Shopper denied $51 refund for 20TB HDD that’s mostly a weighted plastic box
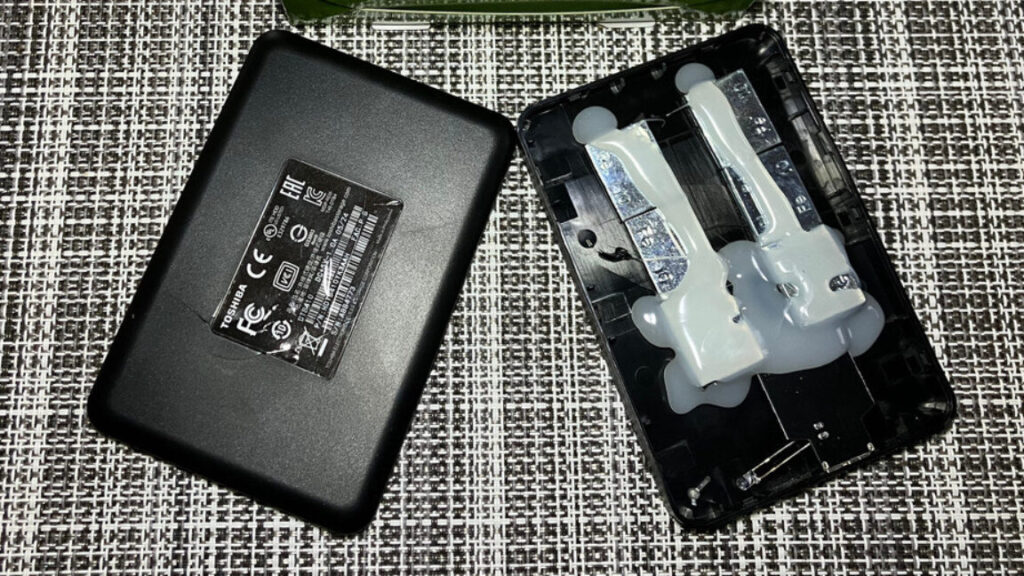
Many Arsians are the go-to IT support representative for family and friends. If you’re lucky, your loved ones’ problems are easily resolved with a reset, update, or new cable. That wasn’t the case for a son who recently had to break the news to his father that the 20TB portable hard drive he purchased for about $50 was mostly just a plastic box with weights and a PCB.
Ars Technica spoke with the Reddit user who posted about his father bringing him a “new 20T[B] HDD to see if I could figure out what was wrong with it.” The Redditor, who asked that we refer to him by his first name, Martin, revealed that his dad paid £38 (about $51.33) for what he thought was a portable HDD. That’s a red flag. HDDs have gotten cheaper over the years, but not that cheap. A 20TB external HDD typically costs over $200, and they’re usually much larger than the portable-SSD-sized device that Martin’s father received. A 20TB HDD in a portable form factor is rarer and can cost well over $300.
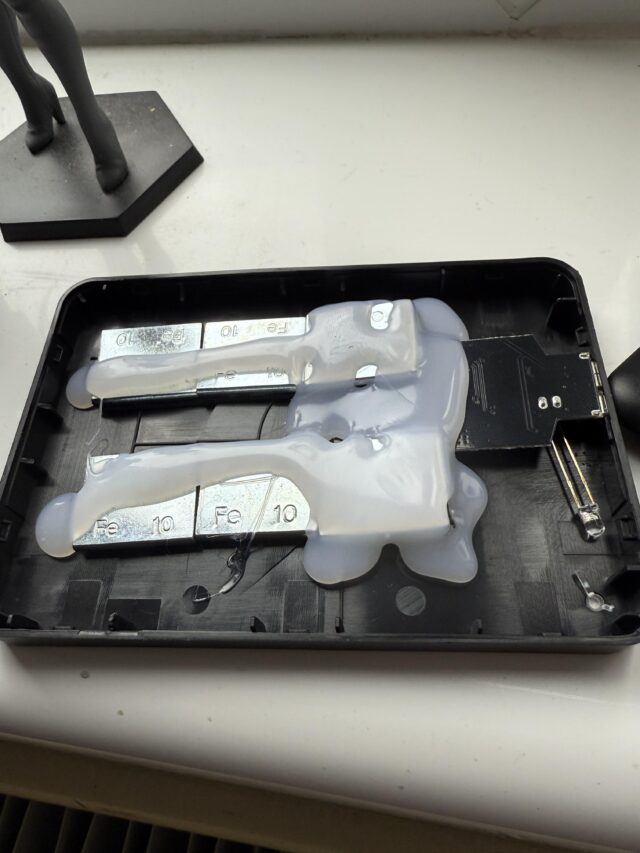
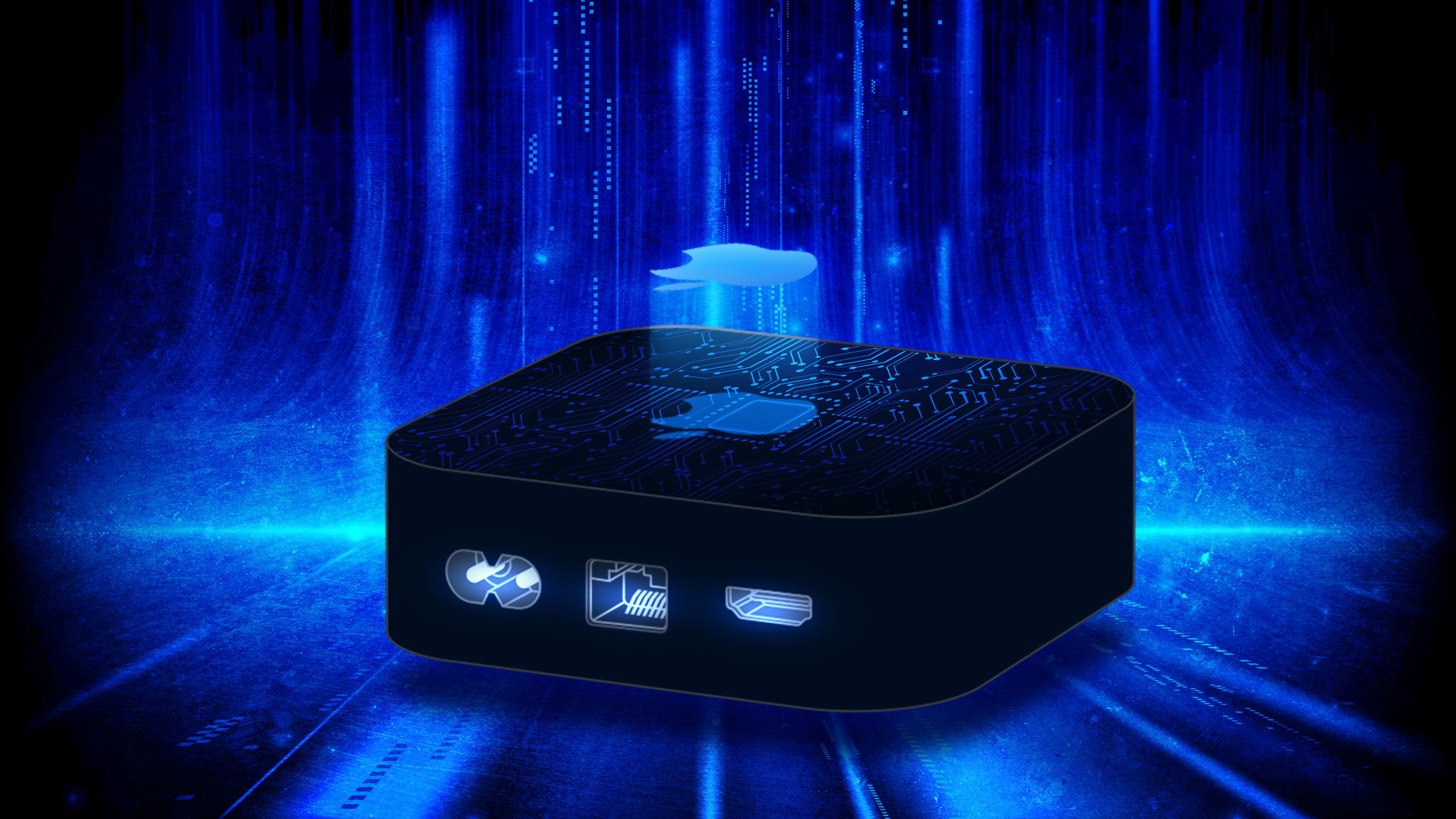
Taking a hammer to the device revealed that the chassis was nearly empty, save for some iron wheel weights sloppily attached to the black plastic with hefty globs of glue and a small PCB with some form of flash storage that could connect to a system via USB-A.
The “HDD” opened up. Credit: The__Unflushable/Reddit
