NASA shakes up its Artemis program to speed up lunar return
“Launching SLS every three and a half years or so is not a recipe for success.”
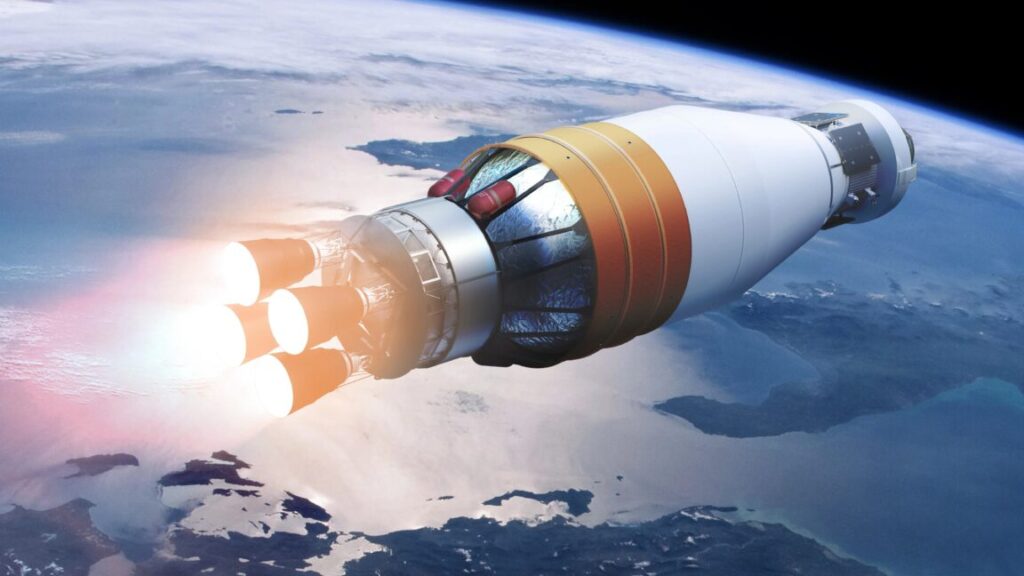
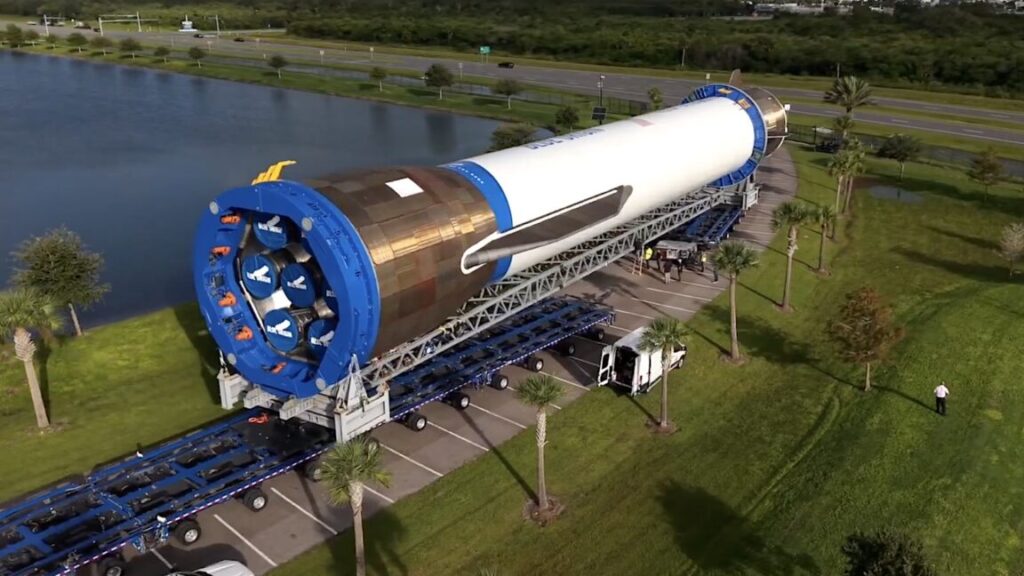
Artist’s illustration of the Boeing-developed Exploration Upper Stage, with four hydrogen-fueled RL10 engines. Credit: NASA
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman announced sweeping changes to the Artemis program on Friday morning, including an increased cadence of missions and cancellation of an expensive rocket stage.
