Ryzen 9 9950X3D review: Seriously fast, if a step backward in efficiency
Even three years later, AMD’s high-end X3D-series processors still aren’t a thing that most people need to spend extra money on—under all but a handful of circumstances, your GPU will be the limiting factor when you’re running games, and few non-game apps benefit from the extra 64MB chunk of L3 cache that is the processors’ calling card. They’ve been a reasonably popular way for people with old AM4 motherboards to extend the life of their gaming PCs, but for AM5 builds, a regular Zen 4 or Zen 5 CPU will not bottleneck modern graphics cards most of the time.
But high-end PC building isn’t always about what’s rational, and people spending $2,000 or more to stick a GeForce RTX 5090 into their systems probably won’t worry that much about spending a couple hundred extra dollars to get the fastest CPU they can get. That’s the audience for the new Ryzen 9 9950X3D, a 16-core, Zen 5-based, $699 monster of a processor that AMD begins selling tomorrow.
If you’re only worried about game performance (and if you can find one), the Ryzen 7 9800X3D is the superior choice, for reasons that will become apparent once we start looking at charts. But if you want fast game performance and you need as many CPU cores as you can get for other streaming or video production or rendering work, the 9950X3D is there for you. (It’s a little funny to me that this a chip made almost precisely for the workload of the PC building tech YouTubers who will be reviewing it.) It’s also a processor that Intel doesn’t have any kind of answer to.
Second-generation 3D V-Cache

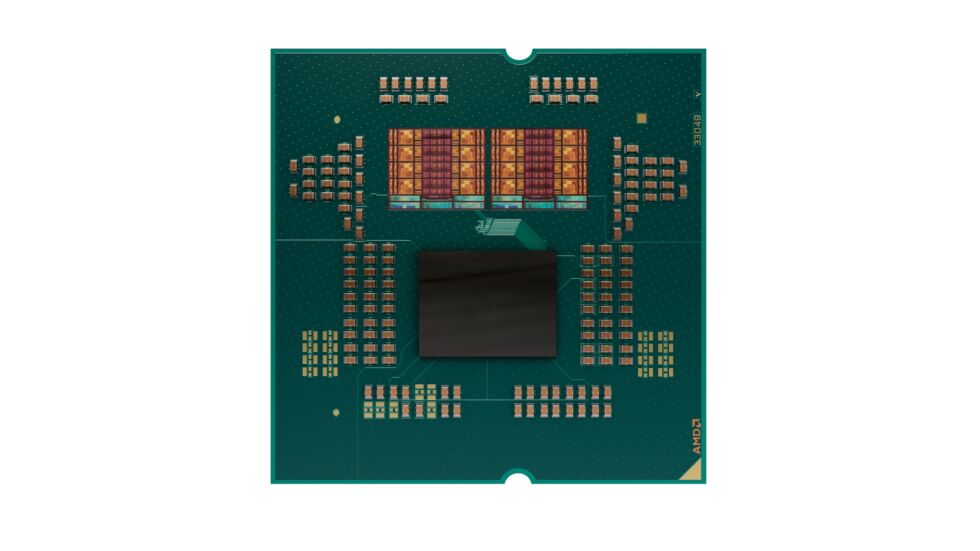
Layering the 3D V-Cache under the CPU die has made most of the 9950X3D’s improvements possible. Credit: AMD
AMD says the 9000X3D chips use a “second-generation” version of its 3D V-Cache technology after using the same approach for the Ryzen 5000 and 7000 processors. The main difference is that, where the older chips stack the 64MB of extra L3 cache on top of the processor die, the 9000 series stacks the cache underneath, making it easier to cool the CPU silicon.
This makes the processors’ thermal characteristics much more like a typical Ryzen CPU without the 3D V-Cache. And because voltage and temperatures are less of a concern, the 9800X3D, 9900X3D, and 9950X3D all support the full range of overclocking and performance tuning tools that other Ryzen CPUs support.
The 12- and 16-core Ryzen X3D chips are built differently from the 8-core. As we’ve covered elsewhere, AMD’s Ryzen desktop processors are a combination of chiplets—up to two CPU core chiplets with up to eight CPU cores each and a separate I/O die that handles things like PCI Express and USB support. In the 9800X3D, you just have one CPU chiplet, and the 64MB of 3D V-Cache is stacked underneath. For the 9900X3D and 9950X3D, you get one 8-core CPU die with V-Cache underneath and then one other CPU die with 4 or 8 cores enabled and no extra cache.