As with other PC storage scams we’ve seen online, Windows read the so-called HDD as a “19TB drive, but would then just hang if you try to do anything with it,” Martin said on Reddit.
Programming the board’s firmware so that the drive appears as a high-capacity storage device on Windows is a clever trick that could convince users they’re to blame. But as Windows-savvy users would point out, Windows reports drive capacities in gibibytes or tebibytes, so a real 20TB HDD would appear as approximately 18.2TB in Windows.
Martin told Ars:
The device appeared to mount on the desktop with the device name in Mandarin (turned out this simply said “Hard Disc”). I tried copying a file, and the name did appear on the “hard disc.” It was only when I tried to open this file from the hard disc that the problems began to emerge. The file could not be opened, no matter how hard I tried, including reformatting the hard disc. At that point nothing was “working” at all.
Sketchy online listing
Martin told Ars that his father purchased the fake HDD from a website called UK.Chicntech, which appears to primarily sell car supplies, kitchen supplies, and home textiles. Currently, the website does not list any PC components or peripherals, but overall, its stock is pretty limited. Chicntech currently lists some other electronics, like a “[With Starry Sky Lid]AI Nano Mist Intelligent Car Aromatherapy Device” (linking for explanatory purposes only; we don’t recommend shopping on this website) for $56.
Shopper denied $51 refund for 20TB HDD that’s mostly a weighted plastic box Read More »