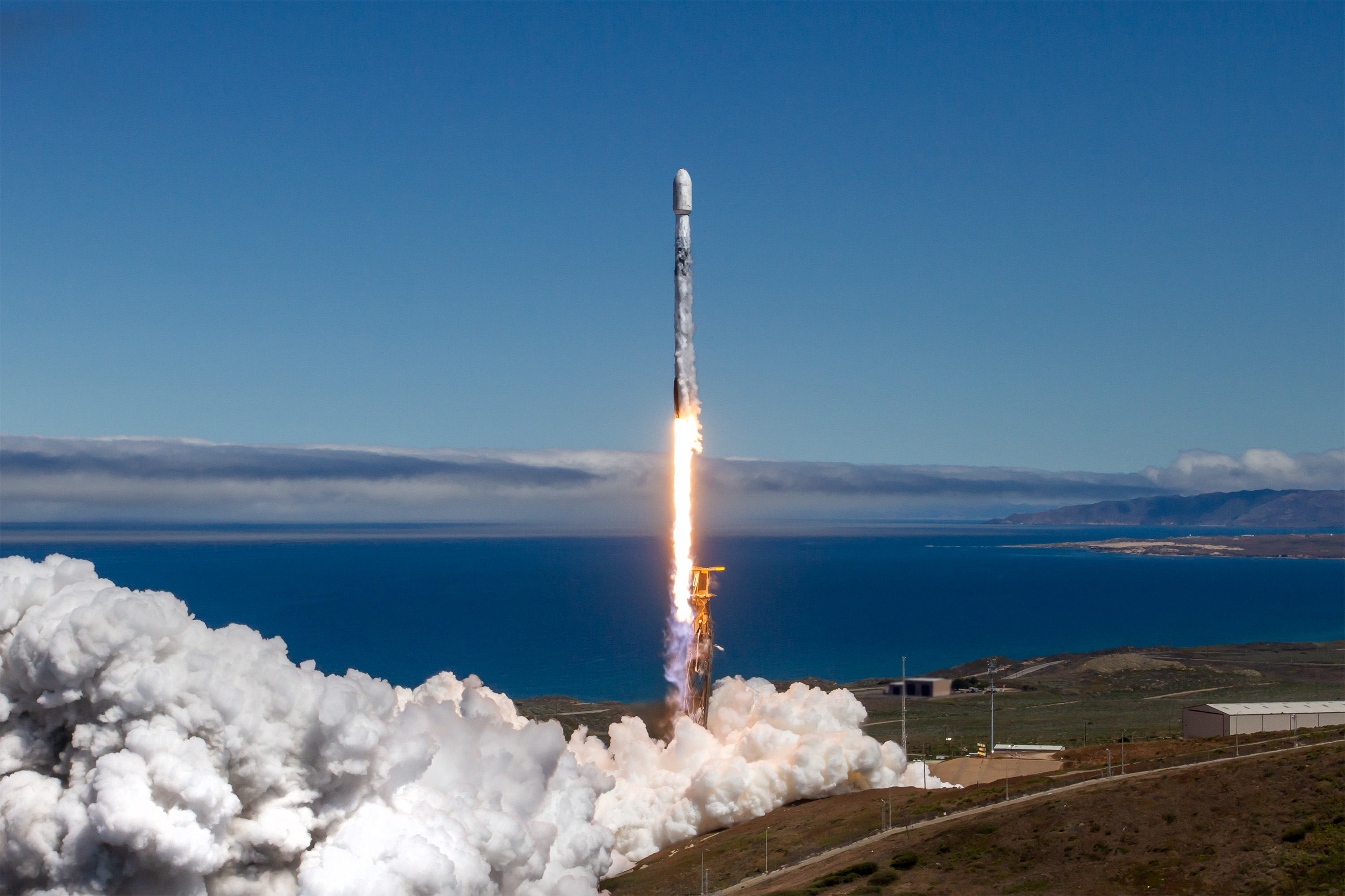
NASA’s Block 1B version of the SLS rocket will be substantially larger than Block 1. Credit: NASA
The EUS is likewise an expensive undertaking. Last year, NASA’s inspector general reported that the new upper stage’s development costs had ballooned from $962 million to $2.8 billion, and the Boeing-led project had been delayed more than six years. The version of the SLS rocket with the EUS, known as Block 1B, is supposed to deliver a 40 percent increase in performance over the Block 1 configuration used on the first three Space Launch System flights. Overall, NASA’s inspector general projected Block 1B’s development costs to total $5.7 billion.