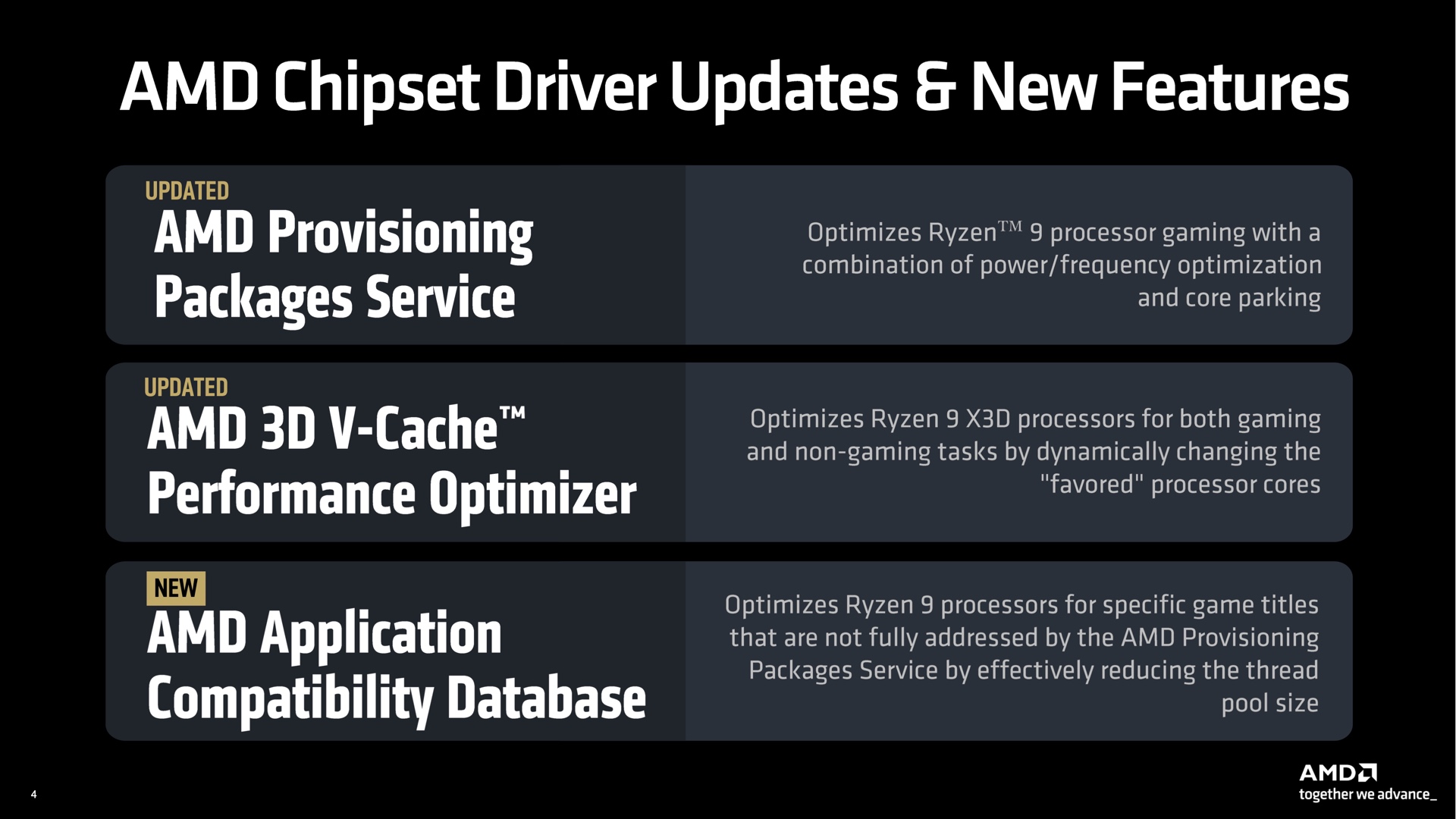
AMD’s driver software is responsible for deciding what apps get run on which CPU cores. Credit: AMD
It’s up to AMD’s chipset software to decide what kinds of apps get to run on each kind of CPU core. Non-gaming workloads prioritize the normal CPU cores, which are generally capable of slightly higher peak clock speeds, while games that benefit disproportionately from the extra cache are run on those cores instead. AMD’s software can “park” the non-V-Cache CPU cores when you’re playing games to ensure they’re not accidentally being run on less-suitable CPU cores.
