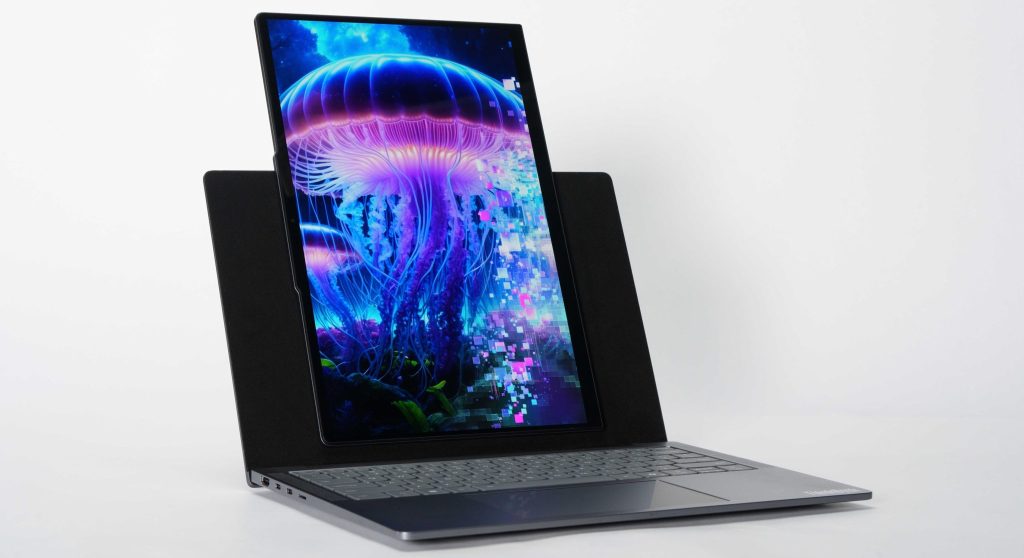
Lenovo demos laptop with a screen you can swivel into portrait mode
Underneath the rotating panel is a “soft, felt-covered backplate,” PCMag reported. I can see this being jarring in a real computer. The textures of felt or other fabrics are uncommon on machines and can result in this part of the computer standing out in an unwelcome fashion. The black felt, however, could eventually fade into the background, depending on the user’s perception.
Lenovo suggested that people could use the felt space to place a smartphone for mirroring with the PC via its Software Connect software; however, that feature requires a Lenovo Motorola phone.
Lenovo suggested other potential use cases for the unique screen in its press release, including “split-screen multitasking, displaying code, and reviewing documents.”
Lenovo’s latest concept laptop continues the OEM’s yearslong exploration of PC screens that adapt to the different ways that people use PCs. I’m skeptical about the use of felt in a laptop, which would likely be thousands of dollars if ever released as a consumer product. A laptop like the VertiFlex would also have to prove that it has a durable pivoting point and can support a lot of spinning over years of use. Still, Lenovo is contemplating ways to offer versatile screens without relying on bending, warping OLED screens that can suffer from reflections, glare, visible creases, or clunky motors.
For those who like to see laptop screen display ideas that don’t rely on bendy OLED, the VertiFlex is the type of concept that makes you wonder why we haven’t seen it earlier.
Lenovo demos laptop with a screen you can swivel into portrait mode Read More »