Eliminating the Block 1B upgrade now would save NASA at least $500 million per year, and perhaps more if NASA could also end work on a costly mobile launch tower specifically designed to support SLS Block 1B missions.
NASA can’t go back to the interim upper stage, which is based on the design of the upper stage that flew on United Launch Alliance’s (ULA’s) now-retired Delta IV Heavy rocket. ULA has shut down its Delta production line, so there’s no way to build any more. What ULA does have is a new high-energy upper stage called Centaur V. This upper stage is sized for ULA’s new Vulcan rocket, with more capability than the interim upper stage but with lower performance than the larger EUS.
A season of compromise, maybe
Ars’ Eric Berger wrote last year about the possibility of flying the Centaur V upper stage on SLS missions.
Incorporating the Centaur V wouldn’t maintain the SLS rocket’s lift capability, as the House committee calls for in its appropriations bill. The primary reason for improving the rocket’s performance is to give SLS Block 1B enough oomph to carry “co-manifested” payloads, meaning it can launch an Orion crew capsule and equipment for NASA’s Gateway lunar space station on a single flight. The lunar Gateway is also teed up for cancellation in Trump’s budget proposal, but both congressional appropriations bills would save it, too. If the Gateway escapes cancellation, there are ways to launch its modules on commercial rockets.
Blue Origin also has an upper stage that could conceivably fly on the Space Launch System. But the second stage for Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket would be a more challenging match for SLS for several reasons, chiefly its 7-meter (23-foot) diameter—too wide to be a drop-in replacement for the interim upper stage used on Block 1. ULA’s Centaur V is much closer in size to the existing upper stage.
The House budget bill has passed a key subcommittee vote but won’t receive a vote from the full appropriations committee until after Congress’s August recess. A markup of the bill by the House Appropriations Committee scheduled for Thursday was postponed after Speaker Mike Johnson announced an early start to the recess this week.
Ars reported last week on the broad strokes of how the House and Senate appropriations bills would affect NASA. Since then, members of the House Appropriations Committee released the text of the report attached to their version of the NASA budget. The report, which includes the paragraph on the Exploration Upper Stage, provides policy guidance and more detailed direction on where NASA should spend its money.
The House’s draft budget includes $2.5 billion for the Space Launch System, close to this year’s funding level and $500 million more than the Trump administration’s request for the next fiscal year, which begins October 1. The budget would continue development of SLS Block 1B and the Exploration Upper Stage while NASA completes a six-month study of alternatives.
The report attached to the Senate appropriations bill for NASA has no specific instructions regarding the Exploration Upper Stage. But like the House bill, the Senate’s draft budget directs NASA to continue ordering spares and long-lead parts for SLS and Orion missions beyond Artemis III. Both versions of the NASA budget require the agency to continue with SLS and Orion until a suitable commercial, human-rated rocket and crew vehicle are proven ready for service.
In a further indication of Congress’ position on the SLS and Orion programs, lawmakers set aside more than $4 billion for the procurement of SLS rockets for the Artemis IV and Artemis V rockets in the reconciliation bill signed into law by President Donald Trump earlier this month.
Congress must pass a series of federal appropriations bills by October 1, when funding for the current fiscal year runs out. If Congress doesn’t act by then, it could pass a continuing resolution to maintain funding at levels close to this year’s budget or face a government shutdown.
Lawmakers will reconvene in Washington, DC, in early September in hopes of finishing work on the fiscal year 2026 budget. The section of the budget that includes NASA still must go through a markup hearing by the House Appropriations Committee and pass floor votes in the House and Senate. Then the two chambers will have to come to a compromise on the differences in their appropriations bill. Only then can the budget be put to another vote in each chamber and go to the White House for Trump’s signature.
Lawmakers writing NASA’s budget want a cheaper upper stage for the SLS rocket Read More »