This technology will work the same basic way for the 9950X3D as it did for the older 7950X3D, but AMD has made some tweaks. Updates to the chipset driver mean that you can swap your current processor out for an X3D model without needing to totally reinstall Windows to get things working, for example, which was AMD’s previous recommendation for the 7000 series. Another update will improve performance for Windows 10 systems with virtualization-based security (VBS) enabled, though if you’re still on Windows 10, you should be considering an upgrade to Windows 11 so you can keep getting security updates past October.
And for situations where AMD’s drivers can’t automatically send the right workloads to the right kinds of cores, AMD also maintains a compatibility database of applications that need special treatment to take advantage of the 3D V-Cache in the 9900X3D and 9950X3D. AMD says it has added a handful of games to that list for the 9900/9950X3D launch, including Far Cry 6, Deus Ex: Mankind Divided, and a couple of Total War games, among others.
Testbed notes
Common elements to all the platforms we test in our CPU testbed include a Lian Li O11 Air Mini case with an EVGA-provided Supernova 850 P6 power supply and a 280 mm Corsair iCue H115i Elite Capellix AIO cooler.
Since our last CPU review, we’ve done a bit of testbed updating to make sure that we’re accounting for a bunch of changes and turmoil on both Intel’s and AMD’s sides of the fence.
For starters, we’re running Windows 11 24H2 on all systems now, which AMD has said should marginally improve performance for architectures going all the way back to Zen 3 (on the desktop, the Ryzen 5000 series). The company made this revelation after early reviewers of the Ryzen 9000 series couldn’t re-create the oddball conditions of their own internal test setups.
As for Intel, the new testing incorporates fixes for the voltage spiking, processor-destroying bugs that affected 13th- and 14th-generation Core processors, issues that Intel fixed in phases throughout 2024. For the latest Core Ultra 200-series desktop CPUs, it also includes performance fixes Intel introduced in BIOS updates and drivers late last year and early this year. (You might have noticed that we didn’t run reviews of the 9800X3D or the Core Ultra 200 series at the time; all of this re-testing of multiple generations of CPUs was part of the reason why).
All of this is to say that any numbers you’re seeing in this review represent recent testing with newer Windows updates, BIOS updates, and drivers all installed.
One thing that isn’t top of the line at the moment is the GeForce RTX 4090, though we are using that now instead of a Radeon RX 7900 XTX.
The RTX 50 series was several months away from being announced when we began collecting updated test data, and we opted to keep the GPU the same for our 9950X3D testing so that we’d have a larger corpus of data to compare the chip to. The RTX 4090 is still, by a considerable margin, the second-fastest consumer GPU that exists right now. But at some point, when we’re ready to do yet another round of totally-from-scratch retesting, we’ll likely swap a 5090 in just to be sure we’re not bottlenecking the processor.