The upheaval comes as NASA has struggled to fuel the massive Space Launch System rocket for the upcoming Artemis II lunar mission, and Isaacman has sought to revitalize an agency that has moved at a glacial pace on its deep space programs. There is ever-increasing concern that, absent a shake-up, China’s rising space program will land humans on the Moon before NASA can return there this decade with Artemis.
“NASA must standardize its approach, increase flight rate safely, and execute on the president’s national space policy,” Isaacman said. “With credible competition from our greatest geopolitical adversary increasing by the day, we need to move faster, eliminate delays, and achieve our objectives.”
Shaking things up
The announced changes to the Artemis program include:
- Cancellation of the Exploration Upper Stage and Block IB upgrade for SLS rocket
- Artemis II and Artemis III missions will use the SLS rocket with existing upper stage
- Artemis IV, V (and any additional missions, should there be) will use a “standardized” upper stage
- Artemis III will no longer land on the Moon; rather Orion will launch on SLS and dock with Starship and/or Blue Moon landers in low-Earth orbit
- Artemis IV is now the first lunar landing mission
- NASA will seek to fly Artemis missions annually, starting with Artemis III in “mid” 2027, followed by at least one lunar landing in 2028
- NASA is working with SpaceX and Blue Origin to accelerate their development of commercial lunar landers for Artemis IV and beyond
At the core of Isaacman’s concerns is the low flight rate of the SLS rocket and Artemis missions. During past exploration missions, from Mercury through Gemini, Apollo, and the Space Shuttle program, NASA has launched humans on average about once every three months. It has been nearly 3.5 years since Artemis I launched.
“This is just not the right pathway forward,” Isaacman said.
A senior NASA official, speaking on background to Ars, noted that the space agency has experienced hydrogen and helium leaks during both the Artemis I and Artemis II pre-launch preparations, and these problems have led to monthslong delays in launch.
“If I recall, the timing between Apollo 7 and 8 was nine weeks,” the official said. “Launching SLS every three and a half years or so is not a recipe for success. Certainly, making each one of them a work of art with some major configuration change is also not helpful in the process, and we’re clearly seeing the results of it, right?”
The goal, therefore, is to standardize the SLS rocket into a single configuration to make it as reliable as possible and to launch it as frequently as every 10 months. NASA will fly the SLS vehicle until there are commercial alternatives to launch crew to the Moon, perhaps through Artemis V as Congress has mandated, or perhaps even a little longer.
Is everyone on board?
The NASA official said all of the agency’s key contractors are on board with the change, and senior leaders in Congress have been briefed on the proposed changes.
The biggest opposition to these proposals would seemingly come from Boeing, which is the prime contractor for the Exploration Upper Stage, a contract worth billions of dollars to develop a more powerful rocket that was due to launch for the first time later this decade. However, in a NASA news release, Boeing appeared to offer at least some support for the revised plans.
“Boeing is a proud partner to the Artemis mission and our team is honored to contribute to NASA’s vision for American space leadership,” said Steve Parker, Boeing Defense, Space & Security president and CEO, in the news release. “The SLS core stage remains the world’s most powerful rocket stage, and the only one that can carry American astronauts directly to the moon and beyond in a single launch. As NASA lays out an accelerated launch schedule, our workforce and supply chain are prepared to meet the increased production needs.”
Solid reasons for changing Artemis III
NASA’s new approach to Artemis reflects a return to the philosophy of the Apollo program. During the late 1960s, the space agency flew a series of preparatory crewed missions before the Apollo 11 lunar landing. These included Apollo 7 (a low-Earth orbit test of the Apollo spacecraft), Apollo 8 (a lunar orbiting mission), Apollo 9 (a low-Earth orbit rendezvous with the lunar lander), and Apollo 10 (a test of the lunar lander descending to the Moon, without touching down).
With its previous Artemis template, NASA skipped the steps taken by Apollo 7, 9, and 10. In the view of many industry officials, this leap from Artemis II—a crewed lunar flyby of the Moon testing only the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft—to Artemis III and a full-on lunar landing was enormous and risky.
The new approach will, in NASA parlance, “buy down” some of the risk for a 21st-century lunar landing, including performance and handling of a lunar lander, rendezvous and docking, communications, spacesuit performance, and more.
It will also increase the challenges for NASA. In particular, the timeline to bring the Orion spacecraft to readiness for a mid-2027 launch will need to be accelerated, and efforts to integrate that vehicle with one or both lander providers will need serious attention.
For the Artemis IV lunar landing mission, NASA will also need to human-rate a new upper stage for the SLS rocket. The vehicle currently uses a modified Delta IV upper stage manufactured by United Launch Alliance. But that rocket production line is closed, and NASA only has two more of these stages. With the cancellation of the Exploration Upper Stage, NASA will now procure a new stage commercially. NASA officials only said they will seek a “standardized” upper stage. As Ars has previously reported, the most likely replacement would be the Centaur V upper stage currently flying on Vulcan rockets.
What of the Lunar Gateway?
Friday’s announcement—which, for the space community, is the equivalent of a major earthquake—left some key details unaddressed. For example, NASA has been developing a larger launch tower to support the Block 1B version of the SLS rocket, with its more powerful upper stage. Development of this tower, finally underway, has been a clown show, with project costs ballooning from an initial estimate of $383 million to $1.8 billion, and delays stacked on delays. Will this tower be scrapped or repurposed?
Isaacman and other NASA officials were also mum on the Lunar Gateway, a proposed space station in a high orbit around the Moon. Key elements of this space station are under construction. However, cancellation of the Exploration Upper Stage raises questions about its future. The main purpose of the Block 1B version of SLS was to launch heavier payloads, most notably elements of the Gateway along with Orion.
“The whole Gateway-Moon base conversation is not for today,” the senior NASA official said. “We, I can assure you, will talk about the Moon base in the weeks ahead. I would just not overly read into this, because we had manifested some Gateway modules on Falcon Heavy already. The implications of standardizing SLS and increasing launch rate are about the ability to return to the Moon. I don’t think we necessarily have to speculate too much on what the other downstream implications are.”
The Gateway program office is based at Johnson Space Center in Houston, where the lunar station is viewed as a successor to the International Space Station in terms of flight operations.
Key politicians, such as Sen. Ted Cruz, R-Texas, have been supportive of this new station. But during some recent congressional hearings, Cruz has indicated he is open to a lunar space station or an outpost on the lunar surface. He just wants to be sure NASA has an enduring presence on or near the Moon. One industry source said Isaacman could be laying the groundwork to replace the Gateway Program with a Moon Base program office in Houston. It is unclear how much of a political battle this would ultimately be.
Some of this has been well-predicted
Although the changes outlined by NASA on Friday are sweeping, they are not completely out of the blue.
In April 2024, Ars reported that some senior NASA officials were considering an Earth-orbit rendezvous between Orion and Starship as a means to buy down risk for a lunar landing. NASA ultimately punted on the idea before it was revived by Isaacman this month.
Additionally, in October 2024, Ars offered a guide to saving the “floundering” Artemis program by canceling the Block 1B upgrade for the SLS rocket, replacing its upper stage with a Centaur V, and canceling the Lunar Gateway. This would free up an estimated $2 billion annually to focus on accelerating a lunar landing, the publication estimated.
That may be the very course the space agency has embarked upon today.
Eric Berger is the senior space editor at Ars Technica, covering everything from astronomy to private space to NASA policy, and author of two books: Liftoff, about the rise of SpaceX; and Reentry, on the development of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon. A certified meteorologist, Eric lives in Houston.
NASA shakes up its Artemis program to speed up lunar return Read More »