Performance and power: Benefits with fewer drawbacks
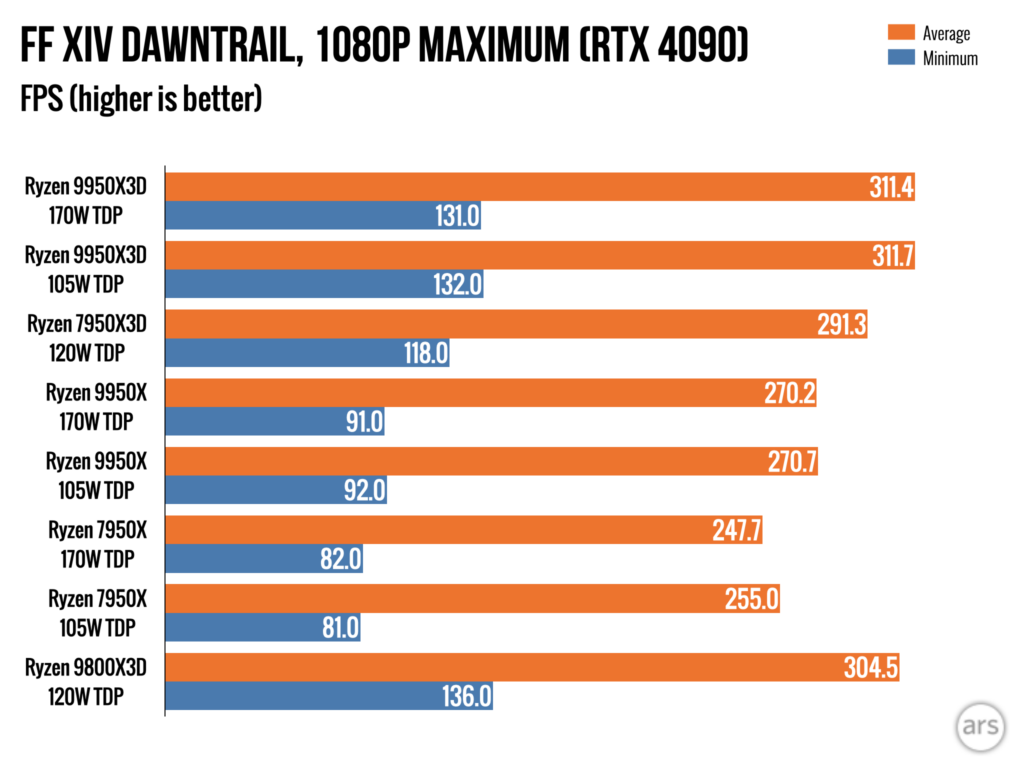
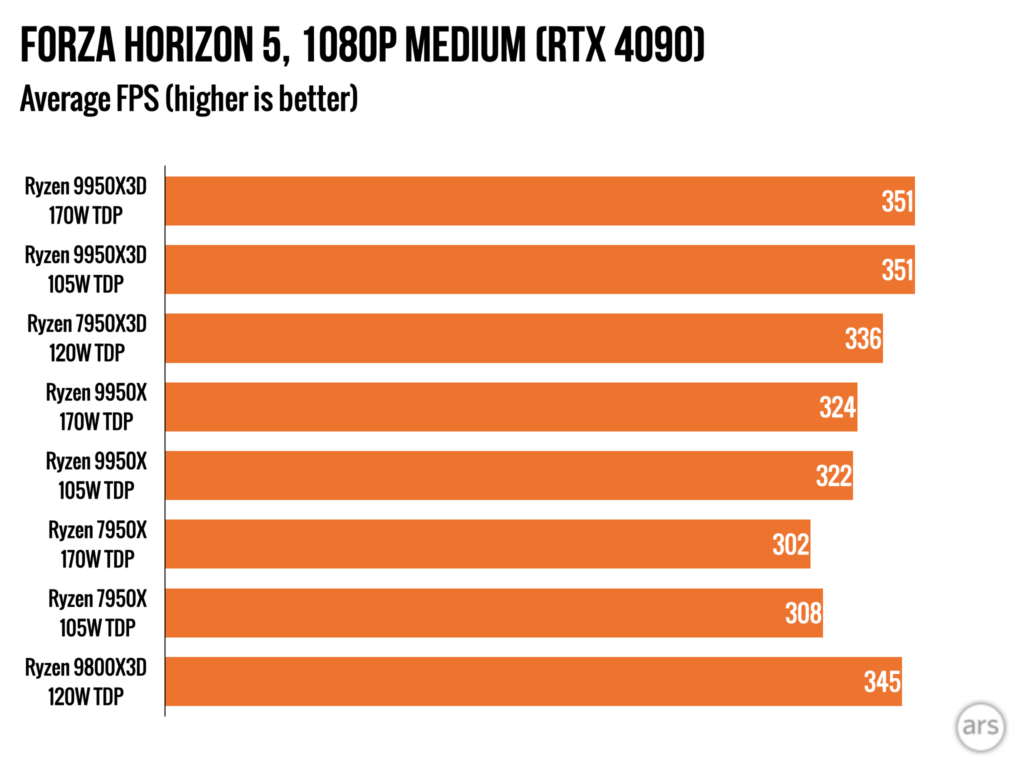
The 9950X3D has the second-highest CPU scores in our gaming benchmarks, and it’s behind the 9800X3D by only a handful of frames. This is one of the things we meant when we said that the 9800X3D was the better choice if you’re only worried about game performance. The same dynamic plays out between other 8- and 16-core Ryzen chips—higher power consumption and heat in the high-core-count chips usually bring game performance down just a bit despite the nominally higher boost clocks.
You’ll also pay for it in power consumption, at least at each chip’s default settings. On average, the 9950X3D uses 40 or 50 percent more power during our gaming benchmarks than the 9800X3D running the same benchmarks, even though it’s not capable of running them quite as quickly. But it’s similar to the power use of the regular 9950X, which is quite a bit slower in these gaming benchmarks, even if it does have broadly similar performance in most non-gaming benchmarks.
What’s impressive is what you see when you compare the 9950X3D to its immediate predecessor, the 7950X3D. The 9950X3D isn’t dramatically faster in games, reflecting Zen 5’s modest performance improvement over Zen 4. But the 9950X3D is a lot faster in our general-purpose benchmarks and other non-gaming CPU benchmarks because the changes to how the X3D chips are packaged have helped AMD keep clock speeds, voltages, and power limits pretty close to the same as they are for the regular 9950X.
In short, the 7950X3D gave up a fair bit of performance relative to the 7950X because of compromises needed to support 3D V-Cache. The 9950X3D doesn’t ask you to make the same compromises.
That comes with both upsides and downsides. For example, the 9950X3D looks a lot less power-efficient under load in our Handbrake video encoding test than the 7950X3D because it is using the same amount of power as a normal Ryzen processor. But that’s the other “normal” thing about the 9950X3D—the ability to manually tune those power settings and boost your efficiency if you’re OK with giving up a little performance. It’s not an either/or thing. And at least in our testing, games run just as fast when you set the 9950X3D to use the 105 W Eco Mode instead of the 170 W default TDP.
As for Intel, it just doesn’t have an answer for the X3D series. The Core Ultra 9 285K is perfectly competitive in our general-purpose CPU benchmarks and efficiency, but the Arrow Lake desktop chips struggle to compete with 14th-generation Core and Ryzen 7000 processors in gaming benchmarks, to say nothing of the Ryzen 9000 and to say even less than nothing of the 9800X3D or 9950X3D. That AMD has closed the gap between the 9950X and 9950X3D’s performance in our general-purpose CPU benchmarks means it’s hard to make an argument for Intel here.
The 9950X3D stands alone
I’m not and have never been the target audience for either the 16-core Ryzen processors or the X3D-series processors. When I’m building for myself (and when I’m recommending mainstream builds for our Ars System Guides), I’m normally an advocate for buying the most CPU you can for $200 or $300 and spending more money on a GPU.
But for the game-playing YouTubing content creators who are the 9950X3D’s intended audience, it’s definitely an impressive chip. Games can hit gobsmackingly high frame rates at lower resolutions when paired with a top-tier GPU, behind (and just barely behind) AMD’s own 9800X3D. At the same time, it’s just as good at general-use CPU-intensive tasks as the regular 9950X, fixing a trade-off that had been part of the X3D series since the beginning. AMD has also removed the limits it has in place on overclocking and adjusting power limits for the X3D processors in the 5000 and 7000 series.
So yes, it’s expensive, and no, most people probably don’t need the specific benefits it provides. It’s also possible that you’ll find edge cases where AMD’s technology for parking cores and sending the right kinds of work to the right CPU cores doesn’t work the way it should. But for people who do need or want ultra-high frame rates at lower resolutions or who have some other oddball workloads that benefit from the extra cache, the 9950X3D gives you all of the upsides with no discernible downsides other than cost. And, hey, even at $699, current-generation GPU prices almost make it look like a bargain.
The good
- Excellent combination of the 9800X3D’s gaming performance and the 9950X’s general-purpose CPU performance
- AMD has removed limitations on overclocking and power limit tweaking
- Pretty much no competition for Intel for the specific kind of person the 9950X3D will appeal to
The bad
- Niche CPUs that most people really don’t need to buy
- Less power-efficient out of the box than the 7950X3D, though users have latitude to tune efficiency manually if they want
- AMD’s software has sometimes had problems assigning the right kinds of apps to the right kinds of CPU cores, though we didn’t have issues with this during our testing
The ugly
- Expensive
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
Ryzen 9 9950X3D review: Seriously fast, if a step backward in efficiency Read More »